11の移動平均の組み合わせクロスオーバー戦略
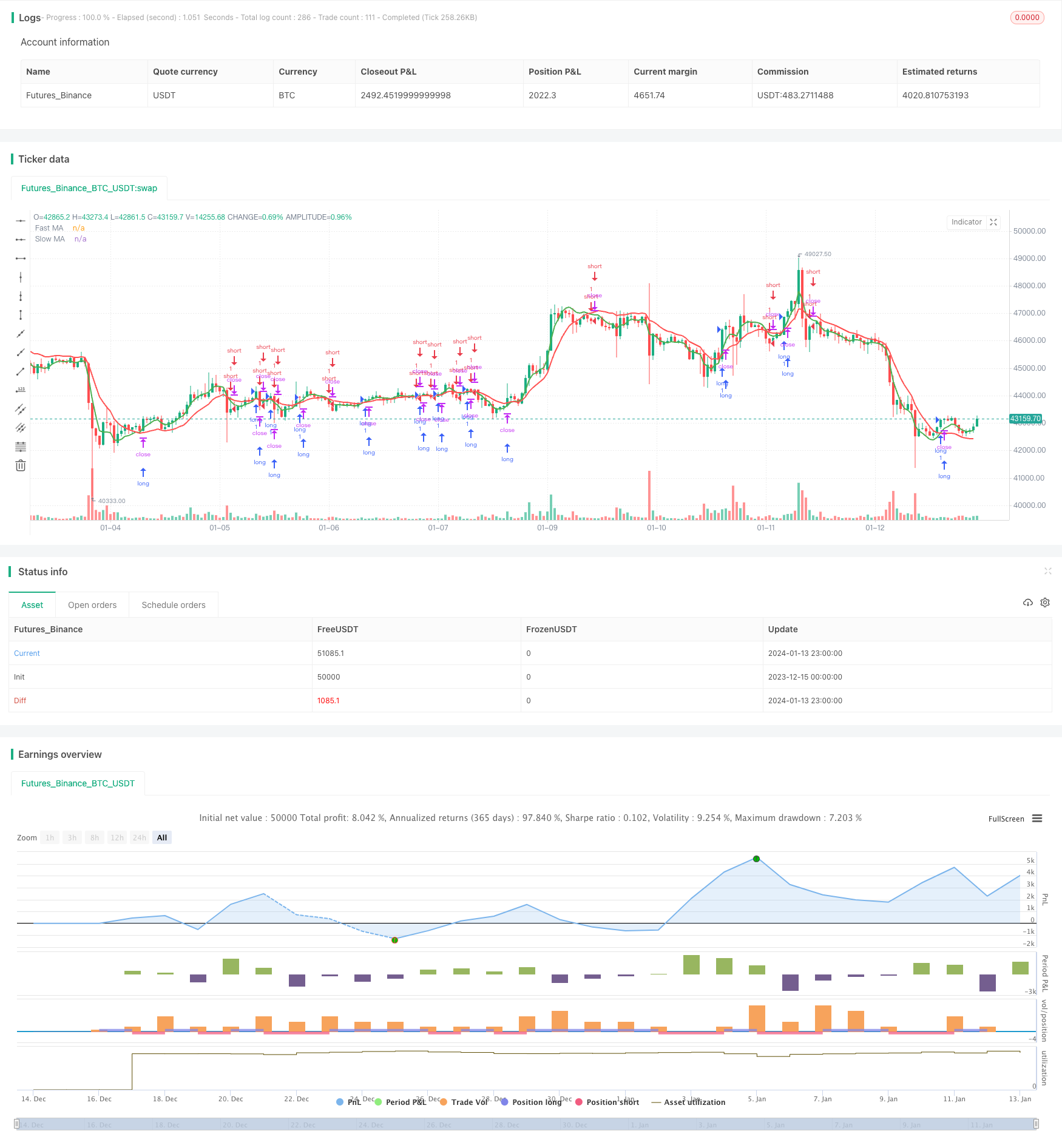
概要
この戦略の組み合わせは,11種類の異なる種類の移動平均の交差を用いて多引と空引を行います.使用されている11種類の移動平均は,単純移動平均 (SMA),指数移動平均 (EMA),加重移動平均 (WMA),交差量加重移動平均 (VWMA),平滑移動平均 (SMMA),二次移動平均 (DEMA),三次移動平均 (TEMA),ヘル移動平均 (HMA),遅滞インデックス0移動平均 (EMAZ),三角移動平均 (TMA) および超平滑移動平均 (SSMA) を含む.
この策略は,2つの移動平均を配置し,1つの速いと1つの遅い,それぞれ11の選択肢から選択することを許可する. 速いMAが遅いMAを交差すると,多信号が生成される. 速いMAが遅いMAを交差すると,空信号が生成される.
追加機能には,梯形設定,停止,および停止レベルが含まれています.
戦略ロジック
核心戦略の論理は,2つの移動平均の間の交差によって入場と退場を決定する.
入場条件は以下の通りです.
複数のエントリー: 速MA > 遅MA
空気入場:高速MA <遅いMA
退出は以下の3つの条件の1つによって決定されます.
- 停止レベルに達しました.
- ストップダメージレベル
- 逆信号を生成する (移動平均は逆方向に交差する)
戦略はMAの種類と長さ,梯形設定,ストップとストップ・パーセンテージなどの重要なパラメータを設定することを許可します.これは,異なる市場条件とリスクの好みに応じて戦略を最適化するための柔軟性を提供します.
利点
- 11種類のMAを組み合わせて 強力な信号を発信します
- 主要パラメータの柔軟な配置
- 利益の保護,損失の制限
- 梯形は強気なトレンドでポジションを増やすことができます.
リスク
- 他の技術指標と同様に,MA交差は誤った信号を生成する可能性があります.
- 現在の市場条件を過度に最適化すると,将来のパフォーマンスを低下させる可能性があります.
- ハードストップは早めに脱退し,波動が大きい正しい取引
入場信号の利用価格の確認,ハードストップではなくトラッキングストップの使用,過度に最適化を回避することによってリスク管理を強化することができる.
空間を最適化する
この戦略を改善する方法は以下の通りです.
- 入場前に追加フィルター,例えば取引量と価格チェック
- 異なるMAタイプを体系的にテストし,最適の1~2種を選びます
- 特定の取引品種と期間でMAの長さを最適化
- ハードストップの代わりにトラッキングストップを使用
- 傾向が長くなるにつれて,段階的な停止が加えられます.
要約する
移動平均クロス戦略は,複数のMA指標の信号を組み合わせて,重要なパラメータを配置することを許可することによって,強力な柔軟な取引の枠組みを提供します.最適化とリスク管理は,パフォーマンスを最適化するために重要な役割を果たします.この戦略は,動量取引において非常に強力な潜在力を持っていますが,異なる市場環境に応じて調整する必要があります.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-15 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-14 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
strategy(title = "[STRATEGY] MA Cross Eleven", overlay = true)
// MA - type, source, length
// MA - type, source, length
// SMA --> Simple
// EMA --> Exponential
// WMA --> Weighted
// VWMA --> Volume Weighted
// SMMA --> Smoothed
// DEMA --> Double Exponential
// TEMA --> Triple Exponential
// HMA --> Hull
// TMA --> Triangular
// SSMA --> SuperSmoother filter
// ZEMA --> Zero Lag Exponential
type = input(defval="ZEMA", title="MA Type: ", options=["SMA", "EMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "HullMA", "ZEMA", "TMA", "SSMA"])
len1 = input(defval=8, title="Fast MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose1 = input(close, "Fast MA Source")
len2 = input(defval=21, title="Slow MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose2 = input(close, "Slow MA Source")
// Returns MA input selection variant, default to SMA if blank or typo.
variant(type, src, len) =>
v1 = sma(src, len) // Simple
v2 = ema(src, len) // Exponential
v3 = wma(src, len) // Weighted
v4 = vwma(src, len) // Volume Weighted
v5 = 0.0
v5 := na(v5[1]) ? sma(src, len) : (v5[1] * (len - 1) + src) / len // Smoothed
v6 = 2 * v2 - ema(v2, len) // Double Exponential
v7 = 3 * (v2 - ema(v2, len)) + ema(ema(v2, len), len) // Triple Exponential
v8 = wma(2 * wma(src, len / 2) - wma(src, len), round(sqrt(len))) // Hull
v11 = sma(sma(src,len),len) // Triangular
// SuperSmoother filter
// © 2013 John F. Ehlers
a1 = exp(-1.414*3.14159 / len)
b1 = 2*a1*cos(1.414*3.14159 / len)
c2 = b1
c3 = (-a1)*a1
c1 = 1 - c2 - c3
v9 = 0.0
v9 := c1*(src + nz(src[1])) / 2 + c2*nz(v9[1]) + c3*nz(v9[2])
// Zero Lag Exponential
e = ema(v2, len)
v10 = v2+(v2-e)
// return variant, defaults to SMA if input invalid.
type=="EMA"?v2 : type=="WMA"?v3 : type=="VWMA"?v4 : type=="SMMA"?v5 : type=="DEMA"?v6 : type=="TEMA"?v7 : type=="HullMA"?v8 : type=="SSMA"?v9 : type=="ZEMA"?v10 : type=="TMA"? v11: v1
ma_1 = variant(type, srcclose1, len1)
ma_2 = variant(type, srcclose2, len2)
plot(ma_1, title="Fast MA", color = green, linewidth=2, transp=0)
plot(ma_2, title="Slow MA", color = red, linewidth=2, transp=0)
longCond = na
shortCond = na
longCond := crossover(ma_1, ma_2)
shortCond := crossunder(ma_1, ma_2)
// Count your long short conditions for more control with Pyramiding
sectionLongs = 0
sectionLongs := nz(sectionLongs[1])
sectionShorts = 0
sectionShorts := nz(sectionShorts[1])
if longCond
sectionLongs := sectionLongs + 1
sectionShorts := 0
if shortCond
sectionLongs := 0
sectionShorts := sectionShorts + 1
// Pyramiding Inputs
pyrl = input(1, "Pyramiding")
// These check to see your signal and cross references it against the pyramiding settings above
longCondition = longCond and sectionLongs <= pyrl
shortCondition = shortCond and sectionShorts <= pyrl
// Get the price of the last opened long or short
last_open_longCondition = na
last_open_shortCondition = na
last_open_longCondition := longCondition ? high[1] : nz(last_open_longCondition[1])
last_open_shortCondition := shortCondition ? low[1] : nz(last_open_shortCondition[1])
// Check if your last postion was a long or a short
last_longCondition = na
last_shortCondition = na
last_longCondition := longCondition ? time : nz(last_longCondition[1])
last_shortCondition := shortCondition ? time : nz(last_shortCondition[1])
in_longCondition = last_longCondition > last_shortCondition
in_shortCondition = last_shortCondition > last_longCondition
// Take profit
isTPl = input(false, "Take Profit Long")
isTPs = input(false, "Take Profit Short")
tpl = input(3, "Take Profit Long %", type=float)
tps = input(30, "Take Profit Short %", type=float)
long_tp = isTPl and crossover(high, (1+(tpl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and in_longCondition == 1
short_tp = isTPs and crossunder(low, (1-(tps/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and in_shortCondition == 1
// Stop Loss
isSLl = input(false, "Stop Loss Long")
isSLs = input(false, "Stop Loss Short")
sl= 0.0
sl := input(3, "Stop Loss %", type=float)
long_sl = isSLl and crossunder(low, (1-(sl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and longCondition == 0 and in_longCondition == 1
short_sl = isSLs and crossover(high, (1+(sl/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and shortCondition == 0 and in_shortCondition == 1
// Create a single close for all the different closing conditions.
long_close = long_tp or long_sl ? 1 : 0
short_close = short_tp or short_sl ? 1 : 0
// Get the time of the last close
last_long_close = na
last_short_close = na
last_long_close := long_close ? time : nz(last_long_close[1])
last_short_close := short_close ? time : nz(last_short_close[1])
// Strategy entries
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long, when=longCondition == true, stop = open[1])
strategy.entry("short", strategy.short, when=shortCondition == true)
strategy.close("long", when = long_sl or long_tp)
strategy.close("short", when = short_sl or short_tp)