Kuberan-Strategie: Schnittpunktstrategie zur Marktkontrolle
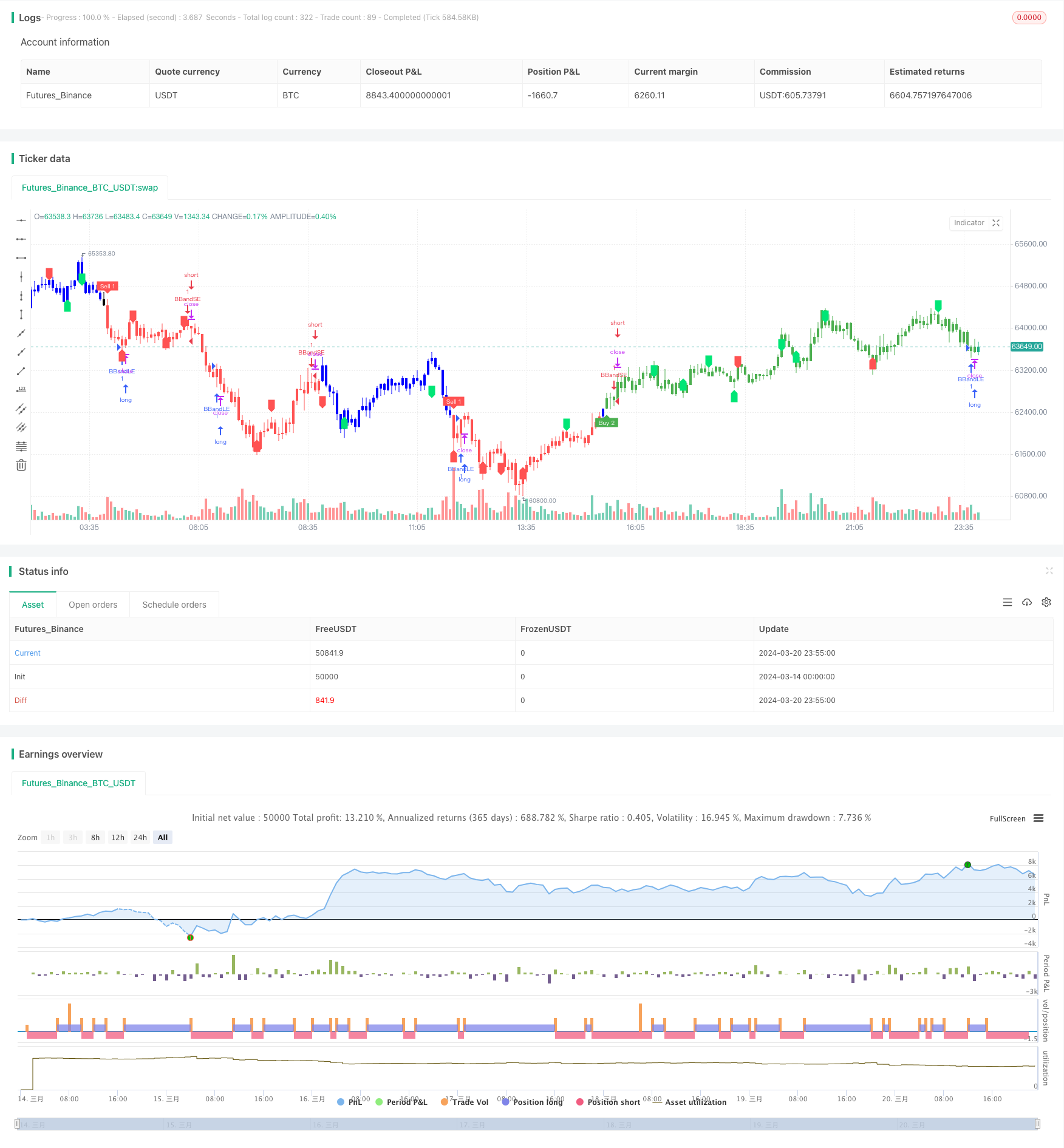
Strategieübersicht
Die Kuberan-Strategie ist eine starke Handelsstrategie, die von Kathir geschrieben wurde. Sie kombiniert mehrere Analysetechniken zu einer einzigartigen und starken Handelsmethode. Die Strategie ist nach dem Gott des Reichtums Kuberan benannt und symbolisiert das Ziel, die Portfolios der Händler zu bereichern.
Kuberan ist mehr als nur eine Strategie, sondern ein umfassendes Handelssystem. Es kombiniert Trendanalyse, Dynamik- und Transaktionsindikatoren, um hochprobable Handelsmöglichkeiten zu identifizieren. Durch die Synergie dieser Elemente bietet Kuberan klare Ein- und Ausstiegssignale für Händler aller Ebenen.
Strategieprinzip
Im Zentrum der Kuberan-Strategie steht das Prinzip der Multi-Indicator-Switching. Es nutzt eine einzigartige Kombination von Indikatoren, die miteinander kombiniert werden, um Geräusche und Fehlsignale zu reduzieren. Insbesondere verwendet die Strategie folgende Schlüsselkomponenten:
- Beurteilung der Richtung des Trends: Beurteilung der Richtung des aktuellen Trends durch Vergleich des aktuellen Preises mit den Unterstützungs- und Widerstandspunkten.
- Unterstützungs- und Widerstandspunkte: Identifizieren Sie wichtige Unterstützungs- und Widerstandspunkte durch Zickzack-Indikatoren und Hubpunkte.
- Abweichungsurteile: Vergleichen von Preisbewegungen mit Dynamikindikatoren, um zu beurteilen, ob Abweichungen aufgetreten sind, was auf eine mögliche Trendwende hinweist.
- Anpassung der Schwankungen: Die Stop-Loss-Position wird dynamisch an die unterschiedlichen Marktschwankungen angepasst.
- K-Linienmodus-Beschluss: Trend- und Umkehrsignale werden durch bestimmte K-Linienkombinationen bestätigt.
Durch die integrierte Berücksichtigung der oben genannten Faktoren ist Kuberan-Strategie in der Lage, sich an verschiedene Marktumgebungen anzupassen, um hohe Wahrscheinlichkeiten zu erfassen.
Strategische Vorteile
- Multi-Meter-Schnittstelle: Die Kuberan-Strategie nutzt die Synergie mehrerer Indikatoren, um die Signalzuverlässigkeit zu erhöhen und die Geräuschstörung zu reduzieren.
- Anpassungsfähigkeit: Durch die dynamische Anpassung der Parameter kann die Strategie an die wechselnden Marktbedingungen angepasst werden und ist nicht anfällig für Ausfälle.
- Klares Signal: Kuberan bietet klare Ein- und Ausstiegssignale und vereinfacht den Handelsprozess.
- Die Strategie wurde durch strenge historische Rückmeldung geprüft und hat sich unter verschiedenen Marktsituationen als stabil erwiesen.
- Breite Anwendbarkeit: Kuberan ist für verschiedene Märkte und Sorten geeignet, nicht nur für bestimmte Handelsmarken.
Strategisches Risiko
- Parameter-sensibel: Die Performance der Kuberan-Strategie ist sehr sensibel für Parameter-Auswahl, und falsche Parameter können zu einer Leistungsabnahme führen.
- Ausnahmesituationen: Die Strategie basiert auf technischen Signalen und hat nur begrenzte Möglichkeiten, auf grundlegende Ausnahmesituationen zu reagieren.
- Überangemessenes Risiko: Wenn bei der Optimierung von Parametern zu viele historische Daten berücksichtigt werden, kann dies dazu führen, dass die Strategie zu sehr auf die Vergangenheit zugeschnitten ist und weniger an die Zukunft angepasst ist.
- Leverage-Risiko: Bei hohem Leverage besteht das Risiko eines Ausbruchs bei einem starken Rückzug.
Angemessene Kontrollmaßnahmen können gegen diese Risiken eingesetzt werden, wie z. B. regelmäßige Anpassung der Parameter, Einrichtung eines angemessenen Stop-Losses, moderate Steuerung der Leverage und Aufmerksamkeit auf grundlegende Veränderungen.
Optimierungsrichtung
- Optimierung durch maschinelles Lernen: Maschinelle Lernalgorithmen können eingesetzt werden, um Strategieparameter dynamisch zu optimieren und die Anpassungsfähigkeit zu verbessern.
- Hinzufügen von Fundamentaldaten: Erwägen Sie die Einbeziehung von Fundamentaldaten in Ihre Handelsentscheidungen, um auf Fehlfunktionen bei technischen Signalen zu reagieren.
- Portfolio-Management: Auf der Ebene des Fondsmanagements kann die Kuberan-Strategie in ein Portfolio aufgenommen werden, um eine effektive Absicherung gegen andere Strategien zu schaffen.
- Optimierung der Marktsegmentation: Merkmale für verschiedene Marktvarianten, individuelle Optimierungsstrategieparameter.
- Hochfrequenz-Umgestaltung: Umgestaltung der Strategie in eine Hochfrequenz-Handelsversion, um mehr Short-Line-Handelsmöglichkeiten zu ergattern.
Zusammenfassen
Kuberan ist eine leistungsstarke, sichere und zuverlässige Handelsstrategie. Es kombiniert geschickt verschiedene Methoden der technischen Analyse und ist hervorragend darin, Trends zu erfassen und Wendepunkte zu erfassen. Obwohl keine Strategie unweigerlich mit Risiken konfrontiert ist, hat Kuberan seine Robustheit in der Rückmeldung bewiesen.
/*backtest
start: 2024-03-14 00:00:00
end: 2024-03-21 00:00:00
period: 5m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © LonesomeThecolor.blue
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © LonesomeThecolor.blue
//@version=5
strategy('Kuberan*', overlay=true, max_lines_count=500)
lb = input.int(5, title='Left Bars', minval=1)
rb = input.int(5, title='Right Bars', minval=1)
showsupres = input.bool(false, title='Support/Resistance', inline='srcol')
supcol = input.color(color.lime, title='', inline='srcol')
rescol = input.color(color.red, title='', inline='srcol')
// srlinestyle = input(line.style_dotted, title='Line Style/Width', inline='style')
srlinewidth = input.int(3, title='', minval=1, maxval=5, inline='style')
changebarcol = input.bool(true, title='Change Bar Color', inline='bcol')
bcolup = input.color(color.blue, title='', inline='bcol')
bcoldn = input.color(color.black, title='', inline='bcol')
ph = ta.pivothigh(lb, rb)
pl = ta.pivotlow(lb, rb)
iff_1 = pl ? -1 : na // Trend direction
hl = ph ? 1 : iff_1
iff_2 = pl ? pl : na // similar to zigzag but may have multTLiple highs/lows
zz = ph ? ph : iff_2
valuewhen_1 = ta.valuewhen(hl, hl, 1)
valuewhen_2 = ta.valuewhen(zz, zz, 1)
zz := pl and hl == -1 and valuewhen_1 == -1 and pl > valuewhen_2 ? na : zz
valuewhen_3 = ta.valuewhen(hl, hl, 1)
valuewhen_4 = ta.valuewhen(zz, zz, 1)
zz := ph and hl == 1 and valuewhen_3 == 1 and ph < valuewhen_4 ? na : zz
valuewhen_5 = ta.valuewhen(hl, hl, 1)
valuewhen_6 = ta.valuewhen(zz, zz, 1)
hl := hl == -1 and valuewhen_5 == 1 and zz > valuewhen_6 ? na : hl
valuewhen_7 = ta.valuewhen(hl, hl, 1)
valuewhen_8 = ta.valuewhen(zz, zz, 1)
hl := hl == 1 and valuewhen_7 == -1 and zz < valuewhen_8 ? na : hl
zz := na(hl) ? na : zz
findprevious() => // finds previous three points (b, c, d, e)
ehl = hl == 1 ? -1 : 1
loc1 = 0.0
loc2 = 0.0
loc3 = 0.0
loc4 = 0.0
xx = 0
for x = 1 to 1000 by 1
if hl[x] == ehl and not na(zz[x])
loc1 := zz[x]
xx := x + 1
break
ehl := hl
for x = xx to 1000 by 1
if hl[x] == ehl and not na(zz[x])
loc2 := zz[x]
xx := x + 1
break
ehl := hl == 1 ? -1 : 1
for x = xx to 1000 by 1
if hl[x] == ehl and not na(zz[x])
loc3 := zz[x]
xx := x + 1
break
ehl := hl
for x = xx to 1000 by 1
if hl[x] == ehl and not na(zz[x])
loc4 := zz[x]
break
[loc1, loc2, loc3, loc4]
float a = na
float b = na
float c = na
float d = na
float e = na
if not na(hl)
[loc1, loc2, loc3, loc4] = findprevious()
a := zz
b := loc1
c := loc2
d := loc3
e := loc4
e
_hh = zz and a > b and a > c and c > b and c > d
_ll = zz and a < b and a < c and c < b and c < d
_hl = zz and (a >= c and b > c and b > d and d > c and d > e or a < b and a > c and b < d)
_lh = zz and (a <= c and b < c and b < d and d < c and d < e or a > b and a < c and b > d)
plotshape(_hl, title='Higher Low', style=shape.labelup, color=color.new(color.lime, 0), textcolor=color.new(color.black, 0), location=location.belowbar, offset=-rb)
plotshape(_hh, title='Higher High', style=shape.labeldown, color=color.new(color.lime, 0), textcolor=color.new(color.black, 0), location=location.abovebar, offset=-rb)
plotshape(_ll, title='Lower Low', style=shape.labelup, color=color.new(color.red, 0), textcolor=color.new(color.white, 0), location=location.belowbar, offset=-rb)
plotshape(_lh, title='Lower High', style=shape.labeldown, color=color.new(color.red, 0), textcolor=color.new(color.white, 0), location=location.abovebar, offset=-rb)
float res = na
float sup = na
res := _lh ? zz : res[1]
sup := _hl ? zz : sup[1]
int trend = na
iff_3 = close < sup ? -1 : nz(trend[1])
trend := close > res ? 1 : iff_3
res := trend == 1 and _hh or trend == -1 and _lh ? zz : res
sup := trend == 1 and _hl or trend == -1 and _ll ? zz : sup
rechange = res != res[1]
suchange = sup != sup[1]
var line resline = na
var line supline = na
if showsupres
if rechange
line.set_x2(resline, bar_index)
line.set_extend(resline, extend=extend.none)
resline := line.new(x1=bar_index - rb, y1=res, x2=bar_index, y2=res, color=rescol, extend=extend.right, style=line.style_dotted, width=srlinewidth)
resline
if suchange
line.set_x2(supline, bar_index)
line.set_extend(supline, extend=extend.none)
supline := line.new(x1=bar_index - rb, y1=sup, x2=bar_index, y2=sup, color=supcol, extend=extend.right, style=line.style_dotted, width=srlinewidth)
supline
iff_4 = trend == 1 ? bcolup : bcoldn
barcolor(color=changebarcol ? iff_4 : na)
// Inputs
A1 = input(5, title='Key Value. \'This changes the sensitivity\' for sell1')
C1 = input(400, title='ATR Period for sell1')
A2 = input(6, title='Key Value. \'This changes the sensitivity\' for buy2')
C2 = input(1, title='ATR Period for buy2')
h = input(false, title='Signals from Heikin Ashi Candles')
xATR1 = ta.atr(C1)
xATR2 = ta.atr(C2)
nLoss1 = A1 * xATR1
nLoss2 = A2 * xATR2
src = h ? request.security(ticker.heikinashi(syminfo.tickerid), timeframe.period, close, lookahead=barmerge.lookahead_off) : close
xATRTrailingStop1 = 0.0
iff_5 = src > nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) ? src - nLoss1 : src + nLoss1
iff_6 = src < nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) and src[1] < nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) ? math.min(nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1]), src + nLoss1) : iff_5
xATRTrailingStop1 := src > nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) and src[1] > nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) ? math.max(nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1]), src - nLoss1) : iff_6
xATRTrailingStop2 = 0.0
iff_7 = src > nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) ? src - nLoss2 : src + nLoss2
iff_8 = src < nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) and src[1] < nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) ? math.min(nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1]), src + nLoss2) : iff_7
xATRTrailingStop2 := src > nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) and src[1] > nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) ? math.max(nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1]), src - nLoss2) : iff_8
pos1 = 0
iff_9 = src[1] > nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) and src < nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) ? -1 : nz(pos1[1], 0)
pos1 := src[1] < nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) and src > nz(xATRTrailingStop1[1], 0) ? 1 : iff_9
pos2 = 0
iff_10 = src[1] > nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) and src < nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) ? -1 : nz(pos2[1], 0)
pos2 := src[1] < nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) and src > nz(xATRTrailingStop2[1], 0) ? 1 : iff_10
xcolor1 = pos1 == -1 ? color.red : pos1 == 1 ? color.green : color.blue
xcolor2 = pos2 == -1 ? color.red : pos2 == 1 ? color.green : color.blue
ema1 = ta.ema(src, 1)
ema2 = ta.ema(src, 1)
above1 = ta.crossover(ema1, xATRTrailingStop1)
below1 = ta.crossover(xATRTrailingStop1, ema1)
above2 = ta.crossover(ema2, xATRTrailingStop2)
below2 = ta.crossover(xATRTrailingStop2, ema2)
buy1 = src > xATRTrailingStop1 and above1
sell1 = src < xATRTrailingStop1 and below1
buy2 = src > xATRTrailingStop2 and above2
sell2 = src < xATRTrailingStop2 and below2
barbuy1 = src > xATRTrailingStop1
barsell1 = src < xATRTrailingStop1
barbuy2 = src > xATRTrailingStop2
barsell2 = src < xATRTrailingStop2
// plotshape(buy1, title="Buy 1", text='Buy 1', style=shape.labelup, location=location.belowbar, color=color.green, textcolor=color.white, transp=0, size=size.tiny)
plotshape(sell1, title='Sell 1', text='Sell 1', style=shape.labeldown, location=location.abovebar, color=color.new(color.red, 0), textcolor=color.new(color.white, 0), size=size.tiny)
plotshape(buy2, title='Buy 2', text='Buy 2', style=shape.labelup, location=location.belowbar, color=color.new(color.green, 0), textcolor=color.new(color.white, 0), size=size.tiny)
// plotshape(sell2, title="Sell 2", text='Sell 2', style=shape.labeldown, location=location.abovebar, color=color.red, textcolor=color.white, transp=0, size=size.tiny)
// barcolor(barbuy1 ? color.green : na)
barcolor(barsell1 ? color.red : na)
barcolor(barbuy2 ? color.green : na)
// barcolor(barsell2 ? color.red : na)
// alertcondition(buy1, "UT Long 1", "UT Long 1")
alertcondition(sell1, 'UT Short 1', 'UT Short 1')
alertcondition(buy2, 'UT Long 2', 'UT Long 2')
// strategy.entry('long', strategy.long, when=buy2)
source = close
length = input.int(20, minval=1)
mult = input.float(2.0, minval=0.001, maxval=50)
basis = ta.sma(source, length)
dev = mult * ta.stdev(source, length)
upper = basis + dev
lower = basis - dev
buyEntry = ta.crossover(source, lower)
sellEntry = ta.crossunder(source, upper)
if (ta.crossover(source, lower) )
strategy.entry("BBandLE", strategy.long, stop=lower, oca_name="BollingerBands", comment="BBandLE")
else
strategy.cancel(id="BBandLE")
if (ta.crossunder(source, upper))
strategy.entry("BBandSE", strategy.short, stop=upper, oca_name="BollingerBands",comment="BBandSE")
else
strategy.cancel(id="BBandSE")
//plot(strategy.equity, title="equity", color=color.red, linewidth=2, style=plot.style_areabr)
lengthTL = input.int(14, 'Swing Detection Lookback')
multTL = input.float(1., 'Slope', minval = 0, step = .1)
calcMethod = input.string('Atr', 'Slope Calculation Method', options = ['Atr','Stdev','Linreg'])
backpaint = input(true, tooltip = 'Backpainting offset displayed elements in the past. Disable backpainting to see real time information returned by the indicator.')
//Style
upCss = input.color(color.teal, 'Up Trendline Color', group = 'Style')
dnCss = input.color(color.red, 'Down Trendline Color', group = 'Style')
showExt = input(true, 'Show Extended Lines')
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------}
//Calculations
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------{
var upperTL = 0.
var lowerTL = 0.
var slope_phTL = 0.
var slope_plTL = 0.
var offset = backpaint ? lengthTL : 0
n = bar_index
srcTL = close
phTL = ta.pivothigh(lengthTL, lengthTL)
plTL = ta.pivotlow(lengthTL, lengthTL)
//Slope Calculation Method
slope = switch calcMethod
'Atr' => ta.atr(lengthTL) / lengthTL * multTL
'Stdev' => ta.stdev(srcTL,lengthTL) / lengthTL * multTL
'Linreg' => math.abs(ta.sma(srcTL * n, lengthTL) - ta.sma(srcTL, lengthTL) * ta.sma(n, lengthTL)) / ta.variance(n, lengthTL) / 2 * multTL
//Get slopes and calculate trendlines
slope_phTL := phTL ? slope : slope_phTL
slope_plTL := plTL ? slope : slope_plTL
upperTL := phTL ? phTL : upperTL - slope_phTL
lowerTL := pl ? pl : lowerTL + slope_plTL
var upos = 0
var dnos = 0
upos := phTL ? 0 : close > upperTL - slope_phTL * lengthTL ? 1 : upos
dnos := pl ? 0 : close < lowerTL + slope_plTL * lengthTL ? 1 : dnos