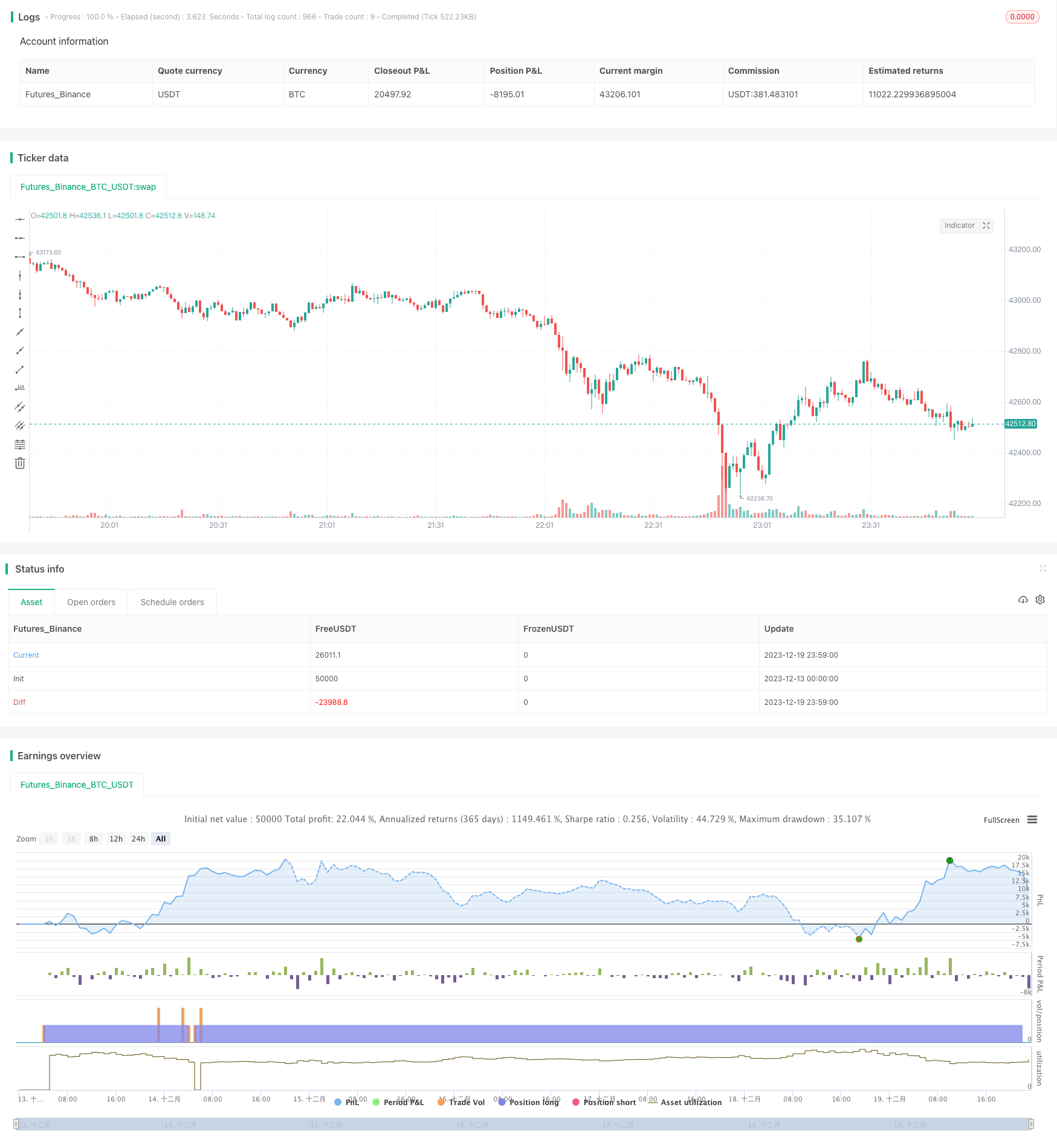
이 전략의 이름은 미안 리버션 리버스 전략 (Mean Reversion Reverse Strategy Based on Moving Average) 이며, 주요 아이디어는 핵심 평균선을 넘어간 후 구매하고, 설정된 목표 수익을 달성한 후 중지하는 것입니다.
이 전략의 주요 원칙은 단기 평균선의 회전을 이용해서, 상반된 상황에서의 반발 기회를 잡는 것이다. 구체적으로, 가격이 더 긴 기간의 평균선 (예: 20일선, 50일선 등) 을 넘어간 후 강한 오프타우스 징후를 나타낼 때, 시장의 변동의 mean reversion 특성으로 인해, 가격은 종종 어느 정도 반발을 일으킨다. 이 때 더 짧은 기간의 평균선 (예: 10일선) 이 상향으로 돌아가는 신호를 나타낸다면, 그것은 비교적 좋은 구매 기회이다.
이 전략의 구체적인 구매 논리는: 가격이 20 일선 아래로 떨어지면 1 손을 구매, 50 일선 아래로 떨어지면 1 손을 상장, 100 일선 아래로 떨어지면 1 손을 계속 상장, 200 일선 아래로 떨어지면 최대 1 손을 상장, 4 손을 추가한다. 미리 설정된 스톱 목표가 달성된 후 평형 상장한다. 동시에 시간과 스톱 손실 조건을 설정한다.
우위 분석
- 평균의 회전 특성을 활용하여 단기 반동 기회를 효과적으로 식별할 수 있습니다.
- 한 점의 위험을 줄이기 위해 수량으로 창고를 짓습니다.
- 수익을 잠금할 수 있는 차단 조건을 설정합니다.
- 오픈 가격과 이전 하락점을 사용하여 필터링하여 가짜 돌파구를 피하십시오.
위험 분석
- 장기간 보유할 경우 반전 위험이 발생할 수 있다. 시장이 계속 하락하면 손실이 더욱 확대될 수 있다.
- 평균선 신호는 잘못된 신호로 인해 손실이 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 설정된 정지 목표가 달성되지 않을 수 있으며, 정지 전부 또는 일부가 불가능합니다.
최적화 방향
- 다양한 변수 설정 하에서 수익률 및 안정성을 테스트 할 수 있습니다.
- MACD, KD와 같은 다른 지표와 함께 고려할 수 있습니다.
- 다양한 품종 특성에 따라 거래 스타일에 적합한 평행 주기를 선택할 수 있습니다
- 기계 학습 알고리즘을 도입하여 동적으로 최적화된 파라미터를 입력할 수 있다.
요약하다
이 전략은 전체적으로 비교적 고전적이고 일반적인 평평선 거래 전략이다. 이 전략은 평평선의 스무팅 특성을 올바르게 사용하고, 동시에 여러 평평선을 결합하여 단기 구매 시기를 식별한다. 포지션을 분산하여 적시에 정지하여 위험을 제어한다. 그러나 중요한 정책 소식과 같은 시장의 갑작스러운 사건에 대한 대응은 상대적으로 수동적일 수 있으며, 이는 계속 최적화 할 수있는 방향이다.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-13 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-20 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("EMA_zorba1", shorttitle="zorba_ema", overlay=true)
// Input parameters
qt1 = input.int(5, title="Quantity 1", minval=1)
qt2 = input.int(10, title="Quantity 2", minval=1)
qt3 = input.int(15, title="Quantity 3", minval=1)
qt4 = input.int(20, title="Quantity 4", minval=1)
ema10 = ta.ema(close, 10)
ema20 = ta.ema(close, 20)
ema50 = ta.ema(close, 50)
ema100 = ta.ema(close, 100)
ema200 = ta.ema(close, 200)
// Date range filter
start_date = timestamp(year=2021, month=1, day=1)
end_date = timestamp(year=2024, month=10, day=27)
in_date_range = true
// Profit condition
profit_percentage = input(1, title="Profit Percentage") // Adjust this value as needed
// Pyramiding setting
pyramiding = input.int(2, title="Pyramiding", minval=1, maxval=10)
// Buy conditions
buy_condition_1 = in_date_range and close < ema20 and close > ema50 and close < open and close < low[1]
buy_condition_2 = in_date_range and close < ema50 and close > ema100 and close < open and close < low[1]
buy_condition_3 = in_date_range and close < ema100 and close > ema200 and close < open and close < low[1]
buy_condition_4 = in_date_range and close < ema200 and close < open and close < low[1]
// Exit conditions
profit_condition = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + profit_percentage / 100) <= close
exit_condition_1 = in_date_range and (close > ema10 and ema10 > ema20 and ema10 > ema50 and ema10 > ema100 and ema10 > ema200 and close < open) and profit_condition and close < low[1] and close < low[2]
exit_condition_2 = in_date_range and (close < ema10 and close[1] > ema10 and close < close[1] and ema10 > ema20 and ema10 > ema50 and ema10 > ema100 and ema10 > ema200 and close < open) and profit_condition and close < low[1] and close < low[2]
// Exit condition for when today's close is less than the previous day's low
//exit_condition_3 = close < low[1]
// Strategy logic
strategy.entry("Buy1", strategy.long, qty=qt1 * pyramiding, when=buy_condition_1)
strategy.entry("Buy2", strategy.long, qty=qt2 * pyramiding, when=buy_condition_2)
strategy.entry("Buy3", strategy.long, qty=qt3 * pyramiding, when=buy_condition_3)
strategy.entry("Buy4", strategy.long, qty=qt4 * pyramiding, when=buy_condition_4)
strategy.close("Buy1", when=exit_condition_1 or exit_condition_2)
strategy.close("Buy2", when=exit_condition_1 or exit_condition_2)
strategy.close("Buy3", when=exit_condition_1 or exit_condition_2)
strategy.close("Buy4", when=exit_condition_1 or exit_condition_2)