移動平均ポリゴン戦略
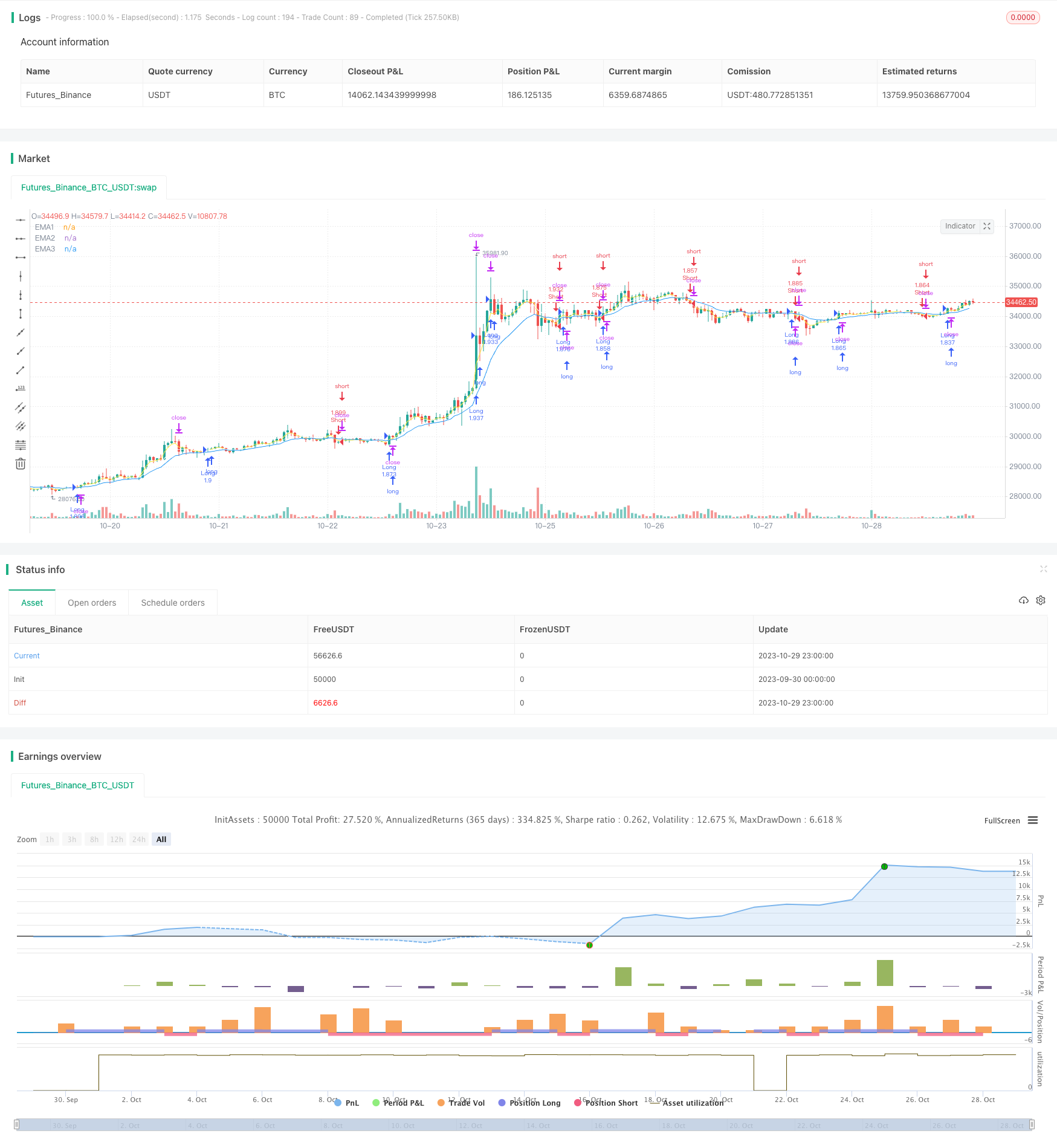
概要
移動均線多辺形戦略は,複数の異なる周期の移動均線を介して多辺形を構成し,多辺形を突破して取引信号としてのトレンド追跡戦略である.この戦略は,複数の時間周期要因を総合的に考慮して,市場騒音を効果的にフィルターし,主要なトレンドを捕捉することができる.
戦略原則
この戦略は,3周期,7周期および13周期のEMAなどの異なる周期のEMA平均線を入力し,それらを価格グラフに描画して多方形チャネルを形成する.価格が複数のEMA平均線を上から穿越すると多信号が生成され,価格が複数のEMA平均線を下から穿越すると空信号が生成される.この方法で,多くの偽突破を排除することができる.
コードで close>ema1 and ema1>ema2 and ema2>ema3によって上穿信号を決定し,close
戦略的優位性
この戦略の最大の優点は,主要トレンドの方向を効果的に把握でき,複数の移動均線を使用して,フィルタリング機構を構築し,市場の短期的なノイズの影響を受けることなく,偽信号を減らすことです.移動ストップは,利益を保護するためにタイムリーにストップを可能にします.
リスクと解決
この戦略の主なリスクは,トレンドの転換点を定義することができないことであり,トレンドが逆転すると,対盤で損失が生じることがあります.また,均線組み合わせの設定が不適切である場合,取引頻度が過高または信号の遅延を引き起こす可能性があります.均線パラメータの組み合わせを最適化し,他の指標を加え,逆転を判断し,止損範囲を広げることなどの方法を使用してリスクを減らすことができます.
最適化の方向
この戦略は以下の点で最適化できます.
移動平均線の周期パラメータを最適化して,最適なパラメータの組み合わせを見つける
トレンドの転換点にRSI,MACDなどの反転シグナルのインジケーターを追加して,タイムリーに外出を停止します.
移動ストップのストップ幅と偏移値を最適化し,ストップがトリガーされる確率を下げる
異なる品種のパラメータを最適化し,戦略の適応性を向上させる
要約する
移動均線多面形戦略は,全体的に見ると,信頼できる,効果的なトレンド追跡戦略である。その最大の優点は,主要なトレンドの方向を捉えながら,大幅なノイズフィルタリングである。しかし,ある逆転認識の不足の問題もある。パラメータ最適化,補助指標の追加などの方法によって戦略のパフォーマンスを向上させることができる。この戦略は,傾向が顕著な品種に適用され,適切な使用であれば,安定した取引収益を得ることができる。
/*backtest
start: 2023-09-30 00:00:00
end: 2023-10-30 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © Crypto-Oli
//@version=4
strategy("BLANK Strategy + TSL", initial_capital=5000, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, pyramiding=1, commission_value=0.075, overlay=true)
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// BACKTESTING RANGE
// From Date Inputs
fromDay = input(defval = 1, title = "From Day", minval = 1, maxval = 31)
fromMonth = input(defval = 1, title = "From Month", minval = 1, maxval = 12)
fromYear = input(defval = 2019, title = "From Year", minval = 1970)
// To Date Inputs
toDay = input(defval = 1, title = "To Day", minval = 1, maxval = 31)
toMonth = input(defval = 1, title = "To Month", minval = 1, maxval = 12)
toYear = input(defval = 2020, title = "To Year", minval = 1970)
// Calculate start/end date and time condition
startDate = timestamp(fromYear, fromMonth, fromDay, 00, 00)
finishDate = timestamp(toYear, toMonth, toDay, 00, 00)
time_cond = true
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/// YOUR INPUTS BELOW - DELET EXAPLES ///
ema1=ema(close,input(3))
ema2=ema(close,input(7))
ema3=ema(close,input(13))
/// PLOTS IF YOU NEED BELOW - DELET EXAPLES ///
plot(ema1, "EMA1", color.yellow)
plot(ema2, "EMA2", color.white)
plot(ema3, "EMA3", color.blue)
/// YOUR CONDITIONS BELOW - DELET EXAPLES ///
longCondition = close>ema1 and ema1>ema2 and ema2>ema3 and time_cond
shortCondition = close<ema1 and ema1<ema2 and ema2<ema3 and time_cond
/// EXECUTION ///
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
strategy.exit("Long Exit", "Long", trail_points = close * 0.05 / syminfo.mintick, trail_offset = close * 0.02 / syminfo.mintick)
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
strategy.exit("Short Exit", "Short", trail_points = close * 0.05 / syminfo.mintick, trail_offset = close * 0.02 / syminfo.mintick)