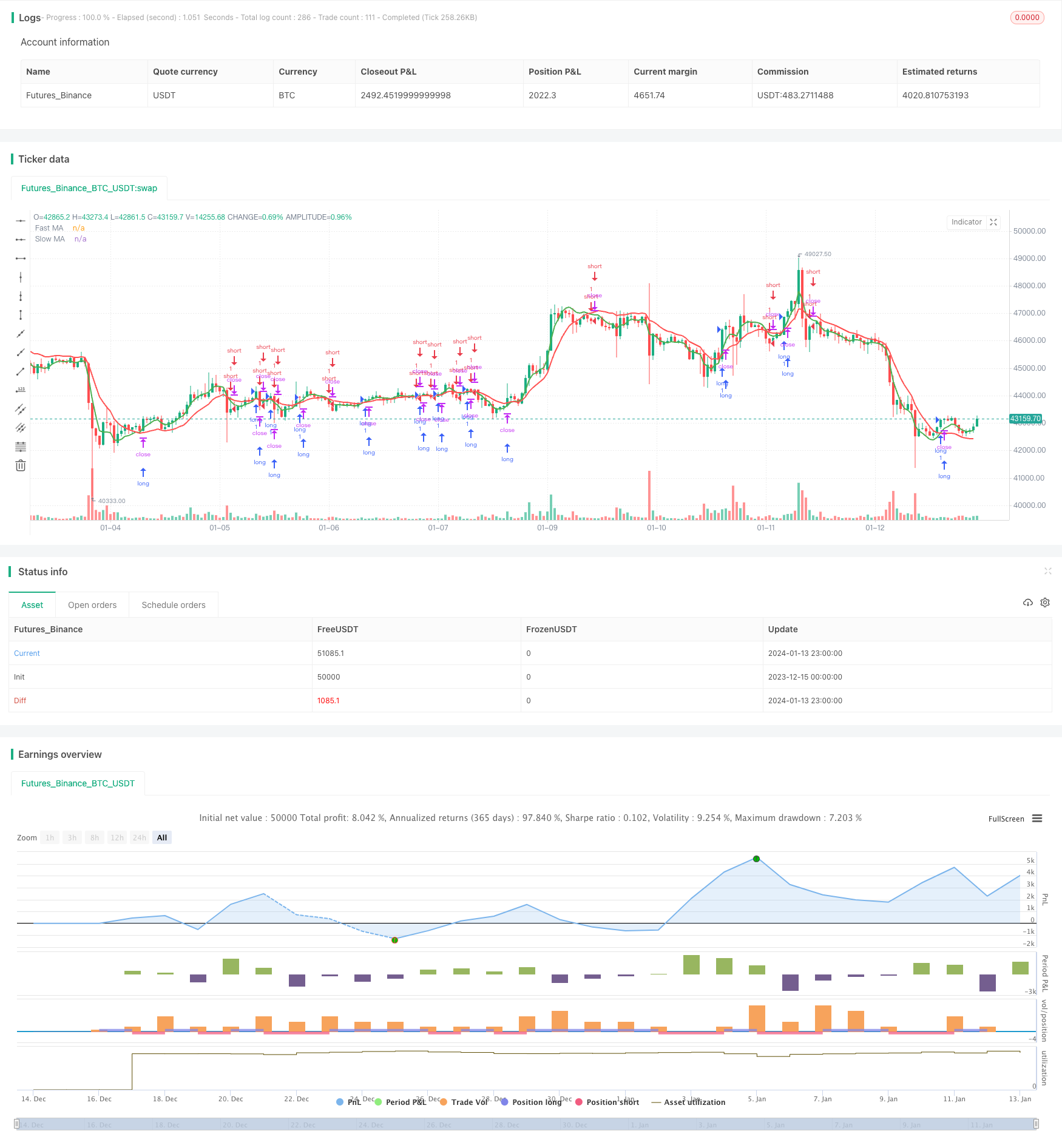
개요
이 전략 포트폴리지는 11개의 다른 유형의 이동 평균의 교차를 사용하여 더 많은 것을 더하고 더 적은 것을 더한다. 사용 된 11개의 이동 평균은 다음과 같습니다: 간단한 이동 평균 (SMA), 지수 이동 평균 (EMA), 가중 이동 평균 (WMA), 교차량 가중 이동 평균 (VWMA), 평면 이동 평균 (SMMA), 쌍 지수 이동 평균 (DEMA), 삼진 지수 이동 평균 (TEMA), 헐 이동 평균 (HMA), 지연 지수 이동 평균 (ZEMA), 삼각형 이동 평균 (TMA) 및 초 평면 슬라이더 (SSMA) ᅳ.
이 전략은 두 개의 이동 평균을 구성할 수 있습니다. 하나는 더 빠른 것이고 하나는 더 느린 것으로, 모두 11 가지 옵션 중 하나를 선택하십시오. 더 빠른 MA가 느린 MA를 넘어서면 다중 신호가 생성됩니다. 더 빠른 MA가 느린 MA보다 낮은 경우 공백 신호가 생성됩니다.
추가 기능으로는 계단 설정, 정지 및 정지 레벨이 포함된다.
전략 논리
핵심 전략 논리는 두 개의 이동 평균 사이의 교차에 의존하여 진입과 퇴출을 결정한다.
참가 조건은 다음과 같습니다.
더 많은 진입: 빠른 MA > 느린 MA
공중 입구: 빠른 MA < 느린 MA
탈퇴는 다음의 세 가지 기준 중 하나에 의해 결정됩니다.
- 정지수준이 도달
- 스톱 손실 수준에 도달
- 반대의 신호를 생성하기 (변동 평균은 반대 방향으로 교차한다)
이 전략은 MA 유형과 길이는, 계단 설정, 중지 및 중지 손실 비율과 같은 중요한 매개 변수를 구성 할 수 있습니다. 이것은 다양한 시장 조건과 위험 선호에 따라 전략을 최적화하는 데 유연성을 제공합니다.
장점
- 11개의 다른 MA 유형을 결합하여 강력한 신호를 생성합니다.
- 주요 변수 구성이 유연하다
- 상쇄 및 손실을 막는 기능 이익 보호, 손실 제한
- 격자 (梯形) 는 강력한 추세에서 지위를 늘리는 것을 허용합니다.
위험
- 어떤 기술적인 지표와 마찬가지로 MA 교차는 잘못된 신호를 생성할 수 있습니다.
- 현재의 시장 조건을 지나치게 최적화하면 미래의 성과가 떨어질 수 있습니다.
- 하드스트로크가 너무 일찍 퇴출해서 큰 변동이 있는 거래가 맞다
입시 신호를 위해 가격을 확인하고, 하드 스톱 대신 추적 스톱을 사용하며, 과도한 최적화를 피함으로써 위험 관리를 강화할 수 있다.
최적화 공간
이 전략은 몇 가지 방법으로 개선될 수 있습니다.
- 입국 전에 추가 필터, 예를 들어 거래량 및 가격 검사
- 다양한 MA 유형의 성능을 체계적으로 테스트하고, 가장 좋은 1-2종을 선택합니다.
- 특정 거래 유형 및 기간에 대한 MA 길이를 최적화하십시오.
- 추적 손실을 사용하여 하드 손실을 대체합니다.
- 추세가 길어지면서 단계적 정지
요약하다
11 이동 평균 크로스 전략은 체계화된 거래 크로스 방법을 제공합니다. 여러 MA 지표의 신호를 결합하고 핵심 매개 변수를 구성할 수 있도록 함으로써 강력하고 유연한 거래 프레임 워크를 제공합니다. 최적화 및 위험 관리는 성과를 최적화하는 데 중요한 역할을합니다. 이 전략은 동적 거래에서 강력한 잠재력을 가지고 있지만 다른 시장 환경에 따라 조정해야합니다.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-15 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-14 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
strategy(title = "[STRATEGY] MA Cross Eleven", overlay = true)
// MA - type, source, length
// MA - type, source, length
// SMA --> Simple
// EMA --> Exponential
// WMA --> Weighted
// VWMA --> Volume Weighted
// SMMA --> Smoothed
// DEMA --> Double Exponential
// TEMA --> Triple Exponential
// HMA --> Hull
// TMA --> Triangular
// SSMA --> SuperSmoother filter
// ZEMA --> Zero Lag Exponential
type = input(defval="ZEMA", title="MA Type: ", options=["SMA", "EMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "HullMA", "ZEMA", "TMA", "SSMA"])
len1 = input(defval=8, title="Fast MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose1 = input(close, "Fast MA Source")
len2 = input(defval=21, title="Slow MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose2 = input(close, "Slow MA Source")
// Returns MA input selection variant, default to SMA if blank or typo.
variant(type, src, len) =>
v1 = sma(src, len) // Simple
v2 = ema(src, len) // Exponential
v3 = wma(src, len) // Weighted
v4 = vwma(src, len) // Volume Weighted
v5 = 0.0
v5 := na(v5[1]) ? sma(src, len) : (v5[1] * (len - 1) + src) / len // Smoothed
v6 = 2 * v2 - ema(v2, len) // Double Exponential
v7 = 3 * (v2 - ema(v2, len)) + ema(ema(v2, len), len) // Triple Exponential
v8 = wma(2 * wma(src, len / 2) - wma(src, len), round(sqrt(len))) // Hull
v11 = sma(sma(src,len),len) // Triangular
// SuperSmoother filter
// © 2013 John F. Ehlers
a1 = exp(-1.414*3.14159 / len)
b1 = 2*a1*cos(1.414*3.14159 / len)
c2 = b1
c3 = (-a1)*a1
c1 = 1 - c2 - c3
v9 = 0.0
v9 := c1*(src + nz(src[1])) / 2 + c2*nz(v9[1]) + c3*nz(v9[2])
// Zero Lag Exponential
e = ema(v2, len)
v10 = v2+(v2-e)
// return variant, defaults to SMA if input invalid.
type=="EMA"?v2 : type=="WMA"?v3 : type=="VWMA"?v4 : type=="SMMA"?v5 : type=="DEMA"?v6 : type=="TEMA"?v7 : type=="HullMA"?v8 : type=="SSMA"?v9 : type=="ZEMA"?v10 : type=="TMA"? v11: v1
ma_1 = variant(type, srcclose1, len1)
ma_2 = variant(type, srcclose2, len2)
plot(ma_1, title="Fast MA", color = green, linewidth=2, transp=0)
plot(ma_2, title="Slow MA", color = red, linewidth=2, transp=0)
longCond = na
shortCond = na
longCond := crossover(ma_1, ma_2)
shortCond := crossunder(ma_1, ma_2)
// Count your long short conditions for more control with Pyramiding
sectionLongs = 0
sectionLongs := nz(sectionLongs[1])
sectionShorts = 0
sectionShorts := nz(sectionShorts[1])
if longCond
sectionLongs := sectionLongs + 1
sectionShorts := 0
if shortCond
sectionLongs := 0
sectionShorts := sectionShorts + 1
// Pyramiding Inputs
pyrl = input(1, "Pyramiding")
// These check to see your signal and cross references it against the pyramiding settings above
longCondition = longCond and sectionLongs <= pyrl
shortCondition = shortCond and sectionShorts <= pyrl
// Get the price of the last opened long or short
last_open_longCondition = na
last_open_shortCondition = na
last_open_longCondition := longCondition ? high[1] : nz(last_open_longCondition[1])
last_open_shortCondition := shortCondition ? low[1] : nz(last_open_shortCondition[1])
// Check if your last postion was a long or a short
last_longCondition = na
last_shortCondition = na
last_longCondition := longCondition ? time : nz(last_longCondition[1])
last_shortCondition := shortCondition ? time : nz(last_shortCondition[1])
in_longCondition = last_longCondition > last_shortCondition
in_shortCondition = last_shortCondition > last_longCondition
// Take profit
isTPl = input(false, "Take Profit Long")
isTPs = input(false, "Take Profit Short")
tpl = input(3, "Take Profit Long %", type=float)
tps = input(30, "Take Profit Short %", type=float)
long_tp = isTPl and crossover(high, (1+(tpl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and in_longCondition == 1
short_tp = isTPs and crossunder(low, (1-(tps/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and in_shortCondition == 1
// Stop Loss
isSLl = input(false, "Stop Loss Long")
isSLs = input(false, "Stop Loss Short")
sl= 0.0
sl := input(3, "Stop Loss %", type=float)
long_sl = isSLl and crossunder(low, (1-(sl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and longCondition == 0 and in_longCondition == 1
short_sl = isSLs and crossover(high, (1+(sl/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and shortCondition == 0 and in_shortCondition == 1
// Create a single close for all the different closing conditions.
long_close = long_tp or long_sl ? 1 : 0
short_close = short_tp or short_sl ? 1 : 0
// Get the time of the last close
last_long_close = na
last_short_close = na
last_long_close := long_close ? time : nz(last_long_close[1])
last_short_close := short_close ? time : nz(last_short_close[1])
// Strategy entries
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long, when=longCondition == true, stop = open[1])
strategy.entry("short", strategy.short, when=shortCondition == true)
strategy.close("long", when = long_sl or long_tp)
strategy.close("short", when = short_sl or short_tp)