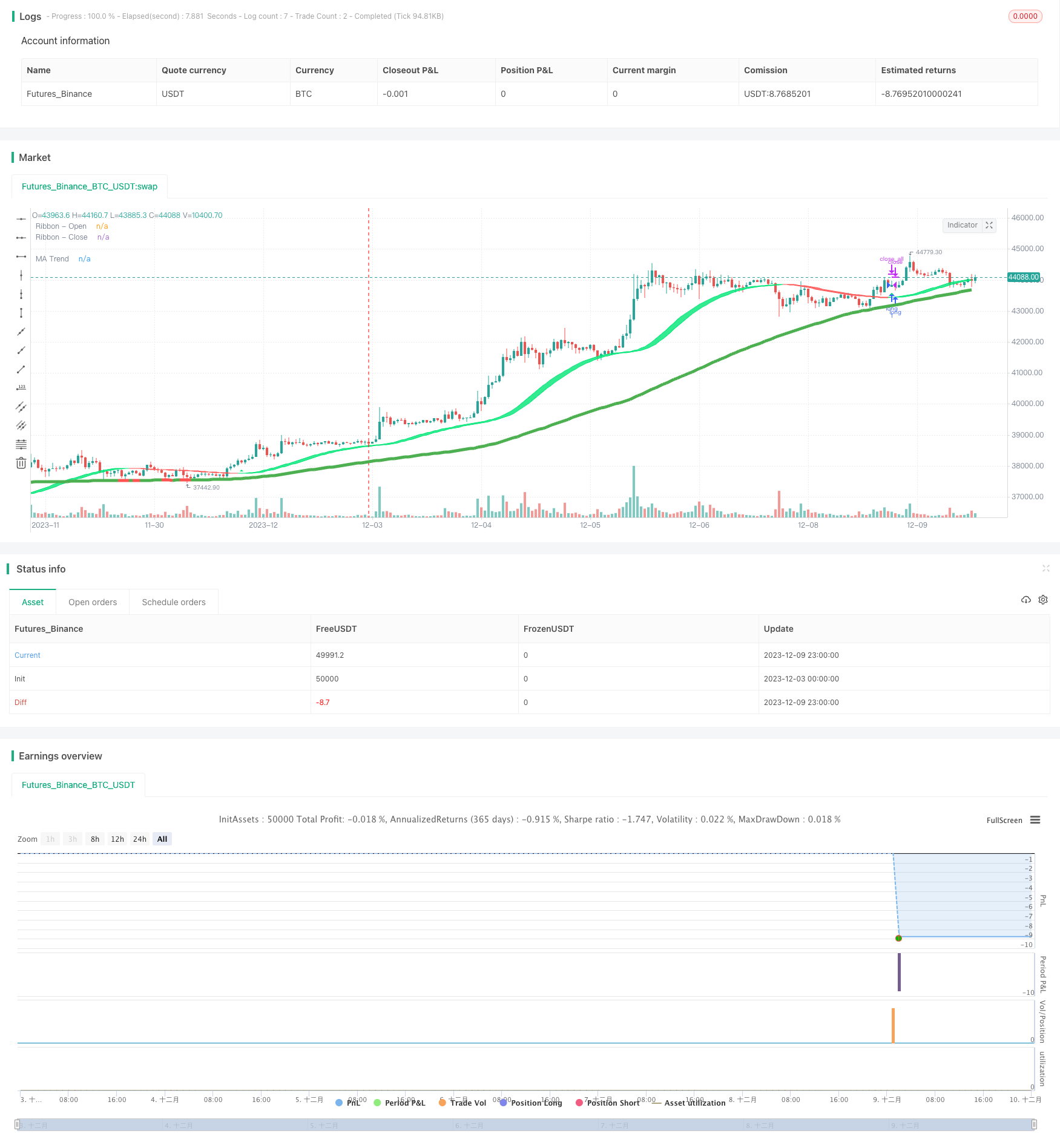
개요
이 전략은 평평한 이동 평균을 사용하여 평평한 가격대를 구성하고, 여러 가지 평평한 이동 평균을 통합하여 실시간으로 추세를 필터링하는 기능을 구현합니다.
전략 원칙
- 평평한 가격대를 구축하여 평평한 이동 평균을 사용하여 가격 변화를 추적하여 가격 변화에 대한 평평한 추적을 구현합니다.
- 정책은 EMA, SMMA, KAMA 등과 같은 다양한 종류의 이동 평균을 입력하여 평평한 이동 평균의 계산 유형으로 지원합니다.
- 이러한 이동 평균을 1-5번의 중첩 평준화를 지원하여 더 평평한 가격대를 얻습니다.
- 가격의 변화를 더 잘 포착하기 위해 가격과 이동 평균 사이의 브린 띠를 사용하는 것을 지원합니다.
- 추가된 이동 평균 필터를 활성화하여, 흔들림을 더 잘 필터링하여 트렌드 방향을 식별할 수 있습니다. 필터는 또한 여러 가지 이동 평균 유형을 지원합니다.
- 형태 인식 지표와 결합하여 구매/판매 신호를 자동으로 인식할 수 있다.
이 전략은 평평한 가격대를 구축하여 가격 트렌드를 포착하고, 이동 평균 필터를 통합하여 트렌드 방향을 확인하는 전형적인 트렌드 추적 전략에 속한다. 파라미터를 조정함으로써 다양한 품종의 다른 주기적인 시장 환경에 유연하게 적응할 수 있다.
전략적 이점
- 가격대를 구성하면 가격 변화의 흐름을 더 부드럽게 추적할 수 있고, 놓친 기회를 효과적으로 줄일 수 있다.
- 여러 가지 이동 평균 유형을 지원하여 다양한 주기 및 품종에 따라 적절한 이동 평균을 선택할 수 있으며, 전략의 적응성을 향상시킵니다.
- 1~5배의 평평한 중첩은 가격 변화를 추적하는 능력을 크게 향상시키고 트렌드 전환점을 더 정확하게 잡을 수 있습니다.
- 이동 평균 필터는 유효하지 않은 신호를 효과적으로 줄이고 승률을 높일 수 있다.
- 이동 평균의 길이를 조정하여 다른 시간 주기에 적응할 수 있으며, 심지어 여러 시간 프레임으로 검증할 수 있어 전략의 효과를 더욱 향상시킬 수 있다.
- 검정색 유리 디스플레이를 지원하여 가격대를 명확하고 직관적으로 관찰할 수 있습니다.
전략적 위험
- 장기적인 경향을 추적하는 것이 강하지만, 단기적인 변동에 대한 추적과 반응은 열악하며, 충격적인 상황에서는 더 많은 무효 신호를 생성하기 쉽다.
- 급격한 가격 변동과 급격한 가격 변동 속에서, 평평한 이동 평균은 약간의 지연성을 가질 수 있으며, 가장 좋은 진입 시기를 놓칠 수 있다.
- 다중 중첩된 이동 평균은 가격 변화를 너무 부드럽게 만들 수 있으며, 이는 구매자 및 판매자 지점을 식별하지 못하게합니다.
- 만약 활성화된 이동 평균 길이 변수가 잘못 설정되면, 많은 가짜 신호가 생성될 수 있다.
해결책:
- 이동 평균의 길이를 적절히 줄여서 가격 변화에 대한 반응을 가속화하십시오.
- 겹치는 횟수를 조정하여 지나치게 부드러운 것을 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 최적화 및 테스트 이동 평균 조합, 최적의 파라미터를 선택하십시오.
- 다른 지표와 결합하여 여러 시간 프레임 검증을 통해 가짜 신호 비율을 줄일 수 있습니다.
전략 최적화 방향
- 이동 평균 타입의 조합을 테스트하여 최적의 파라미터를 선택하십시오.
- 테스트는 이동 평균 길이 변수를 최적화하여 보다 넓은 품종과 시간 주기에도 적용한다.
- 다른 평준화 과정을 시도해 가장 좋은 평형점을 찾아보세요.
- 브린 밴드를 추가해 보시면 됩니다.
- 다른 이동 평균을 필터로 테스트하십시오.
- 다른 지표와 함께 다중 시간 프레임 검증을 수행하십시오.
요약하다
이 전략은 전형적인 트렌드 추적 전략에 속하며, 평평한 이동 평균대를 구성하여 가격 트렌드를 지속적으로 추적하고, 보조 필터와 결합하여 무효 신호를 피한다. 전략의 장점은 평평한 가격대를 구성하여 가격 트렌드의 전환을 더 잘 포착 할 수 있다는 것이다. 동시에 약간의 후퇴 위험도 존재한다. 매개 변수 최적화 및 지표 최적화를 통해 전략 효과를 지속적으로 향상시킬 수 있으며, 추가 연구를 할 가치가 있다.
전략 소스 코드
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-03 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-10 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
// Copyright (c) 2007-present Jurik Research and Consulting. All rights reserved.
// Copyright (c) 2018-present, Alex Orekhov (everget)
// Thanks to everget for code for more advanced moving averages
// Smooth Moving Average Ribbon [STRATEGY] @PuppyTherapy script may be freely distributed under the MIT license.
strategy( title="Smooth Moving Average Ribbon [STRATEGY] @PuppyTherapy", overlay=true )
// ---- CONSTANTS ----
lsmaOffset = 1
almaOffset = 0.85
almaSigma = 6
phase = 2
power = 2
// ---- GLOBAL FUNCTIONS ----
kama(src, len)=>
xvnoise = abs(src - src[1])
nfastend = 0.666
nslowend = 0.0645
nsignal = abs(src - src[len])
nnoise = sum(xvnoise, len)
nefratio = iff(nnoise != 0, nsignal / nnoise, 0)
nsmooth = pow(nefratio * (nfastend - nslowend) + nslowend, 2)
nAMA = 0.0
nAMA := nz(nAMA[1]) + nsmooth * (src - nz(nAMA[1]))
t3(src, len)=>
xe1_1 = ema(src, len)
xe2_1 = ema(xe1_1, len)
xe3_1 = ema(xe2_1, len)
xe4_1 = ema(xe3_1, len)
xe5_1 = ema(xe4_1, len)
xe6_1 = ema(xe5_1, len)
b_1 = 0.7
c1_1 = -b_1*b_1*b_1
c2_1 = 3*b_1*b_1+3*b_1*b_1*b_1
c3_1 = -6*b_1*b_1-3*b_1-3*b_1*b_1*b_1
c4_1 = 1+3*b_1+b_1*b_1*b_1+3*b_1*b_1
nT3Average_1 = c1_1 * xe6_1 + c2_1 * xe5_1 + c3_1 * xe4_1 + c4_1 * xe3_1
// The general form of the weights of the (2m + 1)-term Henderson Weighted Moving Average
getWeight(m, j) =>
numerator = 315 * (pow(m + 1, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (pow(m + 2, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (pow(m + 3, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (3 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 11 * pow(j, 2) - 16)
denominator = 8 * (m + 2) * (pow(m + 2, 2) - 1) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 1) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 9) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 25)
denominator != 0
? numerator / denominator
: 0
hwma(src, termsNumber) =>
sum = 0.0
weightSum = 0.0
termMult = (termsNumber - 1) / 2
for i = 0 to termsNumber - 1
weight = getWeight(termMult, i - termMult)
sum := sum + nz(src[i]) * weight
weightSum := weightSum + weight
sum / weightSum
get_jurik(length, phase, power, src)=>
phaseRatio = phase < -100 ? 0.5 : phase > 100 ? 2.5 : phase / 100 + 1.5
beta = 0.45 * (length - 1) / (0.45 * (length - 1) + 2)
alpha = pow(beta, power)
jma = 0.0
e0 = 0.0
e0 := (1 - alpha) * src + alpha * nz(e0[1])
e1 = 0.0
e1 := (src - e0) * (1 - beta) + beta * nz(e1[1])
e2 = 0.0
e2 := (e0 + phaseRatio * e1 - nz(jma[1])) * pow(1 - alpha, 2) + pow(alpha, 2) * nz(e2[1])
jma := e2 + nz(jma[1])
variant(src, type, len ) =>
v1 = sma(src, len) // Simple
v2 = ema(src, len) // Exponential
v3 = 2 * v2 - ema(v2, len) // Double Exponential
v4 = 3 * (v2 - ema(v2, len)) + ema(ema(v2, len), len) // Triple Exponential
v5 = wma(src, len) // Weighted
v6 = vwma(src, len) // Volume Weighted
v7 = na(v5[1]) ? sma(src, len) : (v5[1] * (len - 1) + src) / len // Smoothed
v8 = wma(2 * wma(src, len / 2) - wma(src, len), round(sqrt(len))) // Hull
v9 = linreg(src, len, lsmaOffset) // Least Squares
v10 = alma(src, len, almaOffset, almaSigma) // Arnaud Legoux
v11 = kama(src, len) // KAMA
ema1 = ema(src, len)
ema2 = ema(ema1, len)
v13 = t3(src, len) // T3
v14 = ema1+(ema1-ema2) // Zero Lag Exponential
v15 = hwma(src, len) // Henderson Moving average thanks to @everget
ahma = 0.0
ahma := nz(ahma[1]) + (src - (nz(ahma[1]) + nz(ahma[len])) / 2) / len //Ahrens Moving Average
v16 = ahma
v17 = get_jurik( len, phase, power, src)
type=="EMA"?v2 : type=="DEMA"?v3 : type=="TEMA"?v4 : type=="WMA"?v5 : type=="VWMA"?v6 :
type=="SMMA"?v7 : type=="Hull"?v8 : type=="LSMA"?v9 : type=="ALMA"?v10 : type=="KAMA"?v11 :
type=="T3"?v13 : type=="ZEMA"?v14 : type=="HWMA"?v15 : type=="AHMA"?v16 : type=="JURIK"?v17 : v1
smoothMA(o, h, l, c, maLoop, type, len) =>
ma_o = 0.0
ma_h = 0.0
ma_l = 0.0
ma_c = 0.0
if maLoop == 1
ma_o := variant(o, type, len)
ma_h := variant(h, type, len)
ma_l := variant(l, type, len)
ma_c := variant(c, type, len)
if maLoop == 2
ma_o := variant(variant(o ,type, len),type, len)
ma_h := variant(variant(h ,type, len),type, len)
ma_l := variant(variant(l ,type, len),type, len)
ma_c := variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 3
ma_o := variant(variant(variant(o ,type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_h := variant(variant(variant(h ,type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_l := variant(variant(variant(l ,type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 4
ma_o := variant(variant(variant(variant(o ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_h := variant(variant(variant(variant(h ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_l := variant(variant(variant(variant(l ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 5
ma_o := variant(variant(variant(variant(variant(o ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_h := variant(variant(variant(variant(variant(h ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_l := variant(variant(variant(variant(variant(l ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
[ma_o, ma_h, ma_l, ma_c]
smoothHA( o, h, l, c ) =>
hao = 0.0
hac = ( o + h + l + c ) / 4
hao := na(hao[1])?(o + c / 2 ):(hao[1] + hac[1])/2
hah = max(h, max(hao, hac))
hal = min(l, min(hao, hac))
[hao, hah, hal, hac]
// ---- Main Ribbon ----
haSmooth = input(true, title=" Use HA as source ? " )
length = input(11, title=" MA1 Length", minval=1, maxval=1000)
maLoop = input(3, title=" Nr. of MA1 Smoothings ", minval=1, maxval=5)
type = input("EMA", title="MA Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "Hull", "LSMA", "ALMA", "KAMA", "ZEMA", "HWMA", "AHMA", "JURIK", "T3"])
haSmooth2 = input(true, title=" Use HA as source ? " )
// ---- Trend ----
ma_use = input(true, title=" ----- Use MA Filter ( For Lower Timeframe Swings / Scalps ) ? ----- " )
ma_source = input(defval = close, title = "MA - Source", type = input.source)
ma_length = input(100,title="MA - Length", minval=1 )
ma_type = input("SMA", title="MA - Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "Hull", "LSMA", "ALMA", "KAMA", "ZEMA", "HWMA", "AHMA", "JURIK", "T3"])
ma_useHA = input(defval = false, title = "Use HA Candles as Source ?")
ma_rsl = input(true, title = "Use Rising / Falling Logic ?" )
// ---- BODY SCRIPT ----
[ ha_open, ha_high, ha_low, ha_close ] = smoothHA(open, high, low, close)
_open_ma = haSmooth ? ha_open : open
_high_ma = haSmooth ? ha_high : high
_low_ma = haSmooth ? ha_low : low
_close_ma = haSmooth ? ha_close : close
[ _open, _high, _low, _close ] = smoothMA( _open_ma, _high_ma, _low_ma, _close_ma, maLoop, type, length)
[ ha_open2, ha_high2, ha_low2, ha_close2 ] = smoothHA(_open, _high, _low, _close)
_open_ma2 = haSmooth2 ? ha_open2 : _open
_high_ma2 = haSmooth2 ? ha_high2 : _high
_low_ma2 = haSmooth2 ? ha_low2 : _low
_close_ma2 = haSmooth2 ? ha_close2 : _close
ribbonColor = _close_ma2 > _open_ma2 ? color.lime : color.red
p_open = plot(_open_ma2, title="Ribbon - Open", color=ribbonColor, transp=70)
p_close = plot(_close_ma2, title="Ribbon - Close", color=ribbonColor, transp=70)
fill(p_open, p_close, color = ribbonColor, transp = 40 )
// ----- FILTER
ma = 0.0
if ma_use == true
ma := variant( ma_useHA ? ha_close : ma_source, ma_type, ma_length )
maFilterShort = ma_use ? ma_rsl ? falling(ma,1) : ma_useHA ? ha_close : close < ma : true
maFilterLong = ma_use ? ma_rsl ? rising(ma,1) : ma_useHA ? ha_close : close > ma : true
colorTrend = rising(ma,1) ? color.green : color.red
plot( ma_use ? ma : na, title="MA Trend", color=colorTrend, transp=80, transp=70, linewidth = 5)
long = crossover(_close_ma2, _open_ma2 ) and maFilterLong
short = crossunder(_close_ma2, _open_ma2 ) and maFilterShort
closeAll = cross(_close_ma2, _open_ma2 )
plotshape( short , title="Short", color=color.red, transp=80, style=shape.triangledown, location=location.abovebar, size=size.small)
plotshape( long , title="Long", color=color.lime, transp=80, style=shape.triangleup, location=location.belowbar, size=size.small)
//* Backtesting Period Selector | Component *//
//* Source: https://www.tradingview.com/script/eCC1cvxQ-Backtesting-Period-Selector-Component *//
testStartYear = input(2018, "Backtest Start Year",minval=1980)
testStartMonth = input(1, "Backtest Start Month",minval=1,maxval=12)
testStartDay = input(1, "Backtest Start Day",minval=1,maxval=31)
testPeriodStart = timestamp(testStartYear,testStartMonth,testStartDay,0,0)
testStopYear = 9999 //input(9999, "Backtest Stop Year",minval=1980)
testStopMonth = 12 // input(12, "Backtest Stop Month",minval=1,maxval=12)
testStopDay = 31 //input(31, "Backtest Stop Day",minval=1,maxval=31)
testPeriodStop = timestamp(testStopYear,testStopMonth,testStopDay,0,0)
testPeriod() => time >= testPeriodStart and time <= testPeriodStop ? true : false
if testPeriod() and long
strategy.entry( "long", strategy.long )
if testPeriod() and short
strategy.entry( "short", strategy.short )
if closeAll
strategy.close_all( when = closeAll )