Estratégia de cruzamento de seta de média móvel dupla
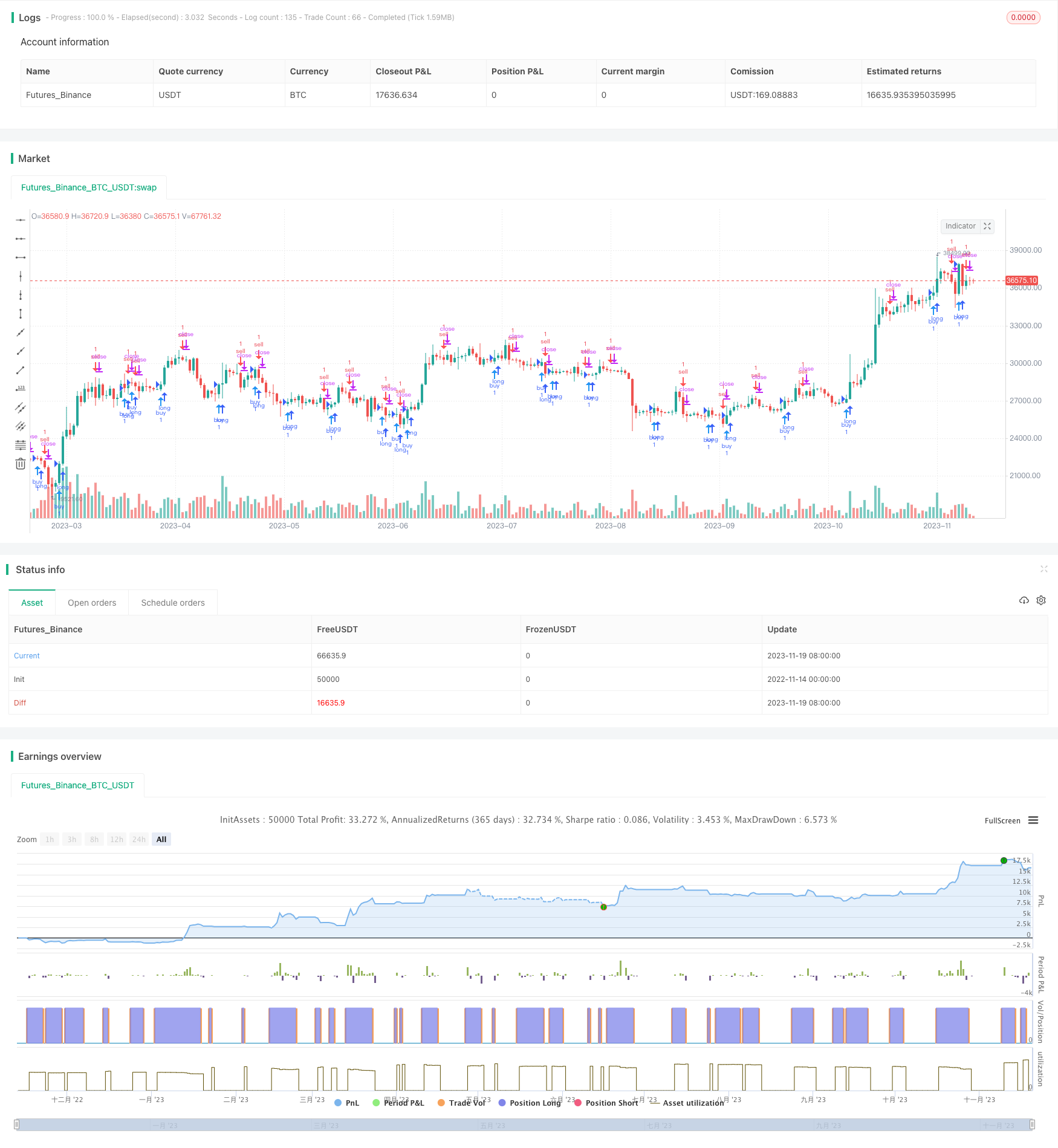
Visão geral
A estratégia determina o momento de comprar e vender através do cálculo da dupla equilíbrio entre os MACDs. A estratégia traça uma forma de flecha no gráfico para indicar um sinal de negociação.
Princípios
A estratégia primeiro calcula a linha rápida (EMA 12), a linha lenta (EMA 26) e a diferença do MACD. Em seguida, os momentos de compra e venda são julgados com base nos forcados de ouro da linha rápida e da linha lenta e no diferencial MACD positivo e negativo:
- Quando a linha rápida atravessa a linha lenta ((Goldfork) e o diferencial MACD atravessa 0 é um sinal de compra
- Quando a linha rápida atravessa a linha lenta (dead fork) e a diferença MACD passa por 0 é um sinal de venda
Para filtrar falsos sinais, o código também julga o estado do sinal da linha K anterior. O sinal atual só é acionado quando a linha K atual é um sinal inverso (compra para venda ou venda para compra).
Além disso, o código também traça um gráfico de setas para indicar quando comprar e vender na linha K.
Vantagens
A estratégia tem as seguintes vantagens:
- O uso de um julgamento de cruzamento de duas equações permite filtrar eficazmente o ruído do mercado e identificar tendências
- Combinação com a avaliação de diferença do MACD para evitar omissões e erros de avaliação
- O uso de setas para indicar a hora de comprar e vender é mais claro.
- Regras simples, claras, fáceis de entender e copiar
Riscos e soluções
A estratégia também apresenta alguns riscos:
- O cruzamento de duas medianas é propenso a produzir falsos sinais, o que pode levar a excesso de negociação. Pode-se ajustar adequadamente os parâmetros de mediana ou adicionar outras condições de filtragem para reduzir os falsos sinais.
- Não é possível avaliar oscilações na tendência, podendo ocorrer prejuízos. Indicadores de tendência como o ADX podem ser usados para evitar isso.
- Condições fixas de compra e venda tornam as estratégias mais mecânicas, não conseguem se adaptar às mudanças do mercado. Pode-se tentar métodos de adaptação como aprendizado de máquina para otimizar
Direção de otimização
A estratégia pode ser otimizada em várias direções:
- Teste diferentes combinações de parâmetros para encontrar a melhor linha rápida, lenta e MACD
- Aumentar os requisitos de entrada, como o volume de transações para filtrar os sinais
- Aumentar o mecanismo de suspensão de prejuízos para controlar as perdas individuais
- Indicadores de volatilidade como o VIX são usados para avaliar a preferência de risco
- Experimentar com modelos de aprendizagem de máquina em vez de regras fixas para a otimização da adaptação das estratégias
Resumir
A estratégia de crossover binário é bastante simples e prática em geral. Com o julgamento de crossover binário e a filtragem de diferença MACD, é possível identificar pontos de compra e venda em tendências de linha média e longa, evitando a mudança de preço perdida. Os avisos de seta também tornam a operação mais clara e clara.
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-14 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-20 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
//Daniels stolen code
strategy(shorttitle="Daniels Stolen Code", title="Daniels Stolen Code", overlay=true, calc_on_order_fills=true, pyramiding=0)
//Define MACD Variables
fast = 12, slow = 26
fastMACD = ema(hlc3, fast)
slowMACD = ema(hlc3, slow)
macd = fastMACD - slowMACD
signal = sma(macd, 9)
hist = macd - signal
currMacd = hist[0]
prevMacd = hist[1]
currPrice = hl2[0]
prevPrice = hl2[1]
buy = currPrice > prevPrice and currMacd > prevMacd
sell = currPrice < prevPrice and currMacd < prevMacd
neutral = (currPrice < prevPrice and currMacd > prevMacd) or (currPrice > prevPrice and currMacd < prevMacd)
//Plot Arrows
timetobuy = buy==1 and (sell[1]==1 or (neutral[1]==1 and sell[2]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and sell[3]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and sell[4]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and sell[5]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and neutral[5]==1 and sell[6]==1))
timetosell = sell==1 and (buy[1]==1 or (neutral[1]==1 and buy[2]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and buy[3]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and buy[4]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and buy[5]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and neutral[5]==1 and buy[6]==1))
plotshape(timetobuy, color=blue, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.arrowup)
plotshape(timetosell, color=red, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.arrowdown)
//plotshape(neutral, color=black, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.circle)
//Test Strategy
// strategy.entry("long", true, 1, when = timetobuy and time > timestamp(2017, 01, 01, 01, 01)) // buy by market if current open great then previous high
// strategy.close("long", when = timetosell and time > timestamp(2017, 01, 01, 01, 01))
strategy.order("buy", true, 1, when=timetobuy==1 and time > timestamp(2019, 01, 01, 01, 01))
strategy.order("sell", false, 1, when=timetosell==1 and time > timestamp(2019, 01, 01, 01, 01))
// strategy.entry(id = "Short", long = false, when = enterShort())
// strategy.close(id = "Short", when = exitShort())
//strategy.entry("long", true, 1, when = open > high[1]) // enter long by market if current open great then previous high
// strategy.exit("exit", "long", profit = 10, loss = 5) // ge