Chiến lược theo xu hướng điển hình
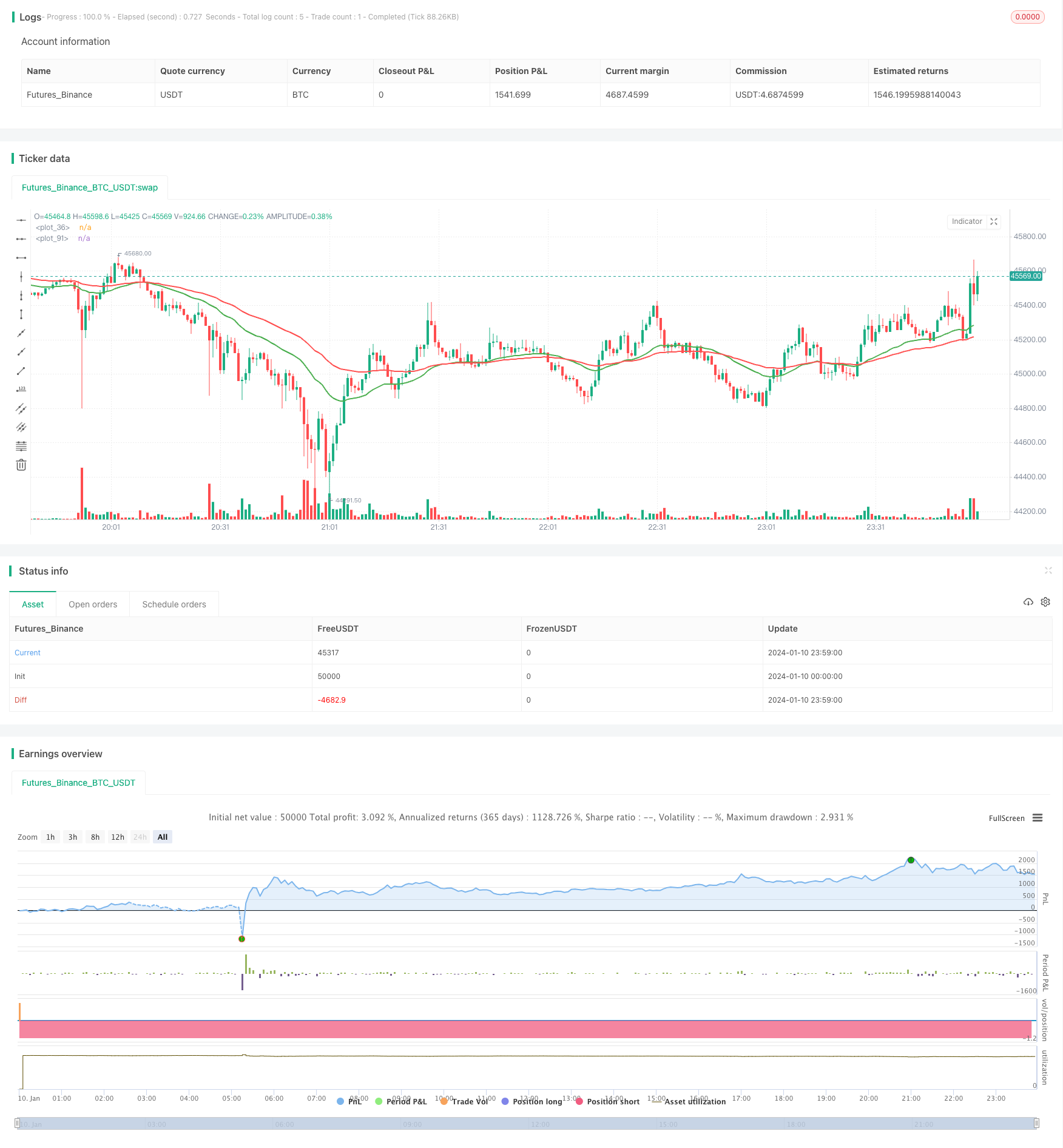
Tổng quan
Chiến lược giao chéo hai đường trung bình là một chiến lược theo dõi xu hướng điển hình. Nó sử dụng đường trung bình EMA của hai chu kỳ khác nhau, làm nhiều khi đường trung bình ngắn xuyên qua đường trung bình dài và làm trống khi đường trung bình ngắn xuyên qua đường trung bình dài để nắm bắt điểm biến của xu hướng giá.
Nguyên tắc chiến lược
Chỉ số cốt lõi của chiến lược là hai đường trung bình EMA, 30 chu kỳ và 60 chu kỳ. Trong mã, hai đường trung bình EMA được tính bằng hàm tùy chỉnh:
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
Tín hiệu giao dịch của chiến lược đến từ sự giao nhau của hai đường trung bình EMA:
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
Khi EMA ngắn hạn trên EMA dài hạn, currentState không bằng với previousState, tín hiệu chéo xuất hiện. Khi EMA ngắn hạn vượt qua EMA dài hạn, currentState không bằng với previousState và có tín hiệu chéo.
Phân tích lợi thế
Chiến lược này có những ưu điểm sau:
- Chiến lược đơn giản, trực quan, dễ hiểu và thực hiện
- Sử dụng tính chất mịn của đường EMA để lọc hiệu quả tiếng ồn thị trường
- Theo dõi xu hướng tự động, không dễ bị bỏ lỡ
Phân tích rủi ro
Chiến lược này cũng có một số rủi ro:
- Tín hiệu giao tuyến hai chiều có thể bị chậm và không thể bắt kịp chuyển hướng.
- Có thể có nhiều tín hiệu sai trong cơn động đất
- Thiết lập tham số không đúng có thể dẫn đến quá nhạy cảm hoặc quá chậm trễ
Có thể tối ưu hóa bằng cách điều chỉnh chu kỳ EMA hoặc thêm điều kiện lọc.
Hướng tối ưu hóa
Chiến lược này có thể được tối ưu hóa theo các khía cạnh sau:
- Kiểm tra các kết hợp chu kỳ EMA với độ dài khác nhau
- Điều kiện tăng giao dịch hoặc dao động lọc tín hiệu giả
- Kết hợp với các chỉ số khác xác nhận xu hướng, ví dụ MACD
- Tối ưu hóa quản lý tài chính, thiết lập chặn lỗ
Tóm tắt
Chiến lược giao chéo hai đường thẳng là một chiến lược theo dõi xu hướng đơn giản và thực tế. Nó là một chiến lược theo dõi xu hướng trực tiếp, dễ thực hiện và có thể tự động theo dõi xu hướng. Nhưng cũng có một số rủi ro bị trễ, tín hiệu giả.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-11 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
strategy("ParkerMAStrat", overlay=true)
lenMA1=input(title="Length 1", defval=30)
lenMA2=input(title="Length 2", defval=60)
x = 0
checkLines(current, last) =>
if current > last
x = 1
else
x = 0
x
//plot ema based on len1
emaFuncOne(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
plot(emaLen1, color=green, transp=0, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwo(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncOneLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwoLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLastLen1 = emaFuncOneLast(close, lenMA1)
emaLastLen2 = emaFuncTwoLast(close, lenMA2)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
plot(emaLen2, color=red, transp=30, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//now we compare the two and when green crosses red we buy/sell (line1 vs line2)
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
lineCheck = if convergence == 1
checkLines(currentState, previousState)
if lineCheck == 1
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
else
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)