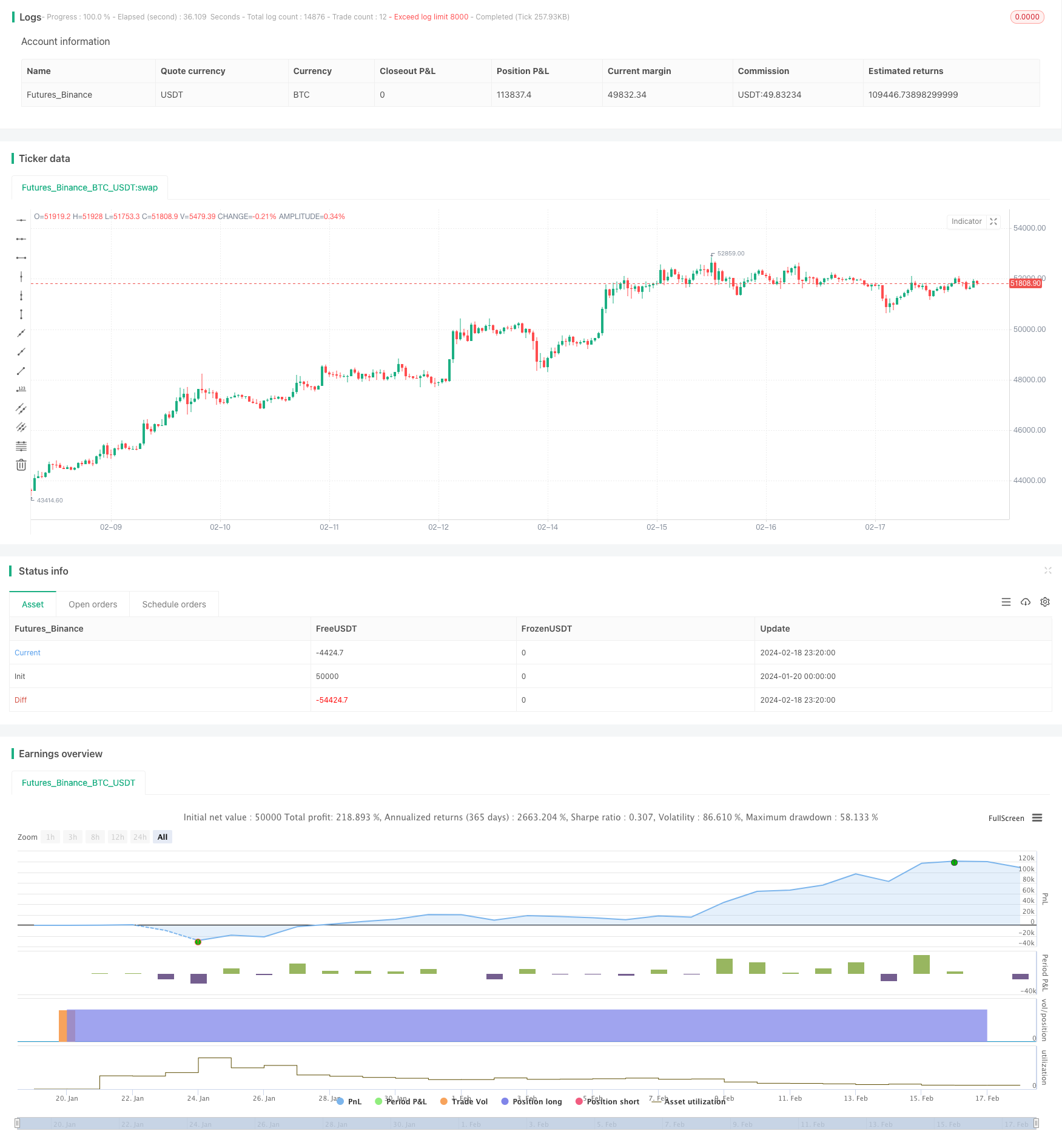
개요
이 전략의 주요 아이디어는 시스템 신호의 동적에 따라 포지션을 올리고, 위험을 통제하고 낮은 평균 입시 가격을 얻기 위해 황소 시장에서 점진적으로 포지션을 구축하는 것이다.
전략 원칙
이 전략은 먼저 시작 자본과 DCA 배열 비율을 설정한다. 각 K 라인 종료 시에는 가격 변화에 따라 조정 배열 비율을 계산한다. 가격이 상승하면, 비율을 줄이고, 가격이 떨어지면 비율을 증가시킨다. 이렇게 하면 가격이 낮을 때 포지션을 증가시킬 수 있다.
이렇게 함으로써, 시장이 변동할 때, 위험을 통제하고, 낮은 평균 입점 가격을 얻을 수 있다. 동시에, 그것은 또한 평균 입점 가격과 중위값을 통계적으로 계산하여, 현재 입점 상황을 판단할 수 있다.
우위 분석
이 전략은 다음과 같은 장점을 가지고 있습니다.
동적으로 포지션을 올릴 수 있고, 시장이 하락할 때 포지션을 늘리고, 시장이 상승할 때 포지션을 줄일 수 있어 위험을 통제한다.
중간값보다 낮은 평균 입점 가격으로 더 많은 수익을 얻을 수 있습니다.
황소 시장에서 변동하는 상황에 맞는 거래는 더 나은 리스크/이익 비율을 얻을 수 있습니다.
시작금액과 DCA 퍼센티지를 미리 설정하여, 매번 추가되는 금액을 제어하고, 과도한 위험을 피한다.
평균 입시 가격과 중수 가격의 통계를 제공하여 입시의 우수성과 저점을 직관적으로 판단할 수 있습니다.
위험 분석
이 전략에는 위험도 있습니다.
시장이 급격히 하락할 때, 이 전략은 계속 포지션이 증가하여 큰 자본 손실을 초래할 수 있다. 위험을 통제하기 위해 손실을 중지할 수 있다.
급격한 시장 상승이 발생하면 이 전략의 가장률이 낮아지며 상승 기회를 대부분 놓칠 수 있다. 이 때 다른 신호를 활용하여 민첩한 LSI가 필요하다.
변수 설정이 잘못되면 위험이 발생할 수 있습니다. 초창기 자본이 너무 많거나 DCA 비율이 너무 높으면 손실이 확대됩니다.
최적화 방향
이 전략은 다음과 같은 부분에서 최적화될 수 있습니다.
이 경우, 상쇄 논리를 추가하여 큰 하락을 겪을 때 포지션을 중단할 수 있습니다.
변동률이나 다른 지표에 따라 DCA 비율을 동적으로 조정할 수 있다.
가격 변화를 예측하는 기계학습 모델을 추가하여 포지션 결정에 도움을 줄 수 있습니다.
다른 기술 지표와 결합하여 시장 구조를 판단할 수 있으며, 구조 전환점에서 포지션을 중단할 수 있다.
재원 관리 모듈을 추가하여 계좌 재원에 따라 매번 재원을 동적으로 조정할 수 있습니다.
요약하다
이 전략은 매우 실용적인 동적 상장 전략이다. 그것은 시장의 변동에 따라 포지션을 유연하게 조정할 수 있으며, 황소 시장에서 낮은 평균 입문 가격을 얻을 수 있다. 동시에, 위험을 제어하기 위해 파라미터 설정을 내장했다. 다른 기술 지표 또는 모델과 결합하면 더 나은 효과를 얻을 수 있다. 이 전략은 장기 투자 수익을 추구하는 투자자에게 적합하다.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-20 00:00:00
end: 2024-02-19 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This Pine Script™ code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © RWCS_LTD
//@version=5
strategy("DCA IN Calculator {RWCS}", overlay=true, pyramiding=999, default_qty_type=strategy.cash, initial_capital=10000, commission_value=0.02)
// User inputs
backtestStartDate = input(timestamp("1 Jan 2024"),
title="Start Date", group="Backtest Time Period",
tooltip="This start date is in the time zone of the exchange " +
"where the chart's instrument trades. It doesn't use the time " +
"zone of the chart or of your computer.")
start_date = true
starting_capital = input.float(defval=5000, title="Starting Capital")
dca_allocation_percentage = input.int(defval=10, title="DCA Allocation Percentage")
// Calculate DCA allocation based on price change
price_change_percentage = ((close - close[1]) / close[1]) * 100
adjusted_allocation_percentage = close > close[1] ? dca_allocation_percentage - price_change_percentage : dca_allocation_percentage + price_change_percentage // If price action is negative, increase allocations
adjusted_allocation_percentage1 = dca_allocation_percentage - price_change_percentage // If price action is positive, reduce allocations
// Calculate order size based on adjusted allocation percentage
order_size = (adjusted_allocation_percentage / 100) * starting_capital
// Track remaining capital
var remaining_capital = starting_capital
// Long on the close of every bar
if true
// Ensure the order size doesn't exceed remaining capital or adjusted allocation
order_size := math.min(order_size, remaining_capital, adjusted_allocation_percentage / 100 * starting_capital)
// Ensure order size is not negative
order_size := math.max(order_size, 0)
strategy.entry("DCA", strategy.long, qty = order_size)
remaining_capital := remaining_capital - order_size
// Plot average entry price
var float total_entry_price = 0.0
var int total_signals = 0
if start_date
total_entry_price := total_entry_price + close
total_signals := total_signals + 1
avg_entry_price = total_entry_price / total_signals
// Calculate and plot median price
var float median_price = na
if start_date
var float sum_prices = 0.0
var int num_prices = 0
for i = 0 to bar_index
if (time[i] >= backtestStartDate)
sum_prices := sum_prices + close[i]
num_prices := num_prices + 1
median_price := sum_prices / num_prices
// Reset variables at the start of each day
if (dayofweek != dayofweek[1])
total_entry_price := 0.0
total_signals := 0
//table colors
borders_col = color.new(color.black, 90)
top_row_col = color.new(color.gray, 90)
size = input.string(defval='Normal', options=['Tiny', 'Small', 'Normal', 'Large'], title='Table size', inline='design', group='Table Design')
table_size = size == 'Tiny' ? size.tiny : size == 'Small' ? size.small : size == 'Normal' ? size.normal : size == 'Large' ? size.large : na
var tablee = table.new(position=position.top_right, columns=2, rows=3, frame_color=borders_col, frame_width=4, border_color=borders_col, border_width=4)
table.cell(tablee, 0, 0, "Average Entry Price", bgcolor=top_row_col, text_color=color.white, text_size=table_size)
table.cell(tablee, 1, 0, str.tostring(avg_entry_price, '#.##'), text_color=color.white, text_size=table_size)
table.cell(tablee, 0, 1, "Median Price", bgcolor=top_row_col, text_color=color.white, text_size=table_size)
table.cell(tablee, 1, 1, str.tostring(median_price, '#.##'), text_color=color.white, text_size=table_size)
table.cell(tablee, 0, 2, "Remaining Capital", bgcolor=top_row_col, text_color=color.white, text_size=table_size)
table.cell(tablee, 1, 2, str.tostring(remaining_capital, '#.##'), text_color=color.white, text_size=table_size)