Estrategia de interés compuesto de inversión fija con costo promedio dinámico
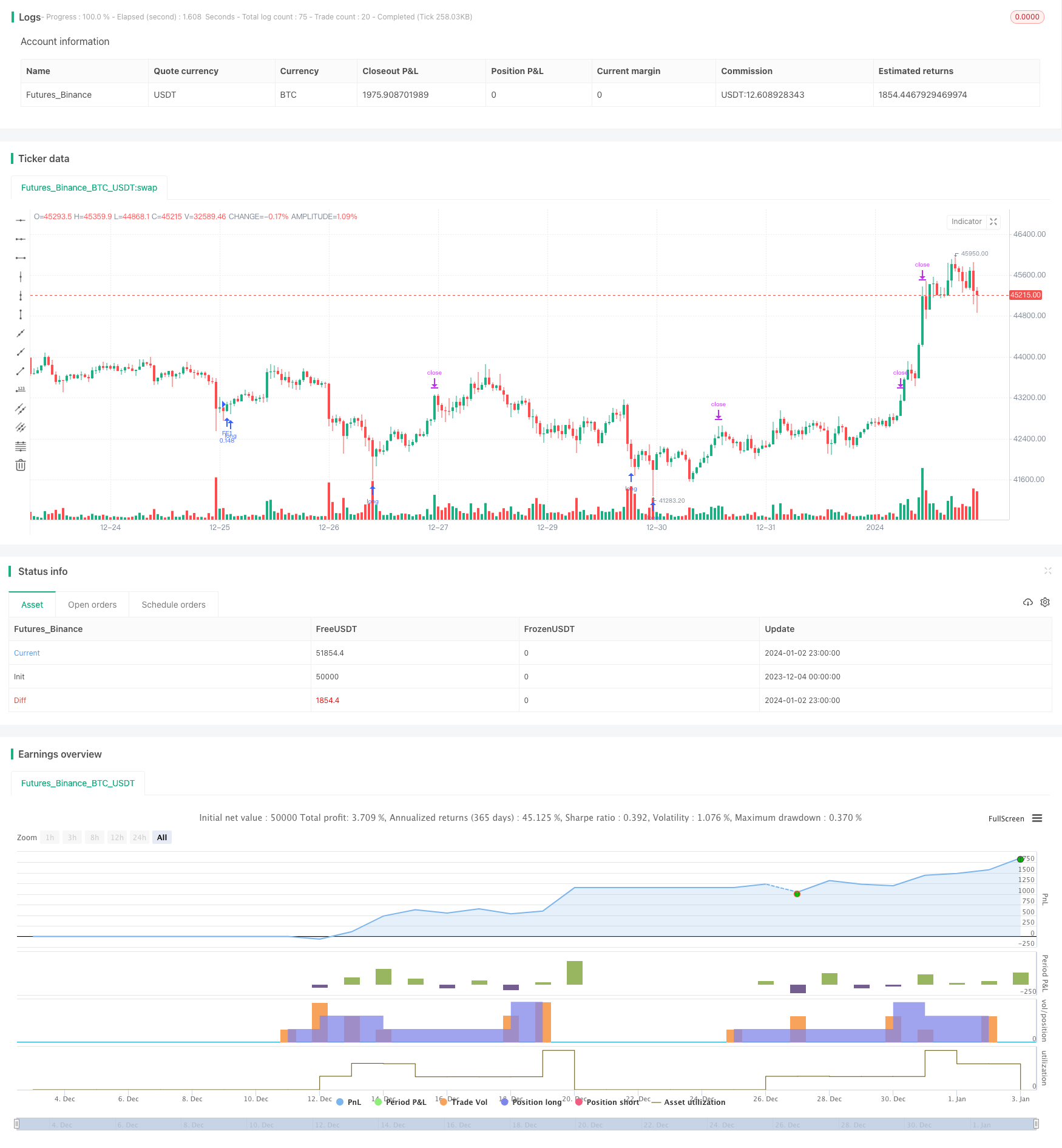
Descripción general
La estrategia de inversión de ganancias y costos promedio dinámico ajusta dinámicamente la cantidad de cada apertura de posición, comienza con una pequeña apertura de posición en la etapa inicial de la tendencia y aumenta gradualmente la posición a medida que aumenta la profundidad de la liquidación. La estrategia utiliza una función de índice para calcular el precio de parada de cada nivel y desencadena la apertura de nuevas posiciones en el nuevo lote, lo que permite mantener la línea de costo de la posición a la baja en el índice.
Principio de estrategia
La estrategia consiste en elegir el momento de abrir una posición mediante una simple combinación de señales RSI de venta por encima de la línea y la elección de la línea media. La primera señal de apertura de posición se produce cuando el RSI está por debajo de la línea de venta por encima de la línea y el precio de cierre es menor que la línea media. A medida que aumenta el número de DCA, el costo de la posición disminuye, y solo se necesita una pequeña rebote para obtener ganancias con cada parada. Una vez que el precio vuelve a romper hacia arriba y supera el precio medio de la posición y la línea de parada, se detiene la salida.
La mayor ventaja de la estrategia es que, a medida que los costos de mantenimiento disminuyen, se pueden reducir gradualmente los costos, incluso si se liquida el mercado. Cuando la tendencia se invierte, se pueden obtener ganancias más significativas, ya que los costos de mantenimiento ya están mucho más bajos que el precio de mercado.
Riesgos y defectos
El mayor riesgo de esta estrategia es que la posición inicial es limitada. Si la tendencia continúa bajando, existe el riesgo de pérdida de parada. Por lo tanto, es necesario establecer el nivel de pérdida de parada que se puede soportar.
Además, la configuración de la amplitud de parada también tiene dos extremos. La configuración de una unidad de parada demasiado grande no tiene un rebote lo suficientemente profundo. La configuración de una amplitud de parada demasiado pequeña tiene una probabilidad más alta de que el precio vuelva a detenerse y se invierta en el ajuste a medio plazo.
Después de un ciclo de DCA más largo y con más niveles, si el precio aumenta mucho, se enfrenta al riesgo de que los costos de la posición sean demasiado altos e irrefrenables. Esto también requiere un nivel razonable de DCA según el total de sus posiciones y el costo de la posición más alto que puede soportar.
Recomendaciones para la optimización
Optimización de la señal de selección. Se pueden probar diferentes parámetros y diferentes combinaciones de indicadores con la esperanza de seleccionar una señal con mayor probabilidad de éxito.
Mecanismos de optimización de los paros. Se puede probar el uso de paros tipo Λ o paros de arco en lugar de paros móviles simples, lo que puede obtener un mejor efecto de paros. También se puede agregar una estrategia para ajustar la amplitud de los paros en el momento de la posición.
Optimización de la suspensión. Se pueden probar diferentes tipos de suspensiones móviles para encontrar mejores oportunidades de salida de suspensión, lo que mejora la rentabilidad general.
La inclusión de un mecanismo de protección contra rebotes. Después de la parada de pérdidas, puede haber situaciones en las que se puede activar una nueva señal DCA para reabrir la posición. En este caso, se puede considerar la inclusión de un rango de protección contra rebotes de cierta amplitud para evitar que la posición se vuelva a activar inmediatamente después de la parada.
Resumir
Esta estrategia utiliza el indicador RSI para determinar el momento de compra y la estrategia de DCA de pérdidas dinámicas calculadas según la función del índice para ajustar dinámicamente el número de posiciones y el costo de la posición, lo que permite obtener una ventaja de precio en el mercado de bandas. El programa de optimización se centra principalmente en las señales de entrada y salida, los paros y los paros. En general, la estrategia utiliza la idea central de la DCA del índice para que los costos de la posición se muevan hacia abajo, lo que permite obtener más espacio de operación durante la liquidación y obtener mayores ganancias en condiciones de tendencia.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-04 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-03 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0///
// © A3Sh
//@version=5
// Study of a Simple RSI based, PA (priceaveraging) and DCA strategy that opens a new position everytime it hits a specified price level below the first entry.
// The first entry is opened when the specified rsi and moving average conditions are met.
// The following DCA levels are calculated exponentially and set, starting with a specified % of price drop.
// The disctance between the dca levels can be changed with the exponential scale.
// Each position closes individually when it reaches a specified take profit.
// The position can re-open again when it hits the price level again.
// Each time a position is closed and reopened, the average price drops a little.
// The position stays open until the first entry closes or when the price reaches the Stop level.
// When the price reaches the Stop level, all positions will close at once.
// The RSI and MA code for opening the entry is adapted from the Optimized RSI Buy the Dips strategy, by Coinrule.
// This code is used for study purposes, but any other low/ dip finding indicator can be used.
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/Pm1WAtyI-Optimized-RSI-Strategy-Buy-The-Dips-by-Coinrule/
// Dynamic DCA layers are inspired by the Backtesting 3commas DCA Bot v2, by rouxam
// This logic gives more flexibility because you can dyanically change the amount of dca entries.
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/8d6Auyst-Backtesting-3commas-DCA-Bot-v2/
// The use of for loops to (re)open and close different entries separately is based on the Simple_Pyramiding strategy.
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/t6cNLqDN-Simple-Pyramiding/
strategy('Simple_RSI+PA+DCA', overlay=true, pyramiding=20, initial_capital=500, calc_on_order_fills=true, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.075, close_entries_rule='FIFO')
// Backtest Window //
start_time = input(defval=timestamp("01 April 2021 20:00"), group = "Backtest Window", title="Start Time")
end_time = input(defval=timestamp("01 Aug 2030 20:00"), group = "Backtest Window", title="End Time")
window() => true
// Inputs //
takeProfit = input.float (3, group = 'Risk', title = 'Take Profit %', step=0.1)
takeProfitAll = input.float (6, group = "Risk", title = 'Close All %', step=0.1)
posCount = input.int (8, group = 'DCA Settings', title = 'Max Amount of Entries')
increment = input.float (2, group = 'DCA Settings', title = 'Price Drop % to open First DCA Order', step=0.5)/100
exponent_scale = input.float (1.4, group = 'DCA Settings', title = 'Exponential Scale DCA levels', step=0.1, minval=1.1)
bar_lookback = input.int (4999, group = 'DCA Settings', title = 'Lines Bar Lookback', maxval = 4999)
plotMA = input.bool (false, group = 'Moving Average', title = 'Plot Moving Average')
moving_average = input.int (100, group = 'Moving Average', title = 'MA Length' )
rsiLengthInput = input.int (14, group = 'RSI Settings', title = "RSI Length", minval=1)
rsiSourceInput = input.source (close, group = 'RSI Settings', title = 'Source')
overSold = input.int (29, group = 'RSI Settings', title = 'Oversold, Trigger to Enter First Position')
// variables //
var open_position = true // true when there are open positions
var entry_price = 0.0 // the entry price of the first entry
var dca_price = 0.0 // the price of the different dca layers
var int count = 0 // bar counter since first open position
var int max_bar = 0 // max bar buffer variable for DCA lines, stop lines, average price
var line dca_line = na // lines variable for creating dca lines
// arrays //
linesArray = array.new_float(posCount,na) // array to store different dca price levels for creating the dca lines
// Create max bar buffer for DCA lines, Stop and average price lines //
max_bar := count >= bar_lookback ? bar_lookback : count
// Order size based on first entry and amount of DCA layers
q = (strategy.equity / posCount + 1) / open
// Calculate Moving Averages
movingaverage_signal = ta.sma(close ,moving_average)
plot (plotMA ? movingaverage_signal : na, color = color.new(#f5ff35, 0))
// RSI calculations //
up = ta.rma(math.max(ta.change(rsiSourceInput), 0), rsiLengthInput)
down = ta.rma(-math.min(ta.change(rsiSourceInput), 0), rsiLengthInput)
rsi = down == 0 ? 100 : up == 0 ? 0 : 100 - (100 / (1 + up / down))
// Buy Signal (co)
co = ta.crossover(rsi, overSold) and close < movingaverage_signal
// Create a white line for average price, since the last opened position //
// average_price = line.new(x1 = bar_index - max_bar, y1 = strategy.position_avg_price, x2 = bar_index, y2 = strategy.position_avg_price, color = color.white)
// Stop //
// Create a red Stop level line based on a specified % above the average price //
stop_level = strategy.position_avg_price + (strategy.position_avg_price / 100 * takeProfitAll)
// stop_line = line.new(x1 = bar_index - max_bar, y1 = stop_level, x2 = bar_index, y2 = stop_level, color = color.red)
// Take profit definition per open position //
take_profit_price = close * takeProfit / 100 / syminfo.mintick
// Make sure the Stop level and average price level don't excied the bar buffer to avoid errors //
// if count <= bar_lookback
// line.set_x1(stop_line, strategy.opentrades.entry_bar_index(strategy.opentrades - 1))
// line.set_x1(average_price, strategy.opentrades.entry_bar_index(strategy.opentrades - 1))
// Exponential DCA Layer Calculation fucntion --> First try, needs more experimentation //
dca_price_level(index,entry_price) =>
entry_price * (1 - (increment * math.pow(exponent_scale, index)))
// Set Entries //
// Open the first entry and set the entry price //
if co and strategy.position_size == 0 and window()
open_position := true
entry_price := close
strategy.entry(id = 'FE1', direction = strategy.long, qty = q)
// first_entry_line = line.new(x1 = bar_index - max_bar, y1 = entry_price, x2 = bar_index, y2 = entry_price, color = color.blue)
// Start bar counting since the position is open //
if open_position == true
count := count + 1
// Set the DCA entries //
// Prices below 1 are not set to avoid negative prices //
if strategy.position_size > 0 and window()
for i = 0 to strategy.opentrades
if strategy.opentrades == i and i < posCount
dca_price := dca_price_level(i,entry_price) > 1 ? dca_price_level(i,entry_price) : na
entry_id = 'DCA' + str.tostring(i + 1)
strategy.entry(id = entry_id, direction = strategy.long, limit = dca_price, qty = q)
// Store the values of the different dca price levels in an array and create the dca lines //
// Prices below 1 are not stored//
if open_position==true and window()
for i = 1 to posCount -1
array.push(linesArray, dca_price_level(i,entry_price) > 1 ? dca_price_level(i,entry_price) : na)
// for i = 1 to array.size(linesArray) - 1
// dca_line := line.new(x1 = bar_index - max_bar, y1 = array.get(linesArray, i), x2 = bar_index, y2 = array.get(linesArray, i),color = color.blue)
// Create thick line to show the last Entry price //
// last_entry_price = line.new(x1 = bar_index[5], y1 = strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1), x2 = bar_index, y2 = strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1),color = color.rgb(255, 0, 204), width = 5)
// Exit the first entry when the take profit triggered //
if strategy.opentrades > 0 and window()
strategy.exit(id = 'Exit FE', from_entry = 'FE1', profit = take_profit_price)
// Exit DCA entries when take profit is triggered //
if strategy.opentrades > 0 and window()
for i = 0 to strategy.opentrades
exit_from = 'DCA' + str.tostring(i + 1)
exit_id = 'Exit_' + str.tostring(i + 1)
strategy.exit(id = exit_id, from_entry = exit_from, profit = take_profit_price)
// Close all positions at once when Stop is crossed //
if strategy.opentrades > 0 and ta.crossover(close,stop_level) and window()
strategy.close_all()
// Make sure nothing is open after alle positions are closed and set the condiftion back to be open for new entries //
if strategy.position_size[1] > 0 and strategy.position_size == 0
strategy.cancel_all()
strategy.close_all()
// line.delete(average_price)
// line.delete(stop_line)
// line.delete(dca_line)
open_position := false // All position are closed, so back to false
count := 0 // Reset bar counter