Estratégia de negociação de média móvel dupla Golden Cross e Death Cross
Visão geral
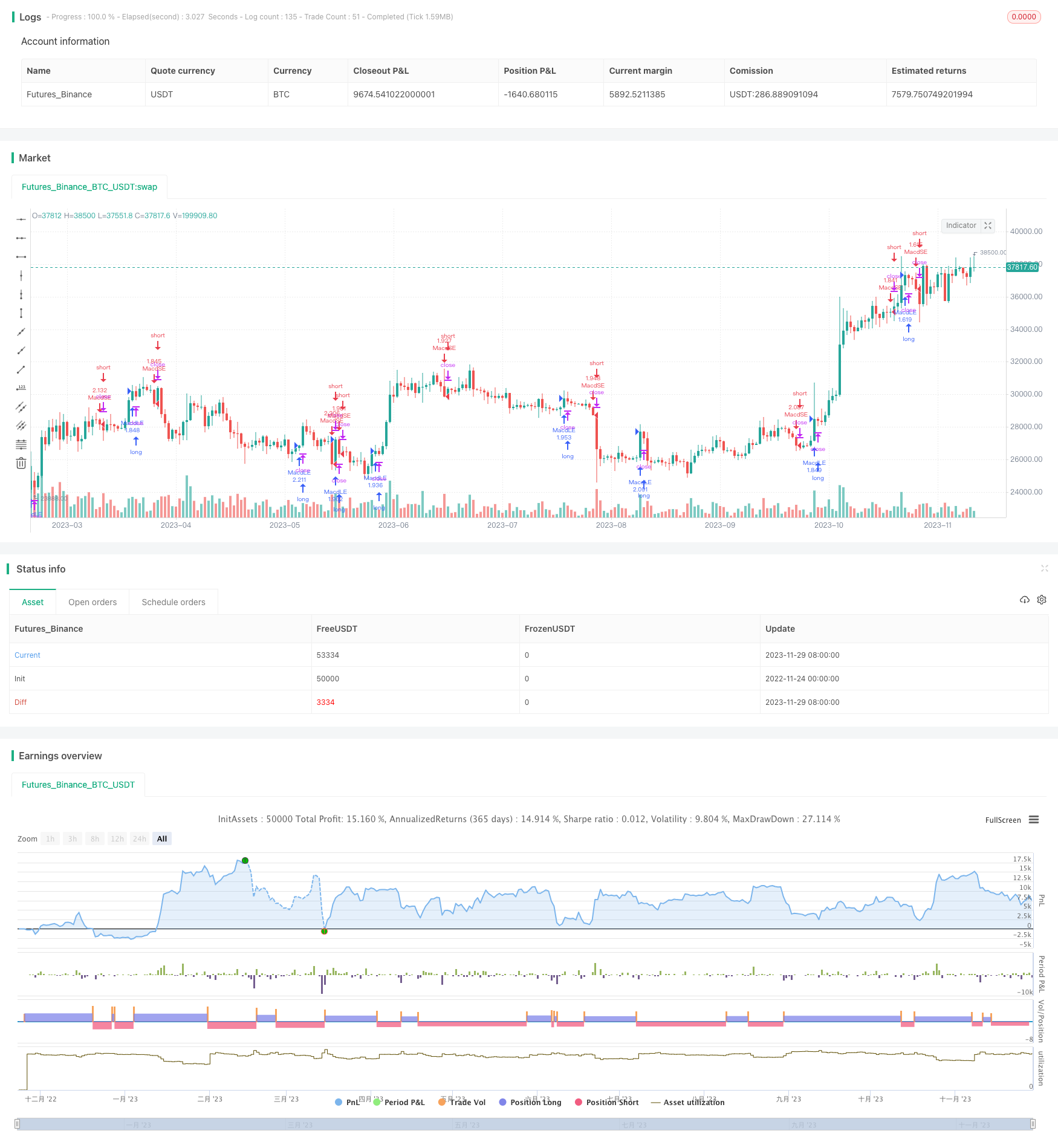
A estratégia de negociação de dupla equilíbrio gera sinais de negociação por meio do cálculo de médias móveis indexadas de diferentes períodos, formando linhas rápidas e lentas, e observando a forma de seus forcados dourados e mortos. Quando a linha rápida atravessa a linha lenta de baixo, faça mais; quando a linha rápida atravessa a linha lenta de cima para baixo, faça zero.
Princípio da estratégia
O indicador central de uma estratégia de negociação em linha dupla é o cálculo da linha rápida e da linha lenta. A linha rápida indica a média móvel do índice de curto período, com o parâmetro padrão de 12 dias; a linha lenta indica a média móvel do índice de longo período, com o parâmetro padrão de 26 dias.
EMA(t) = (C(t) - EMA(t-1)) * SF + EMA(t-1)
Dentre eles, C (t) é o preço de fechamento do dia e SF é o factor de suavização do factor de suavização. A diferença entre a média móvel indexada e a média móvel aritmética comum é que a média móvel indexada dá maior peso aos dados mais recentes e pode responder mais rapidamente às mudanças de preço.
As regras de negociação para uma estratégia de dupla linha são:
- Quando a linha rápida atravessa a linha lenta de baixo, a golden cross é formada, fazendo mais entradas;
- Quando a linha rápida atravessa a linha lenta de cima para baixo, a cruz morta se forma, fazendo a entrada em branco;
- Quando a linha rápida e a linha lenta se afastam, o equilíbrio sai do jogo.
Capturar e monitorar a trajetória da linha de equilíbrio, reagir em tempo hábil às mudanças nas relações de oferta e demanda do mercado e obter lucro.
Análise de vantagens
A estratégia de negociação binária é uma estratégia de indicadores técnicos mais madura, com as seguintes vantagens:
- A ideia é clara, fácil de entender e de implementar.
- A avaliação da oferta e da procura no mercado é mais acurada, com maior probabilidade de sucesso;
- O mercado de criptomoedas é um mercado de criptomoedas que tem como objetivo capturar as principais tendências.
- Aplicável em diferentes mercados e prazos;
- A combinação com outros indicadores tecnológicos enriquece a estratégia;
- A taxa de aproveitamento dos fundos é alta, o que corresponde a uma grande necessidade de capital.
Análise de Riscos
A estratégia de negociação em linha dupla também apresenta alguns defeitos e riscos:
- A falta de capacidade para lidar com situações extremas, como o mercado de ações de baixa voltagem;
- A tendência é para que os sinais falsos e os frequentes e pequenos turbulências conduzam a transações intensas.
- Parâmetros precisam ser otimizados para diferentes variedades e períodos de tempo;
- Não é possível avaliar a localização razoável de uma inversão de tendência.
Para os riscos acima, pode ser otimizado por meio de ajustes nos parâmetros de ciclo de média linha, introdução de filtros adicionais e outros métodos, garantindo uma estratégia mais robusta.
Direção de otimização
A estratégia de negociação em linha dupla pode ser otimizada em vários aspectos:
- A introdução de indicadores MACD para avaliar tendências fortes e fracas, evitando erros de negociação em situações de fraqueza e agitação;
- Aumentar os volumes de negociação como indicador de confirmação, evitando falsas rupturas de reversão de tendência;
- Combinação com outros indicadores técnicos, como linhas Brin e K, para definir condições de entrada e saída mais precisas;
- Utilizando métodos de aprendizagem de máquina, como o LSTM, para otimizar automaticamente os parâmetros da linha média, para uma melhor adaptabilidade ao mercado.
Resumir
A estratégia de negociação de linha dupla capta oportunidades de negociação de forcas de ouro e forcas mortas em linha dupla, determina o ponto de reversão da tendência dos preços e gera lucros estáveis. A vantagem da estratégia é a clareza e a eficiência do capital, e é a estratégia preferida para o ingresso quantitativo. Mas também há certas falhas, como a criação de falsos sinais, que precisam de mais indicadores para otimização, para que possam ser melhor adaptados a uma variedade específica e ao ambiente de negociação.
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-24 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-30 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © antondmt
//@version=5
strategy("Returns & Drawdowns Table", "R & DD", true, calc_on_every_tick = false, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 100, process_orders_on_close = true)
i_eq_to_dd = input.string("Compound Equity", "Mode", ["Simple Equity", "Compound Equity", "Drawdown"], group = "R & DD Table")
i_precision = input.int(2, "Return Precision", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_col = input.color(#D4D4D4, "Headers Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_text_col = input.color(color.black, "Headers Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_pos_col = input.color(color.green, "Positive Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_neg_col = input.color(color.red, "Negative Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_zero_col = input.color(#DDDDDD, "Zero Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_cell_text_col = input.color(color.white, "Cell Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
// TIME {
var month_times = array.new_int(0) // Array of all month times
new_month = month(time) != month(time[1])
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(month_times, time)
var year_times = array.new_int(0)
new_year = year(time) != year(time[1])
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(year_times, time)
//}
// SIMPLE EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Simple equity is strictly calculated from start to end of each month/year equity. There is no compound
var monthly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Simple Equity")
var initial_monthly_equity = strategy.equity // Starting equity for each month
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_monthly_equity) / initial_monthly_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
initial_monthly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(monthly_simp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_simp_pnls, array.size(monthly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
var initial_yearly_equity = strategy.equity
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_yearly_equity) / initial_yearly_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
initial_yearly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(yearly_simp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_simp_pnls, array.size(yearly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// COMPOUND EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Compound equity is strictly calculated based on equity state from the beginning of time until the end of each month/year equity. It shows the exact equity movement through time
var monthly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Compound Equity")
var initial_equity = strategy.equity
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(monthly_comp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_comp_pnls, array.size(monthly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(yearly_comp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_comp_pnls, array.size(yearly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// DRAWDOWN CALCULATIONS {
// Drawdowns are calculated from highest equity to lowest trough for the month/year
var monthly_dds = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly drawdowns
var yearly_dds = array.new_float(0)
if (i_eq_to_dd == "Drawdown")
total_equity = strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
var cur_month_dd = 0.0
var m_ATH = total_equity // Monthly All-Time-High (ATH). It is reset each month
m_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(m_ATH[1]))
m_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / m_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100 // Drawdown at current bar
if(m_drawdown < cur_month_dd)
cur_month_dd := m_drawdown
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
cur_month_dd := 0.0
m_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(monthly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(monthly_dds, array.size(monthly_dds) - 1, cur_month_dd)
var cur_year_dd = 0.0
var y_ATH = total_equity
y_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(y_ATH[1]))
y_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / y_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100
if(y_drawdown < cur_year_dd)
cur_year_dd := y_drawdown
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
cur_year_dd := 0.0
y_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(yearly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(yearly_dds, array.size(yearly_dds) - 1, cur_year_dd)
// }
// TABLE LOGIC {
var main_table = table(na)
table.clear(main_table, 0, 0, 13, new_year ? array.size(year_times) - 1 : array.size(year_times))
main_table := table.new(position.bottom_right, columns = 14, rows = array.size(year_times) + 1, border_width = 1)
t_set_headers() => // Sets time headers of the table
// Set month headers
table.cell(main_table, 0, 0, "", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 1, 0, "Jan", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 2, 0, "Feb", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 3, 0, "Mar", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 4, 0, "Apr", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 5, 0, "May", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 6, 0, "Jun", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 7, 0, "Jul", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 8, 0, "Aug", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 9, 0, "Sep", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 10, 0, "Oct", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 11, 0, "Nov", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 12, 0, "Dec", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 13, 0, str.tostring(i_eq_to_dd), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
// Set year headers
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
table.cell(main_table, 0, i + 1, str.tostring(year(array.get(year_times, i))), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
t_set_months() => // Sets inner monthly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => monthly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => monthly_comp_pnls
=> monthly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(month_times) - 1
m_row = year(array.get(month_times, i)) - year(array.get(year_times, 0)) + 1
m_col = month(array.get(month_times, i))
m_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 30) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 30)
table.cell(main_table, m_col, m_row, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = m_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_years() => // Sets inner yearly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => yearly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => yearly_comp_pnls
=> yearly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
y_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 20) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 20)
table.cell(main_table, 13, i + 1, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = y_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_headers()
t_set_months()
t_set_years()
// }
// PLACE YOUR STRATEGY CODE HERE {
// This is a sample code of a working strategy to show the table in action
fastLength = input(12)
slowlength = input(26)
MACDLength = input(9)
MACD = ta.ema(close, fastLength) - ta.ema(close, slowlength)
aMACD = ta.ema(MACD, MACDLength)
delta = MACD - aMACD
if (ta.crossover(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdLE", strategy.long, comment = "MacdLE")
if (ta.crossunder(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdSE", strategy.short, comment = "MacdSE")
// }