Trend biasa mengikut strategi
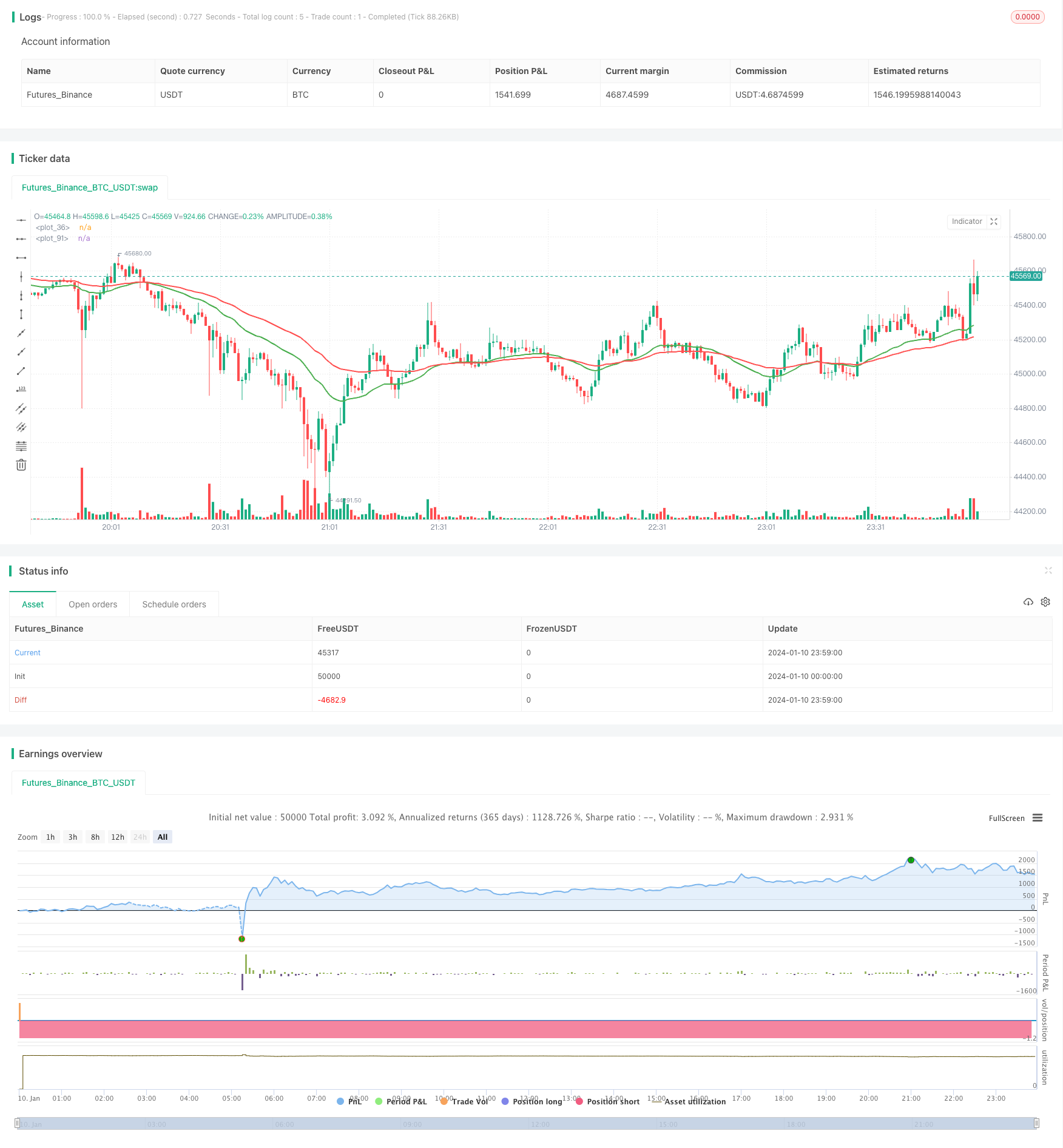
Gambaran keseluruhan
Strategi persilangan dua rata-rata adalah strategi pengesanan trend yang tipikal. Ia menggunakan rata-rata EMA dari dua tempoh yang berbeza, melakukan lebih banyak ketika melewati rata-rata jangka panjang di atas rata-rata jangka pendek, dan kosong ketika melewati rata-rata jangka panjang di bawah rata-rata jangka pendek, untuk menangkap titik perubahan trend harga.
Prinsip Strategi
Penunjuk teras strategi ini adalah dua garis purata EMA, 30 dan 60 kitaran. Dua garis purata EMA dikira dalam kod melalui fungsi tersuai:
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
Isyarat perdagangan strategi datang dari persilangan dua garis rata EMA:
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
Apabila EMA jangka pendek di atas EMA jangka panjang, currentState tidak sama dengan previousState, terdapat isyarat silang. Apabila EMA jangka pendek melintasi EMA jangka panjang, currentState tidak sama dengan previousState, dan isyarat silang berlaku.
Analisis kelebihan
Strategi ini mempunyai kelebihan berikut:
- Strategi mudah, mudah difahami, dan mudah dilaksanakan
- Menggunakan ciri-ciri lancar EMA untuk menapis bunyi pasaran
- Automatik untuk mengesan trend, tidak mudah untuk ketinggalan
Analisis risiko
Strategi ini mempunyai beberapa risiko:
- Isyarat persilangan dua hala mungkin terlewat dan tidak dapat menangkap perubahan dalam masa yang tepat
- Beberapa isyarat silap mungkin berlaku semasa gempa.
- Tetapan parameter yang tidak betul boleh menyebabkan terlalu sensitif atau terlalu lambat
Ia boleh dioptimumkan dengan menyesuaikan kitaran EMA, atau menambah syarat penapisan.
Arah pengoptimuman
Strategi ini boleh dioptimumkan dalam beberapa aspek:
- Uji kombinasi kitaran EMA dengan panjang yang berbeza
- Menapis isyarat palsu untuk meningkatkan jumlah transaksi atau kadar turun naik
- Pengesahan trend dalam kombinasi dengan penunjuk lain, seperti MACD
- Mengoptimumkan pengurusan wang, menetapkan stop loss
ringkaskan
Strategi penyambungan dua garis sejajar secara keseluruhan adalah strategi trend-following yang mudah dan praktikal. Ia lurus ke hadapan, mudah dilaksanakan, dan dapat mengikuti trend secara automatik. Tetapi ada juga risiko beberapa lag, isyarat palsu.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-11 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
strategy("ParkerMAStrat", overlay=true)
lenMA1=input(title="Length 1", defval=30)
lenMA2=input(title="Length 2", defval=60)
x = 0
checkLines(current, last) =>
if current > last
x = 1
else
x = 0
x
//plot ema based on len1
emaFuncOne(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
plot(emaLen1, color=green, transp=0, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwo(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncOneLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwoLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLastLen1 = emaFuncOneLast(close, lenMA1)
emaLastLen2 = emaFuncTwoLast(close, lenMA2)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
plot(emaLen2, color=red, transp=30, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//now we compare the two and when green crosses red we buy/sell (line1 vs line2)
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
lineCheck = if convergence == 1
checkLines(currentState, previousState)
if lineCheck == 1
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
else
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)