Handelsstrategie „Golden Cross“ und „Death Cross“ mit doppeltem gleitenden Durchschnitt
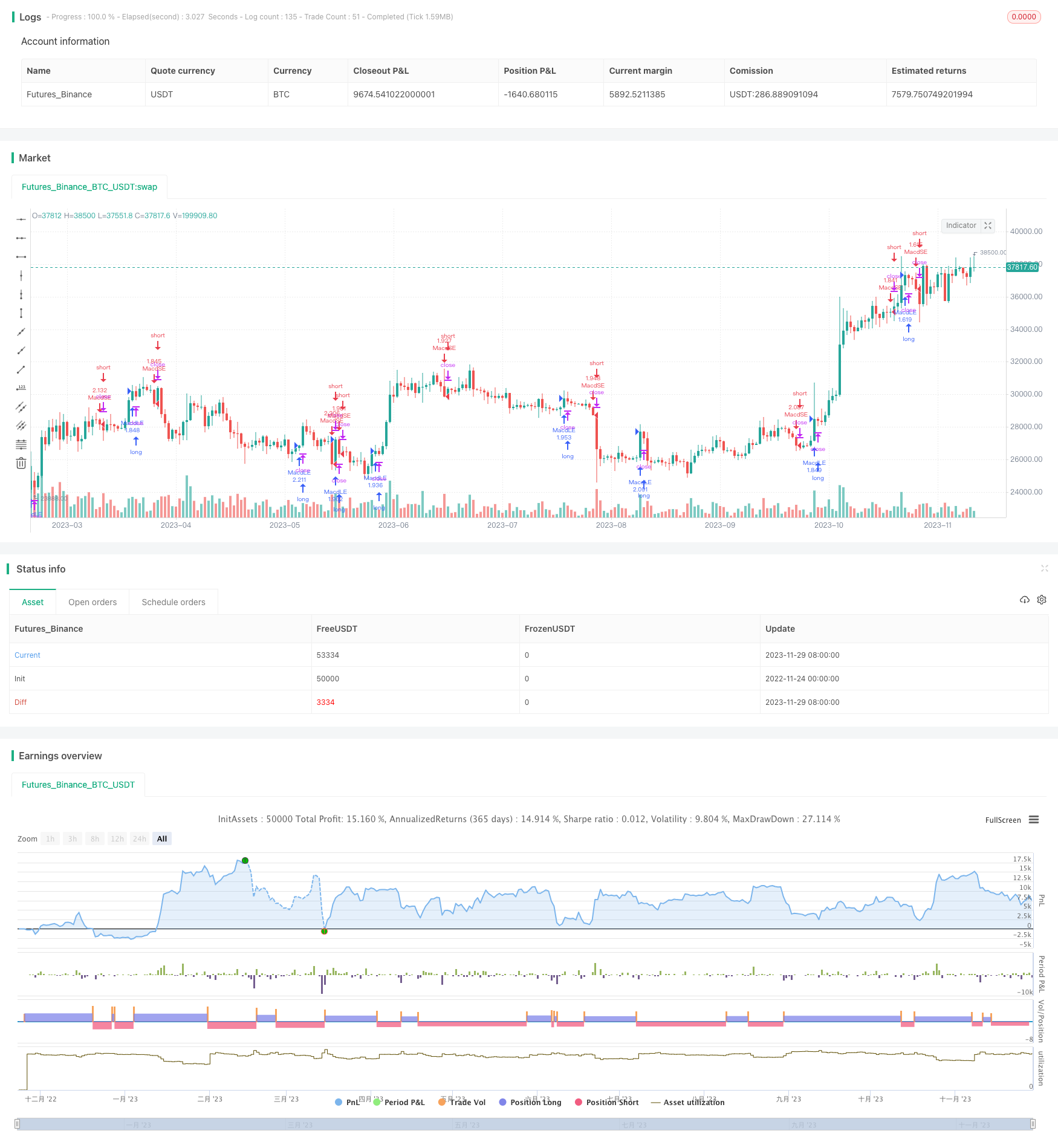
Überblick
Die Doppel-Gleichgewichts-Handelsstrategie erzeugt Handelssignale durch die Berechnung von Index-Moving-Averagen für verschiedene Perioden, die die Form von Schnell- und Langstrecken bilden, und beobachtet ihre Gold- und Todesforken. Wenn die Schnelllinie die Langstrecke von unten durchbricht, macht man mehr; wenn die Schnelllinie die Langstrecke von oben durchbricht, macht man null.
Strategieprinzip
Der Kern der Binary Equity Trading Strategie ist die Berechnung von Schnell- und Langlauflinien. Die Schnelllinie zeigt den Index-Moving-Average für kurze Perioden mit dem Standardwert von 12 Tagen; die Langlauflinie zeigt den Index-Moving-Average für lange Perioden mit dem Standardwert von 26 Tagen.
EMA(t) = (C(t) - EMA(t-1)) * SF + EMA(t-1)
Der Indikator bewegt sich im Unterschied zu einem Arithmetischen Moving Average, indem er den jüngsten Daten mehr Gewicht verleiht und schneller auf Preisänderungen reagiert.
Die Handelsregeln für eine Doppel-Einheit-Strategie sind:
- Wenn die schnelle Linie die langsame Linie von unten durchquert, wird ein goldener Kreuz gebildet, der mehrere Einstiege macht.
- Wenn die schnelle Linie die langsame Linie von oben nach unten durchbricht, entsteht ein “Dead Cross”, der den freien Eintritt ermöglicht.
- Wenn die Schnell- und die Langstrecke sich voneinander entfernen, verlässt der Spieler den Platz.
Durch die Überwachung der Kreuzungen der Gleichgewichtlinie, die durch Capture erfasst wird, können Sie die Veränderungen der Angebots- und Nachfragebeziehungen und -trends des Marktes rechtzeitig reagieren und profitabel sein.
Analyse der Stärken
Die Binäroption-Strategie ist eine ausgereiftere Technik, die folgende Vorteile hat:
- Es ist wichtig zu wissen, dass es sich um eine klare Idee handelt, die leicht zu verstehen und umzusetzen ist.
- Das ist eine sehr gute Möglichkeit, um die Nachfrage und die Versorgung des Marktes zu beurteilen.
- Wird der Markt geräuscht, um die wichtigsten Trends zu filtern?
- Die Anwendung ist in verschiedenen Märkten und Zeitrahmen möglich.
- Die Strategie kann mit anderen technischen Indikatoren kombiniert werden, um sie zu erweitern.
- Die Kapitalnutzung ist hoch und entspricht dem hohen Kapitalbedarf.
Risikoanalyse
Die Strategie des Binär-Einzelhandels birgt auch einige Mängel und Risiken:
- Es ist nicht möglich, sich mit extremen Ereignissen, wie einer schnellen Bärenmarkt, auseinanderzusetzen.
- Es gibt viele Möglichkeiten, wie man sich mit dem Internet in Verbindung setzen kann, und es gibt viele Möglichkeiten.
- Die Parameter müssen für verschiedene Sorten und Zeiträume optimiert werden.
- Es ist unmöglich zu beurteilen, wo sich der Trend rational umkehren könnte.
Diese Risiken können optimiert werden, indem die Parameter für die Durchschnittslinie angepasst und zusätzliche Filter eingeführt werden, um eine stabilere Strategie zu gewährleisten.
Optimierungsrichtung
Die Strategie des binären Gleichgewichtshandelns kann in folgenden Bereichen optimiert werden:
- Die Einführung eines MACD-Indikators, um starke und schwache Trends zu erkennen und Fehltrades bei schwachen und wackligen Trends zu vermeiden;
- Erhöhung des Handelsvolumens als Bestätigungsindikator, um falsche Durchbrüche mit Trendumkehr zu vermeiden;
- In Kombination mit anderen technischen Indikatoren wie Brin- und K-Linien werden präzisere Ein- und Ausstiegsbedingungen festgelegt.
- Die automatische Optimierung der Mittellinienparameter durch Machine Learning Methoden wie LSTM ermöglicht eine bessere Marktausrichtung.
Zusammenfassen
Die Strategie bietet die Vorteile der Kurzfassung, Klarheit, hohe Kapital-Effizienz und ist die bevorzugte Strategie für die Quantifizierung des Einstiegs. Es gibt jedoch auch einige Mängel, wie die Erzeugung von Falschsignalen, die durch die Einführung von mehr Indikatoren optimiert werden müssen, damit sie besser für bestimmte Sorten und Handelsumgebungen geeignet sind.
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-24 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-30 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © antondmt
//@version=5
strategy("Returns & Drawdowns Table", "R & DD", true, calc_on_every_tick = false, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 100, process_orders_on_close = true)
i_eq_to_dd = input.string("Compound Equity", "Mode", ["Simple Equity", "Compound Equity", "Drawdown"], group = "R & DD Table")
i_precision = input.int(2, "Return Precision", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_col = input.color(#D4D4D4, "Headers Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_text_col = input.color(color.black, "Headers Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_pos_col = input.color(color.green, "Positive Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_neg_col = input.color(color.red, "Negative Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_zero_col = input.color(#DDDDDD, "Zero Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_cell_text_col = input.color(color.white, "Cell Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
// TIME {
var month_times = array.new_int(0) // Array of all month times
new_month = month(time) != month(time[1])
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(month_times, time)
var year_times = array.new_int(0)
new_year = year(time) != year(time[1])
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(year_times, time)
//}
// SIMPLE EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Simple equity is strictly calculated from start to end of each month/year equity. There is no compound
var monthly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Simple Equity")
var initial_monthly_equity = strategy.equity // Starting equity for each month
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_monthly_equity) / initial_monthly_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
initial_monthly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(monthly_simp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_simp_pnls, array.size(monthly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
var initial_yearly_equity = strategy.equity
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_yearly_equity) / initial_yearly_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
initial_yearly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(yearly_simp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_simp_pnls, array.size(yearly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// COMPOUND EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Compound equity is strictly calculated based on equity state from the beginning of time until the end of each month/year equity. It shows the exact equity movement through time
var monthly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Compound Equity")
var initial_equity = strategy.equity
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(monthly_comp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_comp_pnls, array.size(monthly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(yearly_comp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_comp_pnls, array.size(yearly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// DRAWDOWN CALCULATIONS {
// Drawdowns are calculated from highest equity to lowest trough for the month/year
var monthly_dds = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly drawdowns
var yearly_dds = array.new_float(0)
if (i_eq_to_dd == "Drawdown")
total_equity = strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
var cur_month_dd = 0.0
var m_ATH = total_equity // Monthly All-Time-High (ATH). It is reset each month
m_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(m_ATH[1]))
m_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / m_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100 // Drawdown at current bar
if(m_drawdown < cur_month_dd)
cur_month_dd := m_drawdown
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
cur_month_dd := 0.0
m_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(monthly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(monthly_dds, array.size(monthly_dds) - 1, cur_month_dd)
var cur_year_dd = 0.0
var y_ATH = total_equity
y_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(y_ATH[1]))
y_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / y_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100
if(y_drawdown < cur_year_dd)
cur_year_dd := y_drawdown
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
cur_year_dd := 0.0
y_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(yearly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(yearly_dds, array.size(yearly_dds) - 1, cur_year_dd)
// }
// TABLE LOGIC {
var main_table = table(na)
table.clear(main_table, 0, 0, 13, new_year ? array.size(year_times) - 1 : array.size(year_times))
main_table := table.new(position.bottom_right, columns = 14, rows = array.size(year_times) + 1, border_width = 1)
t_set_headers() => // Sets time headers of the table
// Set month headers
table.cell(main_table, 0, 0, "", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 1, 0, "Jan", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 2, 0, "Feb", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 3, 0, "Mar", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 4, 0, "Apr", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 5, 0, "May", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 6, 0, "Jun", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 7, 0, "Jul", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 8, 0, "Aug", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 9, 0, "Sep", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 10, 0, "Oct", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 11, 0, "Nov", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 12, 0, "Dec", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 13, 0, str.tostring(i_eq_to_dd), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
// Set year headers
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
table.cell(main_table, 0, i + 1, str.tostring(year(array.get(year_times, i))), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
t_set_months() => // Sets inner monthly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => monthly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => monthly_comp_pnls
=> monthly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(month_times) - 1
m_row = year(array.get(month_times, i)) - year(array.get(year_times, 0)) + 1
m_col = month(array.get(month_times, i))
m_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 30) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 30)
table.cell(main_table, m_col, m_row, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = m_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_years() => // Sets inner yearly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => yearly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => yearly_comp_pnls
=> yearly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
y_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 20) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 20)
table.cell(main_table, 13, i + 1, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = y_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_headers()
t_set_months()
t_set_years()
// }
// PLACE YOUR STRATEGY CODE HERE {
// This is a sample code of a working strategy to show the table in action
fastLength = input(12)
slowlength = input(26)
MACDLength = input(9)
MACD = ta.ema(close, fastLength) - ta.ema(close, slowlength)
aMACD = ta.ema(MACD, MACDLength)
delta = MACD - aMACD
if (ta.crossover(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdLE", strategy.long, comment = "MacdLE")
if (ta.crossunder(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdSE", strategy.short, comment = "MacdSE")
// }