Chiến lược giao dịch đường trung bình động kép Golden Cross và Death Cross
Tổng quan
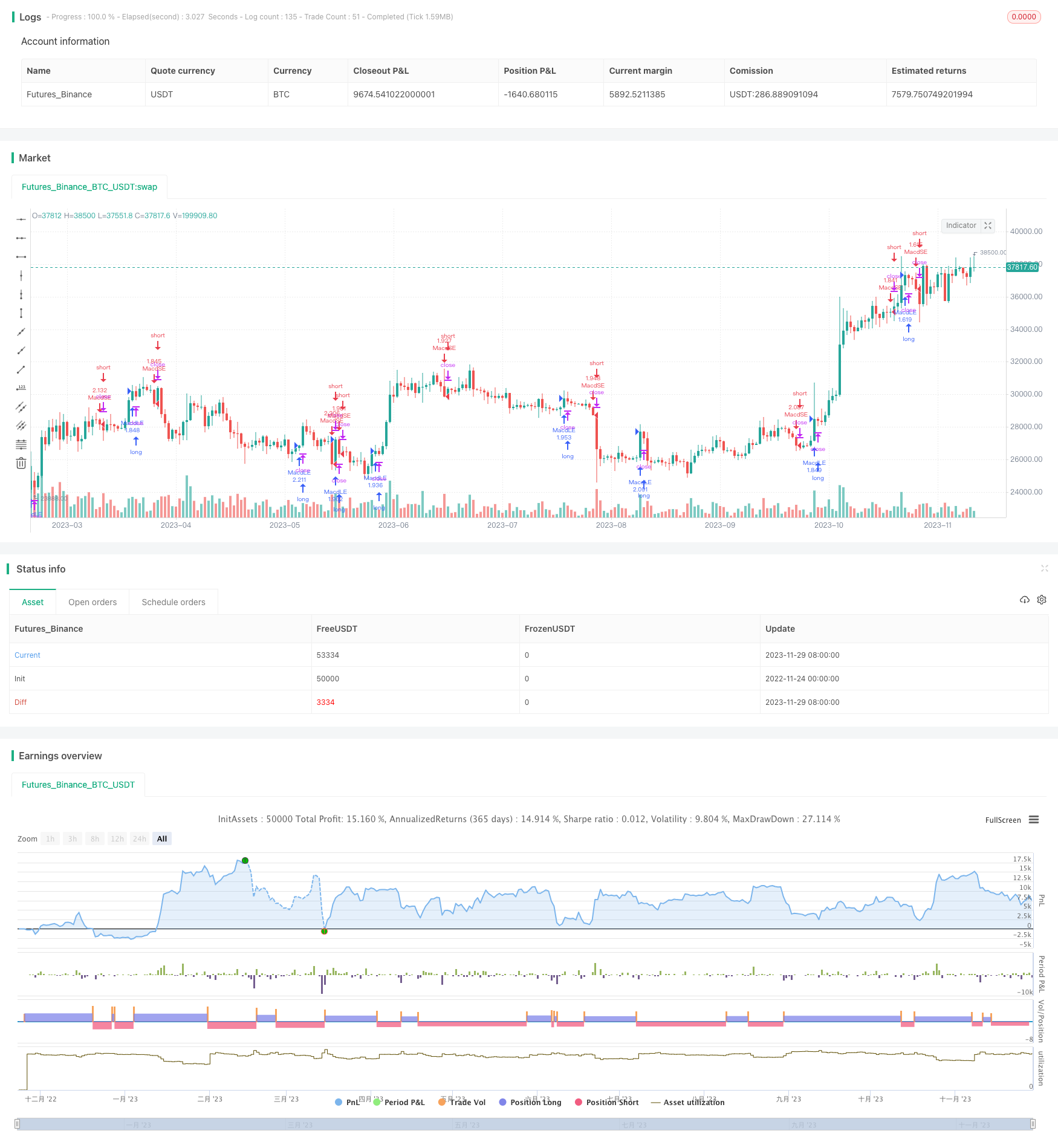
Chiến lược giao dịch hai đường cong tạo ra tín hiệu giao dịch bằng cách tính toán các đường trung bình di chuyển chỉ số của các chu kỳ khác nhau, tạo thành đường nhanh và đường chậm và quan sát hình dạng của họ. Khi đường nhanh đi qua đường chậm từ dưới, hãy làm nhiều; Khi đường nhanh đi qua đường chậm từ trên xuống, hãy làm trống.
Nguyên tắc chiến lược
Các chỉ số cốt lõi của chiến lược giao dịch hai dòng đều là tính toán đường nhanh và đường chậm. Đường nhanh là đường trung bình di chuyển chỉ số của chu kỳ ngắn, tham số mặc định là đường 12 ngày; đường chậm là đường trung bình di chuyển chỉ số của chu kỳ dài, tham số mặc định là đường 26 ngày. Công thức tính toán đường trung bình di chuyển chỉ số là:
EMA(t) = (C(t) - EMA(t-1)) * SF + EMA(t-1)
Trong đó, C (t) là giá đóng cửa trong ngày, SF là yếu tố làm mịn. Sự khác biệt giữa trung bình di chuyển chỉ số và trung bình di chuyển toán học thông thường là trung bình di chuyển chỉ số có trọng lượng lớn hơn cho dữ liệu gần đây và có thể phản ứng nhanh hơn với sự thay đổi giá.
Các quy tắc giao dịch của chiến lược hai đường đều là:
- Khi đường nhanh đi xuyên qua đường chậm từ phía dưới, tức là hình thành hình nẻo vàng, làm nhiều lượt vào;
- Khi đường nhanh đi qua đường chậm từ trên xuống, tức là hình thành dead cross, tạo ra lối vào trống;
- Khi đường nhanh và đường chậm bị tách ra, các cầu thủ phải rời khỏi sân.
Bằng cách nắm bắt các hình thức giao thoa của đường cân bằng, phản ứng kịp thời với sự thay đổi của mối quan hệ cung cầu và xu hướng thị trường, để đạt được lợi nhuận.
Phân tích lợi thế
Chiến lược giao dịch hai dòng như là một chiến lược chỉ số kỹ thuật trưởng thành hơn, có những ưu điểm sau:
- Những ý tưởng rõ ràng, dễ hiểu và dễ thực hiện.
- Đánh giá chính xác về mối quan hệ cung cầu trên thị trường, tỷ lệ thắng cao hơn;
- Nó có thể được sử dụng để lọc tiếng ồn của thị trường và nắm bắt các xu hướng chính.
- Có thể áp dụng trong các thị trường và khung thời gian khác nhau;
- Có thể kết hợp với các chỉ số kỹ thuật khác để làm phong phú chiến lược;
- Tỷ lệ sử dụng vốn cao, phù hợp với nhu cầu tài chính lớn.
Phân tích rủi ro
Chiến lược giao dịch hai dòng đồng đều cũng có một số nhược điểm và rủi ro:
- Các nhà đầu tư không thể đối phó với những biến động như thị trường gấu nhanh.
- Các tín hiệu giả và các biến động nhỏ thường xuyên dẫn đến giao dịch dày đặc;
- Cần tối ưu hóa các tham số để phù hợp với các giống và chu kỳ thời gian khác nhau;
- Không thể xác định được vị trí hợp lý của sự thay đổi xu hướng.
Đối với các rủi ro trên, có thể được tối ưu hóa bằng cách điều chỉnh tham số chu kỳ trung bình, giới thiệu bộ lọc bổ sung, và các phương pháp khác để đảm bảo chiến lược mạnh hơn.
Hướng tối ưu hóa
Chiến lược giao dịch hai dòng đồng đều có thể được tối ưu hóa theo các khía cạnh sau:
- Việc đưa ra chỉ số MACD để đánh giá xu hướng mạnh và yếu, tránh giao dịch sai lầm khi thị trường bị dao động trong khu vực yếu;
- Tăng khối lượng giao dịch như một chỉ số xác nhận, tránh phá vỡ giả để đảo ngược xu hướng;
- Kết hợp với các chỉ số kỹ thuật khác như đường Brin, đường K, để thiết lập các điều kiện nhập cảnh và xuất cảnh chính xác hơn;
- Sử dụng các phương pháp học máy như LSTM để tự động tối ưu hóa các tham số đường trung bình, cho phép thích ứng tốt hơn với thị trường.
Tóm tắt
Chiến lược giao dịch hai đường bằng phẳng bằng cách nắm bắt cơ hội giao dịch vàng và chết của đường bằng phẳng, đánh giá điểm đảo ngược xu hướng giá và tạo ra lợi nhuận ổn định. Ưu điểm của chiến lược này là đơn giản, rõ ràng, hiệu quả về tài chính, là chiến lược ưu tiên cho phép nhập định lượng. Nhưng cũng có một số thiếu sót nhất định, chẳng hạn như tạo ra tín hiệu giả, cần giới thiệu nhiều chỉ số để tối ưu hóa để phù hợp hơn với loại cụ thể và môi trường giao dịch.
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-24 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-30 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © antondmt
//@version=5
strategy("Returns & Drawdowns Table", "R & DD", true, calc_on_every_tick = false, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 100, process_orders_on_close = true)
i_eq_to_dd = input.string("Compound Equity", "Mode", ["Simple Equity", "Compound Equity", "Drawdown"], group = "R & DD Table")
i_precision = input.int(2, "Return Precision", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_col = input.color(#D4D4D4, "Headers Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_headers_text_col = input.color(color.black, "Headers Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_pos_col = input.color(color.green, "Positive Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_neg_col = input.color(color.red, "Negative Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_zero_col = input.color(#DDDDDD, "Zero Color", group = "R & DD Table")
i_cell_text_col = input.color(color.white, "Cell Text Color", group = "R & DD Table")
// TIME {
var month_times = array.new_int(0) // Array of all month times
new_month = month(time) != month(time[1])
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(month_times, time)
var year_times = array.new_int(0)
new_year = year(time) != year(time[1])
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(year_times, time)
//}
// SIMPLE EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Simple equity is strictly calculated from start to end of each month/year equity. There is no compound
var monthly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_simp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Simple Equity")
var initial_monthly_equity = strategy.equity // Starting equity for each month
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_monthly_equity) / initial_monthly_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
initial_monthly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(monthly_simp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_simp_pnls, array.size(monthly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
var initial_yearly_equity = strategy.equity
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_yearly_equity) / initial_yearly_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
initial_yearly_equity := strategy.equity
array.push(yearly_simp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_simp_pnls, array.size(yearly_simp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// COMPOUND EQUITY CALCULATIONS {
// Compound equity is strictly calculated based on equity state from the beginning of time until the end of each month/year equity. It shows the exact equity movement through time
var monthly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly profits and losses
var yearly_comp_pnls = array.new_float(0)
if(i_eq_to_dd == "Compound Equity")
var initial_equity = strategy.equity
cur_month_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity) // Current month's equity change
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(monthly_comp_pnls, cur_month_pnl)
else
array.set(monthly_comp_pnls, array.size(monthly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_month_pnl)
cur_year_pnl = nz((strategy.equity - initial_equity) / initial_equity)
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
array.push(yearly_comp_pnls, cur_year_pnl)
else
array.set(yearly_comp_pnls, array.size(yearly_comp_pnls) - 1, cur_year_pnl)
// }
// DRAWDOWN CALCULATIONS {
// Drawdowns are calculated from highest equity to lowest trough for the month/year
var monthly_dds = array.new_float(0) // Array of all monthly drawdowns
var yearly_dds = array.new_float(0)
if (i_eq_to_dd == "Drawdown")
total_equity = strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
var cur_month_dd = 0.0
var m_ATH = total_equity // Monthly All-Time-High (ATH). It is reset each month
m_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(m_ATH[1]))
m_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / m_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100 // Drawdown at current bar
if(m_drawdown < cur_month_dd)
cur_month_dd := m_drawdown
if(new_month or barstate.isfirst)
cur_month_dd := 0.0
m_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(monthly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(monthly_dds, array.size(monthly_dds) - 1, cur_month_dd)
var cur_year_dd = 0.0
var y_ATH = total_equity
y_ATH := math.max(total_equity, nz(y_ATH[1]))
y_drawdown = -math.abs(total_equity / y_ATH * 100 - 100) / 100
if(y_drawdown < cur_year_dd)
cur_year_dd := y_drawdown
if (new_year or barstate.isfirst)
cur_year_dd := 0.0
y_ATH := strategy.equity - strategy.openprofit
array.push(yearly_dds, 0)
else
array.set(yearly_dds, array.size(yearly_dds) - 1, cur_year_dd)
// }
// TABLE LOGIC {
var main_table = table(na)
table.clear(main_table, 0, 0, 13, new_year ? array.size(year_times) - 1 : array.size(year_times))
main_table := table.new(position.bottom_right, columns = 14, rows = array.size(year_times) + 1, border_width = 1)
t_set_headers() => // Sets time headers of the table
// Set month headers
table.cell(main_table, 0, 0, "", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 1, 0, "Jan", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 2, 0, "Feb", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 3, 0, "Mar", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 4, 0, "Apr", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 5, 0, "May", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 6, 0, "Jun", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 7, 0, "Jul", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 8, 0, "Aug", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 9, 0, "Sep", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 10, 0, "Oct", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 11, 0, "Nov", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 12, 0, "Dec", text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
table.cell(main_table, 13, 0, str.tostring(i_eq_to_dd), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
// Set year headers
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
table.cell(main_table, 0, i + 1, str.tostring(year(array.get(year_times, i))), text_color = i_headers_text_col, bgcolor = i_headers_col)
t_set_months() => // Sets inner monthly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => monthly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => monthly_comp_pnls
=> monthly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(month_times) - 1
m_row = year(array.get(month_times, i)) - year(array.get(year_times, 0)) + 1
m_col = month(array.get(month_times, i))
m_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 30) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 30)
table.cell(main_table, m_col, m_row, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = m_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_years() => // Sets inner yearly data of the table
display_array = switch i_eq_to_dd
"Simple Equity" => yearly_simp_pnls
"Compound Equity" => yearly_comp_pnls
=> yearly_dds
for i = 0 to array.size(year_times) - 1
y_color = array.get(display_array, i) == 0 ? color.new(i_zero_col, transp = 30) : array.get(display_array, i) > 0 ? color.new(i_pos_col, transp = 20) : color.new(i_neg_col, transp = 20)
table.cell(main_table, 13, i + 1, str.tostring(math.round(array.get(display_array, i) * 100, i_precision)), bgcolor = y_color, text_color = i_cell_text_col)
t_set_headers()
t_set_months()
t_set_years()
// }
// PLACE YOUR STRATEGY CODE HERE {
// This is a sample code of a working strategy to show the table in action
fastLength = input(12)
slowlength = input(26)
MACDLength = input(9)
MACD = ta.ema(close, fastLength) - ta.ema(close, slowlength)
aMACD = ta.ema(MACD, MACDLength)
delta = MACD - aMACD
if (ta.crossover(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdLE", strategy.long, comment = "MacdLE")
if (ta.crossunder(delta, 0))
strategy.entry("MacdSE", strategy.short, comment = "MacdSE")
// }