Stratégie de moyenne mobile lissée
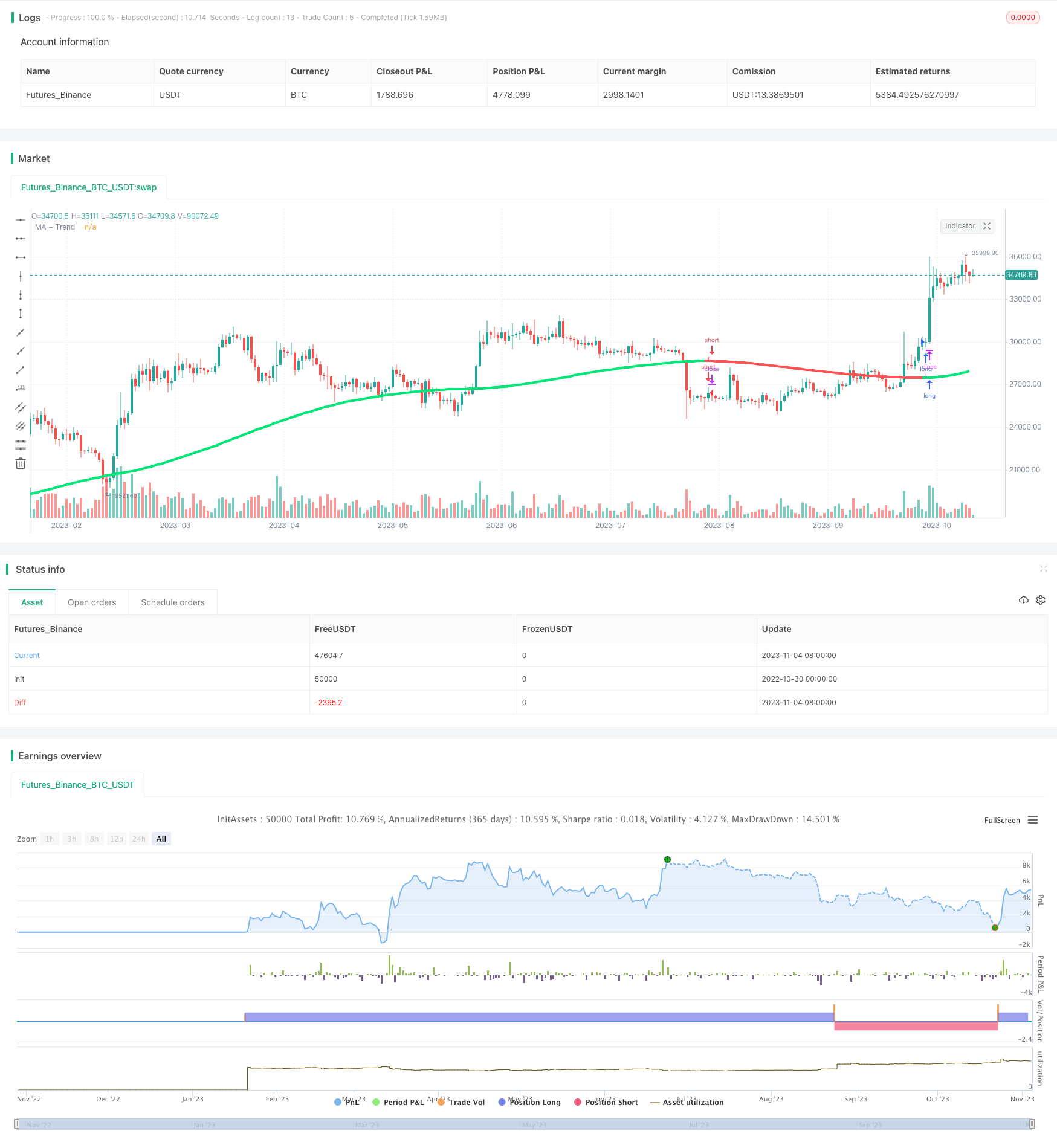
Aperçu
Cette stratégie combine plusieurs moyennes mobiles différentes pour réaliser une stratégie simple de suivi des tendances. La stratégie a également la fonction de filtrage du bruit.
Principe de stratégie
La stratégie commence par l’aplatissement du prix de clôture, qui permet de choisir d’utiliser ou non le prix de clôture Heiken Ashi. Ensuite, la fonction smoothMA est appelée, ce qui permet de superposer plusieurs fois des moyennes mobiles lisses. La fonction smoothMA appelle d’abord une fonction variante, qui peut générer plusieurs types de moyennes mobiles, telles que SMA, EMA, DEMA, etc. Après que la fonction variante a généré des moyennes mobiles de type et de longueur spécifiés, la fonction smoothMA est appelée à superposer plusieurs fois les fonctions variantes de manière récurrente, ce qui permet de réaliser des multiples aplatissements.
Analyse des avantages
- Les moyennes mobiles sont superposées de manière à filtrer efficacement le bruit du marché et à identifier les tendances.
- Il prend en charge plusieurs types de moyennes mobiles, telles que SMA, EMA, DEMA, etc., et peut être utilisé de manière flexible.
- Il est possible de filtrer les fausses intrusions avec la technologie Heiken Ashi.
- Les stratégies sont simples et faciles à utiliser.
- Permet de personnaliser la longueur, le type et le nombre de glissades des moyennes mobiles et d’optimiser les paramètres pour différentes variétés.
Analyse des risques
- Les moyennes mobiles qui se superposent peuvent être retardées, et manquer les premières variations de tendance.
- Il n’est pas possible de faire des bénéfices efficaces dans une situation de choc en utilisant uniquement un système de moyenne mobile simple.
- Les coûts de transaction dans les transactions réelles, sans tenir compte des coûts de transaction, réduisent la rentabilité.
- Il n’y a pas de stop loss, il y a un risque d’augmentation des pertes.
On peut envisager d’utiliser d’autres indicateurs comme le MACD, le KDJ, etc. pour identifier les signaux de tendance avec plus de précision. Optimiser les paramètres des moyennes mobiles, réduire le retard.
Direction d’optimisation
- Il est possible d’essayer différentes combinaisons de moyennes mobiles de longueurs et de types différents pour trouver le paramètre optimal.
- Il est possible d’envisager d’inclure d’autres indicateurs techniques dans la stratégie, afin de former des règles d’entrée et de sortie plus systématiques.
- Les heures de négociation peuvent être réglées afin d’éviter que les événements macroéconomiques majeurs n’affectent la stratégie.
- Les paramètres peuvent être ajustés en fonction des caractéristiques de la variété pour trouver la combinaison optimale de paramètres.
- Il est possible de définir des niveaux de stop loss et de stop-loss pour contrôler le risque de transaction.
Résumer
La stratégie permet de suivre les tendances en superposant plusieurs moyennes mobiles, ce qui permet d’éliminer efficacement le bruit du marché. L’avantage est la simplicité et la facilité d’utilisation, et la flexibilité d’ajuster les paramètres. Cependant, l’utilisation d’un système de moyennes mobiles uniquement reste un problème de rentabilité limitée.
/*backtest
start: 2022-10-30 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-05 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
// Copyright (c) 2007-present Jurik Research and Consulting. All rights reserved.
// Copyright (c) 2018-present, Alex Orekhov (everget)
// Thanks to everget for code for more advanced moving averages
// Smooth Moving Average [STRATEGY] @PuppyTherapy script may be freely distributed under the MIT license.
strategy( title="Smooth Moving Average [STRATEGY] @PuppyTherapy", overlay=true )
// ---- CONSTANTS ----
lsmaOffset = 1
almaOffset = 0.85
almaSigma = 6
phase = 2
power = 2
// ---- GLOBAL FUNCTIONS ----
kama(src, len)=>
xvnoise = abs(src - src[1])
nfastend = 0.666
nslowend = 0.0645
nsignal = abs(src - src[len])
nnoise = sum(xvnoise, len)
nefratio = iff(nnoise != 0, nsignal / nnoise, 0)
nsmooth = pow(nefratio * (nfastend - nslowend) + nslowend, 2)
nAMA = 0.0
nAMA := nz(nAMA[1]) + nsmooth * (src - nz(nAMA[1]))
t3(src, len)=>
xe1_1 = ema(src, len)
xe2_1 = ema(xe1_1, len)
xe3_1 = ema(xe2_1, len)
xe4_1 = ema(xe3_1, len)
xe5_1 = ema(xe4_1, len)
xe6_1 = ema(xe5_1, len)
b_1 = 0.7
c1_1 = -b_1*b_1*b_1
c2_1 = 3*b_1*b_1+3*b_1*b_1*b_1
c3_1 = -6*b_1*b_1-3*b_1-3*b_1*b_1*b_1
c4_1 = 1+3*b_1+b_1*b_1*b_1+3*b_1*b_1
nT3Average_1 = c1_1 * xe6_1 + c2_1 * xe5_1 + c3_1 * xe4_1 + c4_1 * xe3_1
// The general form of the weights of the (2m + 1)-term Henderson Weighted Moving Average
getWeight(m, j) =>
numerator = 315 * (pow(m + 1, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (pow(m + 2, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (pow(m + 3, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (3 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 11 * pow(j, 2) - 16)
denominator = 8 * (m + 2) * (pow(m + 2, 2) - 1) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 1) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 9) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 25)
denominator != 0
? numerator / denominator
: 0
hwma(src, termsNumber) =>
sum = 0.0
weightSum = 0.0
termMult = (termsNumber - 1) / 2
for i = 0 to termsNumber - 1
weight = getWeight(termMult, i - termMult)
sum := sum + nz(src[i]) * weight
weightSum := weightSum + weight
sum / weightSum
get_jurik(length, phase, power, src)=>
phaseRatio = phase < -100 ? 0.5 : phase > 100 ? 2.5 : phase / 100 + 1.5
beta = 0.45 * (length - 1) / (0.45 * (length - 1) + 2)
alpha = pow(beta, power)
jma = 0.0
e0 = 0.0
e0 := (1 - alpha) * src + alpha * nz(e0[1])
e1 = 0.0
e1 := (src - e0) * (1 - beta) + beta * nz(e1[1])
e2 = 0.0
e2 := (e0 + phaseRatio * e1 - nz(jma[1])) * pow(1 - alpha, 2) + pow(alpha, 2) * nz(e2[1])
jma := e2 + nz(jma[1])
variant(src, type, len ) =>
v1 = sma(src, len) // Simple
v2 = ema(src, len) // Exponential
v3 = 2 * v2 - ema(v2, len) // Double Exponential
v4 = 3 * (v2 - ema(v2, len)) + ema(ema(v2, len), len) // Triple Exponential
v5 = wma(src, len) // Weighted
v6 = vwma(src, len) // Volume Weighted
v7 = na(v5[1]) ? sma(src, len) : (v5[1] * (len - 1) + src) / len // Smoothed
v8 = wma(2 * wma(src, len / 2) - wma(src, len), round(sqrt(len))) // Hull
v9 = linreg(src, len, lsmaOffset) // Least Squares
v10 = alma(src, len, almaOffset, almaSigma) // Arnaud Legoux
v11 = kama(src, len) // KAMA
ema1 = ema(src, len)
ema2 = ema(ema1, len)
v13 = t3(src, len) // T3
v14 = ema1+(ema1-ema2) // Zero Lag Exponential
v15 = hwma(src, len) // Henderson Moving average thanks to @everget
ahma = 0.0
ahma := nz(ahma[1]) + (src - (nz(ahma[1]) + nz(ahma[len])) / 2) / len //Ahrens Moving Average
v16 = ahma
v17 = get_jurik( len, phase, power, src)
type=="EMA"?v2 : type=="DEMA"?v3 : type=="TEMA"?v4 : type=="WMA"?v5 : type=="VWMA"?v6 :
type=="SMMA"?v7 : type=="Hull"?v8 : type=="LSMA"?v9 : type=="ALMA"?v10 : type=="KAMA"?v11 :
type=="T3"?v13 : type=="ZEMA"?v14 : type=="HWMA"?v15 : type=="AHMA"?v16 : type=="JURIK"?v17 : v1
smoothMA(c, maLoop, type, len) =>
ma_c = 0.0
if maLoop == 1
ma_c := variant(c, type, len)
if maLoop == 2
ma_c := variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 3
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 4
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 5
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_c
// Smoothing HA Function
smoothHA( o, h, l, c ) =>
hao = 0.0
hac = ( o + h + l + c ) / 4
hao := na(hao[1])?(o + c / 2 ):(hao[1] + hac[1])/2
hah = max(h, max(hao, hac))
hal = min(l, min(hao, hac))
[hao, hah, hal, hac]
// ---- Main Selection ----
haSmooth = input(false, title=" Use HA as source ? " )
length = input(60, title=" MA1 Length", minval=1, maxval=1000)
maLoop = input(2, title=" Nr. of MA1 Smoothings ", minval=1, maxval=5)
type = input("EMA", title="MA Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "Hull", "LSMA", "ALMA", "KAMA", "ZEMA", "HWMA", "AHMA", "JURIK", "T3"])
// ---- BODY SCRIPT ----
[ ha_open, ha_high, ha_low, ha_close ] = smoothHA(open, high, low, close)
_close_ma = haSmooth ? ha_close : close
_close_smoothed_ma = smoothMA( _close_ma, maLoop, type, length)
maColor = _close_smoothed_ma > _close_smoothed_ma[1] ? color.lime : color.red
plot(_close_smoothed_ma, title= "MA - Trend", color=maColor, transp=85, linewidth = 4)
long = _close_smoothed_ma > _close_smoothed_ma[1] and _close_smoothed_ma[1] < _close_smoothed_ma[2]
short = _close_smoothed_ma < _close_smoothed_ma[1] and _close_smoothed_ma[1] > _close_smoothed_ma[2]
plotshape( short , title="Short", color=color.red, transp=80, style=shape.triangledown, location=location.abovebar, size=size.small)
plotshape( long , title="Long", color=color.lime, transp=80, style=shape.triangleup, location=location.belowbar, size=size.small)
//* Backtesting Period Selector | Component *//
//* Source: https://www.tradingview.com/script/eCC1cvxQ-Backtesting-Period-Selector-Component *//
testStartYear = input(2018, "Backtest Start Year",minval=1980)
testStartMonth = input(1, "Backtest Start Month",minval=1,maxval=12)
testStartDay = input(1, "Backtest Start Day",minval=1,maxval=31)
testPeriodStart = timestamp(testStartYear,testStartMonth,testStartDay,0,0)
testStopYear = 9999 //input(9999, "Backtest Stop Year",minval=1980)
testStopMonth = 12 // input(12, "Backtest Stop Month",minval=1,maxval=12)
testStopDay = 31 //input(31, "Backtest Stop Day",minval=1,maxval=31)
testPeriodStop = timestamp(testStopYear,testStopMonth,testStopDay,0,0)
testPeriod() => time >= testPeriodStart and time <= testPeriodStop ? true : false
if testPeriod() and long
strategy.entry( "long", strategy.long )
if testPeriod() and short
strategy.entry( "short", strategy.short )