Chiến lược theo xu hướng dựa trên đường trung bình động thích ứng
Tổng quan
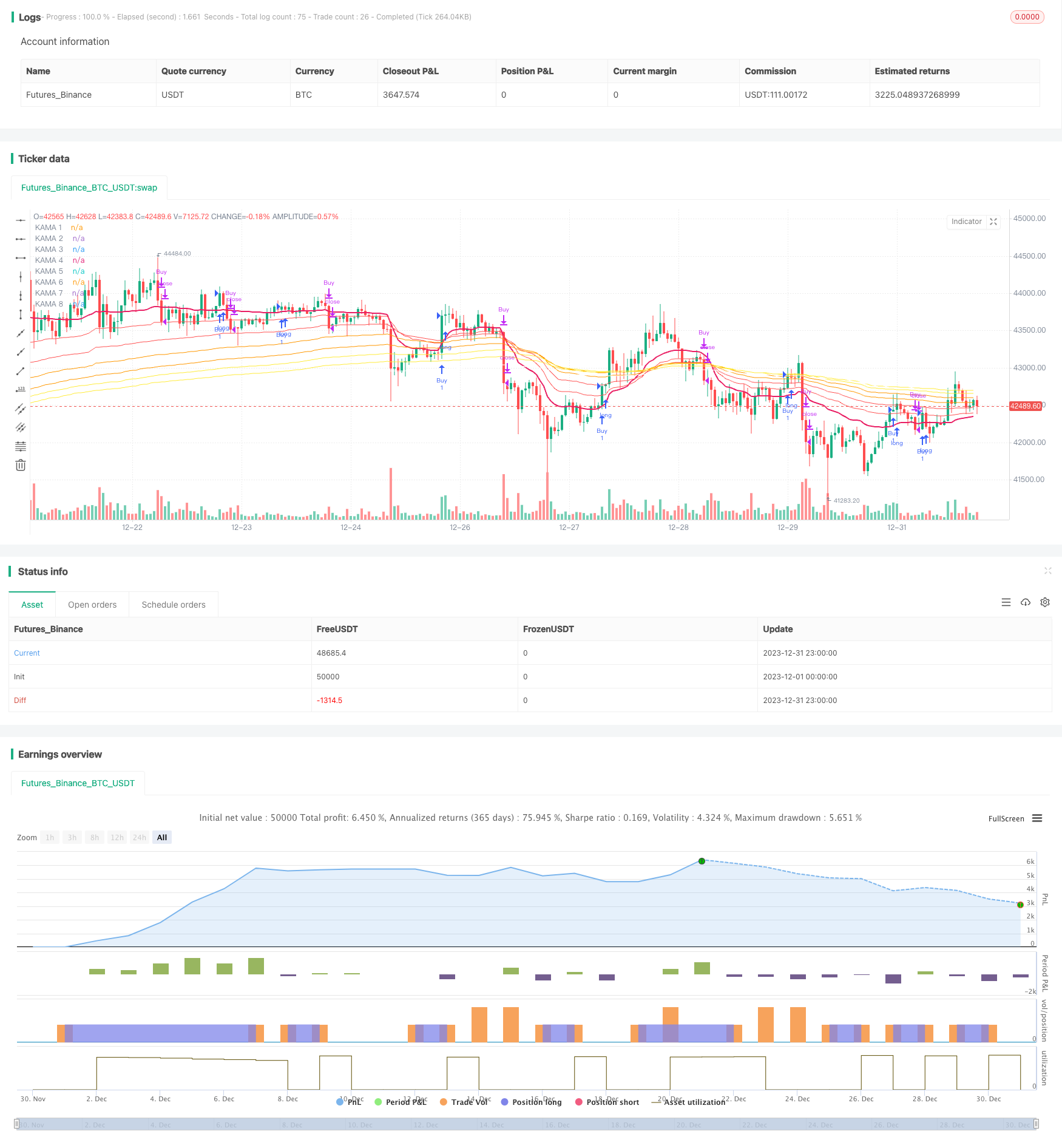
Chiến lược này sử dụng chỉ số Kaufman Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA) để thiết kế một hệ thống giao dịch theo dõi xu hướng. Hệ thống này có thể theo dõi xu hướng nhanh chóng khi xu hướng hình thành và lọc tiếng ồn trong trường hợp biến động. Đồng thời, hệ thống cũng tích hợp hệ thống chuyển đổi đường phân cực (PSAR) và theo dõi mức biến động thực trung bình (ATR Trailing Stop) làm cơ chế dừng lỗ, có khả năng kiểm soát rủi ro mạnh mẽ hơn.
Nguyên tắc chiến lược
Chiều dài của chỉ số KAMA được điều chỉnh theo động lực biến động của thị trường trong một khoảng thời gian gần đây. Cửa sổ EMA ngắn hơn khi biến đổi giá lớn hơn tiếng ồn gần đây; Cửa sổ EMA dài hơn khi biến đổi giá nhỏ hơn tiếng ồn gần đây. Điều này cho phép KAMA theo dõi xu hướng nhanh chóng và lọc tiếng ồn trong các tình huống xung đột.
Hệ thống chủ yếu đánh giá hướng xu hướng dựa trên KAMA 1 nhanh nhất. Khi KAMA 1 đi lên, nó sẽ làm nhiều hơn và khi đi xuống, nó sẽ làm trống. Để lọc sự phá vỡ giả, bộ lọc KAMA được thiết lập. Chỉ khi sự thay đổi của KAMA 1 vượt quá một độ phân biệt chuẩn của biến động gần đây, tín hiệu giao dịch sẽ được tạo ra.
Về dừng lỗ, hệ thống cung cấp ba phương thức dừng lỗ có thể lựa chọn: dựa trên KAMA reversal, PSAR reversal, ATR mobile stop. Các nhà đầu tư có thể lựa chọn một hoặc nhiều loại kết hợp tùy theo từng cá nhân.
Phân tích lợi thế
Thiết kế độc đáo của chỉ số KAMA cho phép hệ thống nhanh chóng nắm bắt các xu hướng mới nảy sinh, dừng giao dịch trong tình huống biến động, kiểm soát hiệu quả tần suất giao dịch, giảm điểm trượt không cần thiết và phí tổn.
Hệ thống này có nhiều cơ chế ngăn chặn thiệt hại. Các nhà đầu tư có thể lựa chọn các chương trình ngăn chặn thiệt hại phù hợp theo sở thích rủi ro cá nhân, kiểm soát mạnh mẽ các tổn thất đơn lẻ.
Hệ thống này hoàn toàn dựa trên chỉ số và đường dừng lỗ, tránh các vấn đề sai lệch giao dịch chuyển vị trí thường gặp.
Các thiết lập đa tham số và các điều kiện kết hợp cung cấp một không gian lớn cho tùy chỉnh hệ thống. Người dùng có thể tùy chỉnh theo địa phương, để tối ưu hóa cho các giống và chu kỳ khác nhau.
Phân tích rủi ro
Hệ thống không tính đến rủi ro hệ thống và không thể kiểm soát hiệu quả tổn thất trong trường hợp cực đoan.
Hệ thống PARAMETERS có thể cần phải điều chỉnh theo chu kỳ khác nhau của các giống khác nhau, nếu không sẽ tạo ra kết quả quá cực đoan hoặc quá bảo thủ.
Nếu chỉ dựa vào chỉ số KAMA để dừng lỗ, nó dễ bị mắc kẹt trong tình huống chấn động. Điều này cần được sử dụng kết hợp với dừng lỗ di động của PSAR hoặc ATR để giải quyết.
Hướng tối ưu hóa
Thêm các chỉ số lọc xu hướng, chẳng hạn như ADX hoặc chỉ số biến động ẩn, để tránh tín hiệu sai trong giai đoạn biến động và chuyển đổi xu hướng.
Tối ưu hóa và kiểm tra PARAMETERS cho từng giống và chu kỳ cố định để tăng sự ổn định. Các chiều tối ưu hóa bao gồm các tham số KAMA, tham số dừng lỗ, v.v.
Thử mô hình học máy thay vì tối ưu hóa tham số. Sử dụng một mạng lưới thần kinh hoặc mô hình cây quyết định để đào tạo thời gian mua và bán và dừng lỗ với một lượng lớn dữ liệu lịch sử.
Thử di chuyển chiến lược sang các loại khác, chẳng hạn như tiền kỹ thuật số. Điều này có thể yêu cầu điều chỉnh PARAMETERS hoặc thêm các chỉ số phụ trợ khác.
Tóm tắt
Chiến lược này tích hợp các biện pháp đánh giá xu hướng KAMA và nhiều biện pháp dừng để theo dõi hiệu quả hướng xu hướng và kiểm soát rủi ro. Tính độc đáo của chỉ số KAMA cho phép chiến lược đánh giá nhanh chóng hướng của xu hướng mới nảy sinh, tránh các vấn đề phá vỡ giả.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-01 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © BenHampson
// @version=4
// Credit to:
// - ChuckBanger for much of the KAMA code
// - cheatcountry for the KAMA Filter code
// - millerrh for much of the ATR Stop code
// - racer8 for much of the Position Sizing code
// I have combined aspects of their work and built upon it to form a strategy I like.
// The KAMA, with its filter, is used for entry.
// An ATR trailing stop loss, PSAR, and the KAMA can all optionally be used as exits, or you can use a combination of the three.
strategy(title="KAMA Strategy - Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average", shorttitle="KAMA Strategy", overlay=true)
src = input(title="Source", type=input.source, defval=close)
// Exits
KAMA1SL = input(title = 'KAMA 1 Stop Loss', type = input.bool, defval = true)
ATRTSL = input(title = 'ATR Trailing Stop Loss', type = input.bool, defval = false)
PSARSL = input(title = 'PSAR Stop Loss', type = input.bool, defval = false)
// KAMA 1 (Fastest)
length1 = input(title="KAMA 1: Length", type=input.integer, defval=14)
fastLength1 = input(title="KAMA 1: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=2)
slowLength1 = input(title="KAMA 1: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=20)
length2 = input(title="KAMA 2: Length 2", type=input.integer, defval=15)
fastLength2 = input(title="KAMA 2: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=3)
slowLength2 = input(title="KAMA 2: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=22)
length3 = input(title="KAMA 3: Length 3", type=input.integer, defval=16)
fastLength3 = input(title="KAMA 3: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=4)
slowLength3 = input(title="KAMA 3: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=24)
length4 = input(title="KAMA 4: Length", type=input.integer, defval=17)
fastLength4 = input(title="KAMA 4: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=5)
slowLength4 = input(title="KAMA 4: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=26)
// KAMA 5 (Medium)
length5 = input(title="KAMA 5: Length", type=input.integer, defval=18)
fastLength5 = input(title="KAMA 5: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=6)
slowLength5 = input(title="KAMA 5: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=28)
length6 = input(title="KAMA 6: Length", type=input.integer, defval=19)
fastLength6 = input(title="KAMA 6: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=7)
slowLength6 = input(title="KAMA 6: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=30)
length7 = input(title="KAMA 7: Length", type=input.integer, defval=20)
fastLength7 = input(title="KAMA 7: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=8)
slowLength7 = input(title="KAMA 7: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=32)
// KAMA 8 (Slowest)
length8 = input(title="KAMA 8: Length", type=input.integer, defval=21)
fastLength8 = input(title="KAMA 8: Fast KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=9)
slowLength8 = input(title="KAMA 8: Slow KAMA Length", type=input.integer, defval=34)
// Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average
getKAMA(src, length1, fastLength1, slowLength1) =>
mom = abs(change(src, length1))
volatility = sum(abs(change(src)), length1)
// Efficiency Ratio
er = volatility != 0 ? mom / volatility : 0
fastAlpha = 2 / (fastLength1 + 1)
slowAlpha = 2 / (slowLength1 + 1)
// KAMA Alpha
sc = pow((er * (fastAlpha - slowAlpha)) + slowAlpha, 2)
kama = 0.0
kama := sc * src + (1 - sc) * nz(kama[1])
kama
kama1 = getKAMA(src, length1, fastLength1, slowLength1)
kama2 = getKAMA(src, length2, fastLength2, slowLength2)
kama3 = getKAMA(src, length3, fastLength3, slowLength3)
kama4 = getKAMA(src, length4, fastLength4, slowLength4)
kama5 = getKAMA(src, length5, fastLength5, slowLength5)
kama6 = getKAMA(src, length6, fastLength6, slowLength6)
kama7 = getKAMA(src, length7, fastLength7, slowLength7)
kama8 = getKAMA(src, length8, fastLength8, slowLength8)
//If the kama1 has increased...
kama1delta = kama1[0] - kama1[1]
kama3delta = kama3[0] - kama3[1]
kama8delta = kama8[0] - kama8[1]
// KAMA Plots
plot(kama1, title="KAMA 1", color=#e91e63, display=display.all, linewidth=2)
plot(kama2, title="KAMA 2", color=color.red, display=display.all)
plot(kama3, title="KAMA 3", color=color.red, display=display.all)
plot(kama4, title="KAMA 4", color=color.orange, display=display.all)
plot(kama5, title="KAMA 5", color=color.orange, display=display.all)
plot(kama6, title="KAMA 6", color=color.yellow, display=display.all)
plot(kama7, title="KAMA 7", color=color.yellow, display=display.all)
plot(kama8, title="KAMA 8", color=color.white, display=display.all)
//========================================= KAMA FILTER ===========================================
// Copyright (c) 2019-present, Franklin Moormann (cheatcountry)
// Moving Average Adaptive Filter [CC] script may be freely distributed under the MIT license.
entryFilter = input(title="KAMA Entry Filter", type=input.float, defval=1, minval=0.01)
exitFilter = input(title="KAMA Exit Filter", type=input.float, defval=0.5, minval=0.01)
entryMAAF = entryFilter * stdev(kama1delta, length1)
exitMAAF = exitFilter * stdev(kama1delta, length1)
srcEma = ema(src, length1)
//========================================= TRAILING ATR STOP ====================================
// The following is an adaptation of Trailing ATR Stops by @millerrh
// He based it on scripts by @garethyeo & @SimpleCryptoLife
// Inputs
atrLookback = input(defval=14,title="Trailing ATR Lookback Period",type=input.integer)
multiplier = input(defval=3,title="Trailing ATR Multiplier",type=input.float, step=0.1, minval=0.5, maxval=4)
trailMode = input(title="Trail Mode", defval="Trailing", options=["Running", "Trailing"])
trigInput = input(title="Trigger Trailing Stop On", defval="Wick", options=["Close","Wick"])
// Calculate ATR
atrValue = atr(atrLookback)
atrMultiplied = atrValue * multiplier
// Plot the price minus the ATR
atrLow = low - atrMultiplied
// Calculate the low trailing ATRs every time. The trailing stop loss never goes down.
// Set them to something to start with
trailAtrLow = atrLow
// If the ATR Low has gone up AND it has gone above the trail, the low trailing ATR should also go up. If the ATR Low has gone up or down, but not below the trail, the ATR trail stays where it is
trailAtrLow := na(trailAtrLow[1]) ? trailAtrLow : atrLow >= trailAtrLow[1] ? atrLow : trailAtrLow[1]
// Trigger stop based on candle close or low
trigSupport = trigInput == "Close" ? close : trigInput == "Wick" ? low : na
// Determine if price is below support
supportHit = trigSupport <= trailAtrLow
// If price is below support, reset the trailing ATR
trailAtrLow := supportHit ? atrLow : trailAtrLow
// Plot Lines
plotLow = ATRTSL ? trailAtrLow : na
plot(plotLow, title="ATR Low", color=color.white, transp=50, style=plot.style_linebr, linewidth=1, display=display.all)
//====================================== PSAR STOP ==========================================
start = input(0.02, "PSAR Start")
increment = input(0.02, "PSAR Increment")
maximum = input(0.2, "PSAR Max Value")
psar = sar(start, increment, maximum)
psarPlot = PSARSL ? psar : na
plot(psarPlot, "Parabolic SAR", style=plot.style_cross, color=#3A6CA8, display=display.all)
//========================================= ENTRY & EXITS =====================================================
// Entry
long = kama1delta > 0 and kama1delta > entryMAAF
strategy.entry("Buy", true, when = long)
// Close
longClose = (PSARSL ? crossunder(close, psar) : na) or (KAMA1SL ? kama1delta < 0 and abs(kama1delta) > exitMAAF : na) or (ATRTSL ? supportHit : na)
strategy.close("Buy", when = longClose, comment = "Sell")