Strategi Kombinasi Crossover Rata-rata Pergerakan Sebelas
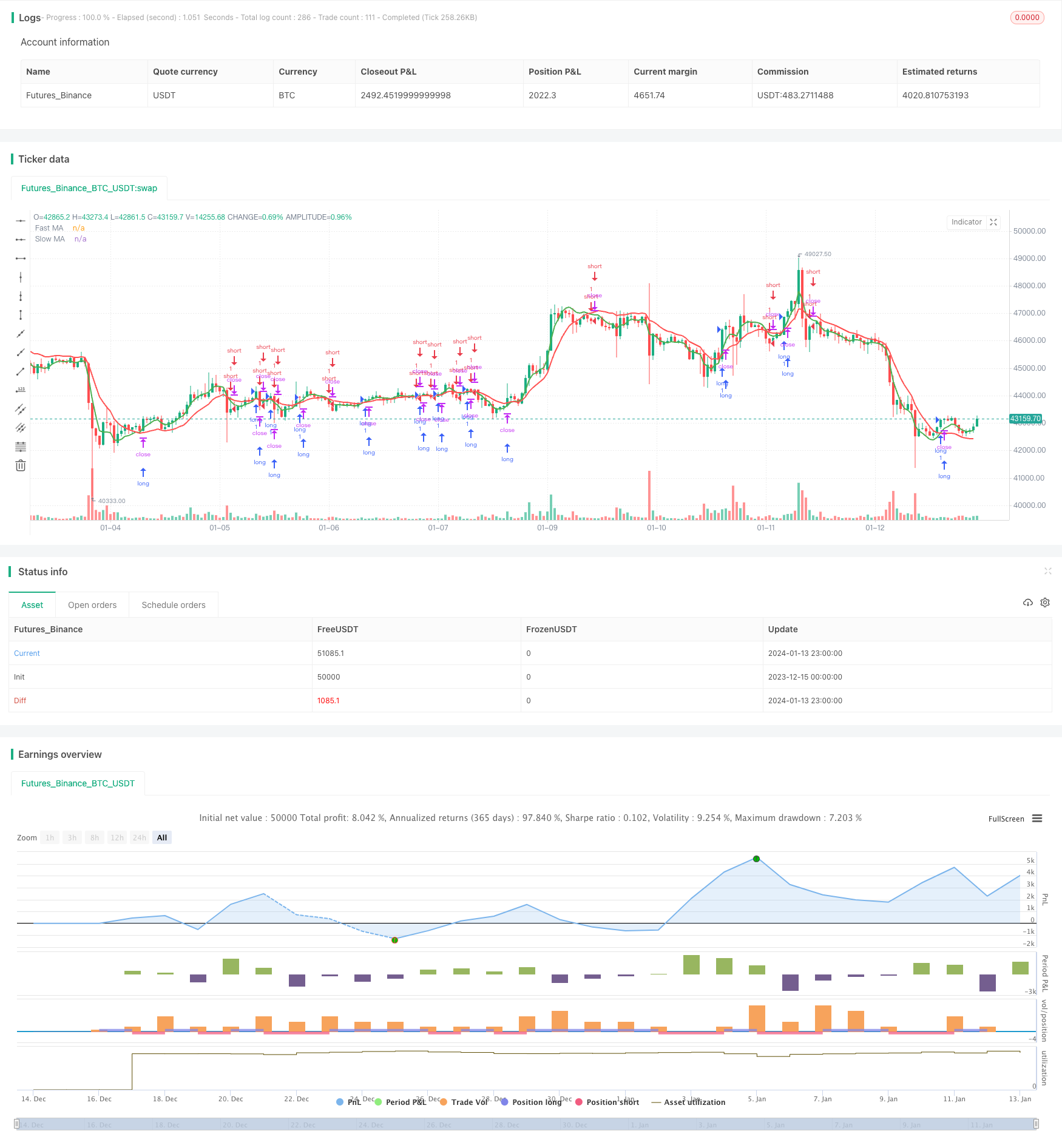
Ringkasan
Kombinasi strategi ini menggunakan persilangan dari 11 jenis rata-rata bergerak yang berbeda untuk melakukan over dan under. 11 rata-rata bergerak yang digunakan meliputi: rata-rata bergerak sederhana (SMA), rata-rata bergerak indeks (EMA), rata-rata bergerak berbobot (WMA), rata-rata bergerak berbobot (VWMA), rata-rata bergerak geser (SMMA), rata-rata bergerak ganda (DEMA), rata-rata bergerak tiga kali lipat (TEMA), rata-rata bergerak Hull (HMA), rata-rata bergerak bergelombang (ZEMA), rata-rata bergerak segitiga (TMA) dan superplanar geser (SSMA).
Strategi ini memungkinkan untuk mengkonfigurasi dua rata-rata bergerak, satu yang lebih cepat dan satu yang lebih lambat, masing-masing dipilih dari 11 pilihan. Ketika MA yang lebih cepat melintasi MA yang lebih lambat, maka akan dihasilkan sinyal multiply. Ketika MA yang lebih cepat melintasi MA yang lebih lambat, maka akan dihasilkan sinyal blank.
Fungsi tambahan termasuk pengaturan tangga, stop dan stop loss level.
Logika Strategi
Logika strategi inti bergantung pada persilangan antara dua rata-rata bergerak untuk menentukan masuk dan keluar.
Syarat untuk masuk adalah:
Masuk lebih banyak: MA cepat > MA lambat
Masuk udara: MA cepat < MA lambat
Keluar ditentukan oleh salah satu dari tiga kriteria berikut:
- Tingkat penghentian mencapai
- Stop loss level mencapai
- menghasilkan sinyal yang berlawanan ((rata-rata bergerak berlawanan dengan arah yang berlawanan)
Strategi ini memungkinkan untuk mengkonfigurasi parameter-parameter penting seperti jenis dan panjang MA, pengaturan gradien, stop-loss dan stop-loss persentase. Ini memberikan fleksibilitas untuk mengoptimalkan strategi sesuai dengan kondisi pasar yang berbeda dan preferensi risiko.
Keunggulan
- Kombinasi dari 11 jenis MA yang berbeda untuk menghasilkan sinyal yang kuat
- Fleksibilitas konfigurasi parameter utama
- Stop loss dan stop loss untuk melindungi keuntungan dan membatasi kerugian
- Grafik memungkinkan untuk menambah posisi dalam tren yang kuat
Risiko
- Seperti indikator teknis lainnya, MA cross mungkin menghasilkan sinyal yang salah
- Over-optimisasi kondisi pasar saat ini dapat menurunkan kinerja di masa depan
- Hard Stop Stop Terlambat Keluar dari Perdagangan yang Benar dan Berfluktuasi
Pengelolaan risiko dapat diperkuat dengan mengkonfirmasi harga untuk sinyal masuk, menggunakan tracking stop loss bukan stop loss keras, dan menghindari optimasi berlebihan.
Optimalisasi ruang
Ada beberapa cara untuk meningkatkan strategi ini:
- Menambahkan filter tambahan sebelum masuk, seperti pemeriksaan volume dan harga
- Sistematis menguji kinerja dari berbagai jenis MA, memilih 1-2 yang terbaik
- Optimalkan panjang MA untuk varietas dan periode perdagangan tertentu
- Menggunakan tracking stop loss sebagai pengganti hard stop loss
- Pada saat itu, ada beberapa hal yang perlu diperhatikan.
Meringkaskan
Strategi crossover Moving Average 11 memberikan cara untuk melakukan crossover perdagangan secara sistematis. Dengan menggabungkan sinyal dari berbagai indikator MA dan memungkinkan untuk mengkonfigurasi parameter-parameter kunci, ini memberikan kerangka perdagangan yang kuat dan fleksibel. Pengoptimalan dan manajemen risiko akan memainkan peran penting untuk mengoptimalkan kinerja.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-15 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-14 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
strategy(title = "[STRATEGY] MA Cross Eleven", overlay = true)
// MA - type, source, length
// MA - type, source, length
// SMA --> Simple
// EMA --> Exponential
// WMA --> Weighted
// VWMA --> Volume Weighted
// SMMA --> Smoothed
// DEMA --> Double Exponential
// TEMA --> Triple Exponential
// HMA --> Hull
// TMA --> Triangular
// SSMA --> SuperSmoother filter
// ZEMA --> Zero Lag Exponential
type = input(defval="ZEMA", title="MA Type: ", options=["SMA", "EMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "HullMA", "ZEMA", "TMA", "SSMA"])
len1 = input(defval=8, title="Fast MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose1 = input(close, "Fast MA Source")
len2 = input(defval=21, title="Slow MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose2 = input(close, "Slow MA Source")
// Returns MA input selection variant, default to SMA if blank or typo.
variant(type, src, len) =>
v1 = sma(src, len) // Simple
v2 = ema(src, len) // Exponential
v3 = wma(src, len) // Weighted
v4 = vwma(src, len) // Volume Weighted
v5 = 0.0
v5 := na(v5[1]) ? sma(src, len) : (v5[1] * (len - 1) + src) / len // Smoothed
v6 = 2 * v2 - ema(v2, len) // Double Exponential
v7 = 3 * (v2 - ema(v2, len)) + ema(ema(v2, len), len) // Triple Exponential
v8 = wma(2 * wma(src, len / 2) - wma(src, len), round(sqrt(len))) // Hull
v11 = sma(sma(src,len),len) // Triangular
// SuperSmoother filter
// © 2013 John F. Ehlers
a1 = exp(-1.414*3.14159 / len)
b1 = 2*a1*cos(1.414*3.14159 / len)
c2 = b1
c3 = (-a1)*a1
c1 = 1 - c2 - c3
v9 = 0.0
v9 := c1*(src + nz(src[1])) / 2 + c2*nz(v9[1]) + c3*nz(v9[2])
// Zero Lag Exponential
e = ema(v2, len)
v10 = v2+(v2-e)
// return variant, defaults to SMA if input invalid.
type=="EMA"?v2 : type=="WMA"?v3 : type=="VWMA"?v4 : type=="SMMA"?v5 : type=="DEMA"?v6 : type=="TEMA"?v7 : type=="HullMA"?v8 : type=="SSMA"?v9 : type=="ZEMA"?v10 : type=="TMA"? v11: v1
ma_1 = variant(type, srcclose1, len1)
ma_2 = variant(type, srcclose2, len2)
plot(ma_1, title="Fast MA", color = green, linewidth=2, transp=0)
plot(ma_2, title="Slow MA", color = red, linewidth=2, transp=0)
longCond = na
shortCond = na
longCond := crossover(ma_1, ma_2)
shortCond := crossunder(ma_1, ma_2)
// Count your long short conditions for more control with Pyramiding
sectionLongs = 0
sectionLongs := nz(sectionLongs[1])
sectionShorts = 0
sectionShorts := nz(sectionShorts[1])
if longCond
sectionLongs := sectionLongs + 1
sectionShorts := 0
if shortCond
sectionLongs := 0
sectionShorts := sectionShorts + 1
// Pyramiding Inputs
pyrl = input(1, "Pyramiding")
// These check to see your signal and cross references it against the pyramiding settings above
longCondition = longCond and sectionLongs <= pyrl
shortCondition = shortCond and sectionShorts <= pyrl
// Get the price of the last opened long or short
last_open_longCondition = na
last_open_shortCondition = na
last_open_longCondition := longCondition ? high[1] : nz(last_open_longCondition[1])
last_open_shortCondition := shortCondition ? low[1] : nz(last_open_shortCondition[1])
// Check if your last postion was a long or a short
last_longCondition = na
last_shortCondition = na
last_longCondition := longCondition ? time : nz(last_longCondition[1])
last_shortCondition := shortCondition ? time : nz(last_shortCondition[1])
in_longCondition = last_longCondition > last_shortCondition
in_shortCondition = last_shortCondition > last_longCondition
// Take profit
isTPl = input(false, "Take Profit Long")
isTPs = input(false, "Take Profit Short")
tpl = input(3, "Take Profit Long %", type=float)
tps = input(30, "Take Profit Short %", type=float)
long_tp = isTPl and crossover(high, (1+(tpl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and in_longCondition == 1
short_tp = isTPs and crossunder(low, (1-(tps/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and in_shortCondition == 1
// Stop Loss
isSLl = input(false, "Stop Loss Long")
isSLs = input(false, "Stop Loss Short")
sl= 0.0
sl := input(3, "Stop Loss %", type=float)
long_sl = isSLl and crossunder(low, (1-(sl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and longCondition == 0 and in_longCondition == 1
short_sl = isSLs and crossover(high, (1+(sl/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and shortCondition == 0 and in_shortCondition == 1
// Create a single close for all the different closing conditions.
long_close = long_tp or long_sl ? 1 : 0
short_close = short_tp or short_sl ? 1 : 0
// Get the time of the last close
last_long_close = na
last_short_close = na
last_long_close := long_close ? time : nz(last_long_close[1])
last_short_close := short_close ? time : nz(last_short_close[1])
// Strategy entries
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long, when=longCondition == true, stop = open[1])
strategy.entry("short", strategy.short, when=shortCondition == true)
strategy.close("long", when = long_sl or long_tp)
strategy.close("short", when = short_sl or short_tp)