Ba chiến lược giao dịch nhanh độ trễ thấp trung bình động
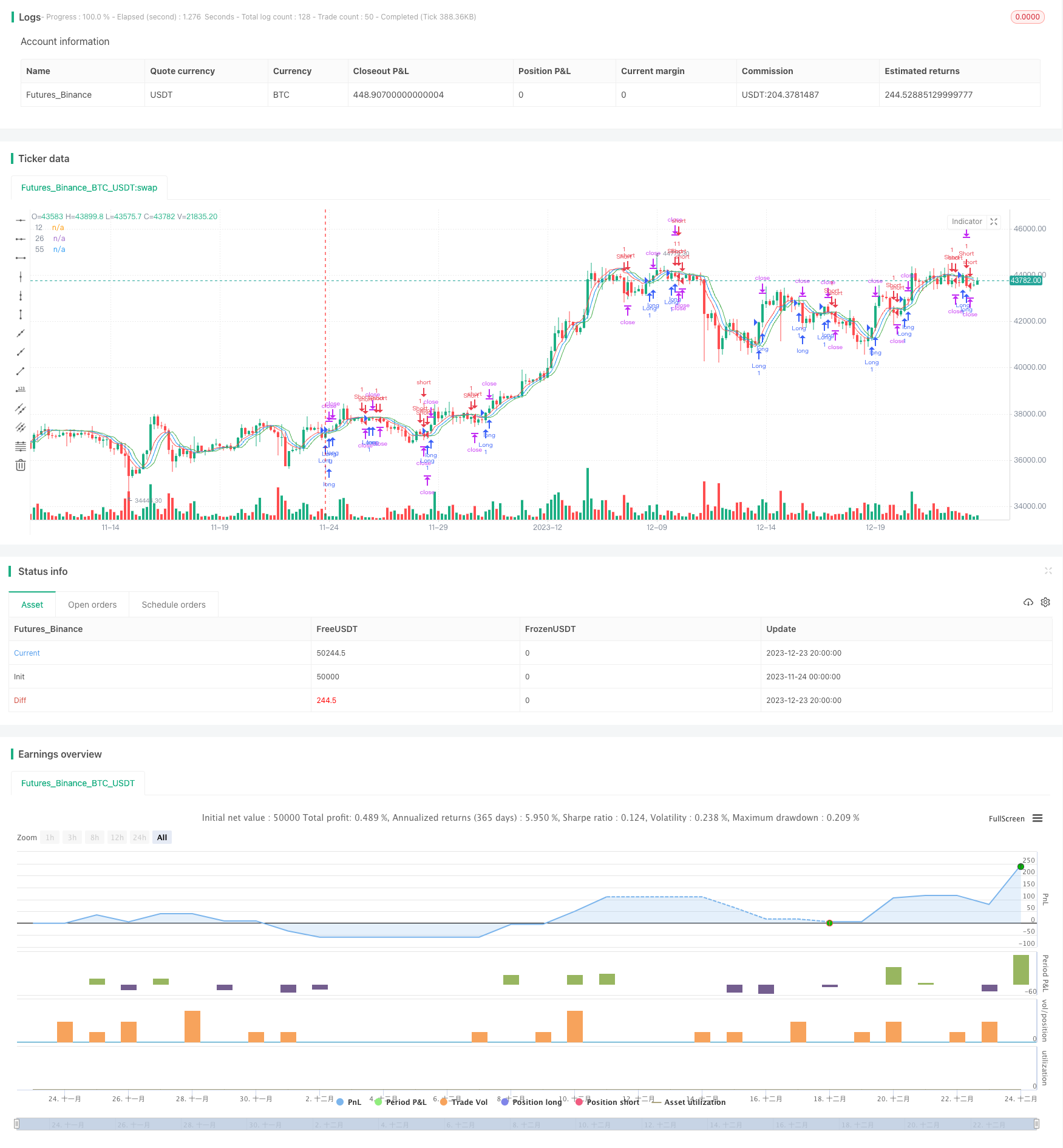
Nguyên tắc chiến lược
Chiến lược này sử dụng ba đường trung bình di chuyển kéo dài thời gian thấp, bao gồm các đường trung bình kéo dài thời gian thấp trong 12 chu kỳ, 26 chu kỳ và 55 chu kỳ. Ba đường trung bình này đại diện cho: đường trung bình nhanh, đường trung bình nhanh và đường trung bình chậm.
Mã định nghĩa hàm mẫu tema () để tính toán đường trung bình của tema với độ trễ thấp. Công thức tính toán của nó là: TEMA = 2*EMA - EMA ((EMA), sử dụng chỉ số di chuyển trung bình thứ hai EWMA để tính toán, về bản chất là một chỉ số di chuyển trung bình trơn kép, lợi thế chính là giảm đáng kể độ trễ. Do đó, có thể phản ứng nhanh hơn với sự thay đổi giá, tăng tính thời gian thực của phán đoán tín hiệu giao dịch.
Cụ thể, đánh giá nhập cảnh của chiến lược này là: tạo ra tín hiệu mua khi đường trung bình nhanh vượt qua đường trung bình nhanh và đường trung bình nhanh cao hơn đường trung bình chậm; tạo ra tín hiệu bán khi đường trung bình nhanh vượt qua đường trung bình nhanh và đường trung bình nhanh thấp hơn đường trung bình chậm.
Phân tích lợi thế
Lợi thế lớn nhất của chiến lược này là phán đoán nhanh và chính xác khi ra sân. Thiết kế trì hoãn thời gian thấp của ba đường trung bình làm giảm đáng kể sự chậm trễ, có thể phản ứng nhanh chóng với sự thay đổi giá. Đồng thời sử dụng ba đường trung bình để phán đoán chéo, tránh sai lầm.
Ngoài ra, chiến lược này phù hợp với giao dịch tần số cao, có thể thu được lợi nhuận từ biến động giá đường ngắn. Với mô hình hoạt động nhanh chóng và nhanh chóng, có thể kiếm được lợi nhuận trong thị trường biến động lớn.
Phân tích rủi ro
Rủi ro lớn nhất của chiến lược này là có thể xảy ra mạo hiểm siêu ngắn. Thiết kế trì hoãn thấp của ba đường trung bình quyết định rằng nó rất nhạy cảm với sự thay đổi giá, trong một số thị trường có thể xảy ra biến động siêu ngắn.
Ngoài ra, giao dịch tần số cao đòi hỏi phải trả nhiều phí và điểm trượt hơn. Nếu khả năng lợi nhuận không đủ, rất dễ bị đánh giá ngược về phí giao dịch.
Ngoài ra, chiến lược này đòi hỏi khả năng giám sát thực tế của nhà giao dịch cao hơn, cần cập nhật điểm dừng lỗ và điểm dừng lại kịp thời.
Hướng tối ưu hóa
Chiến lược này có thể được tối ưu hóa theo các khía cạnh sau:
Tối ưu hóa các tham số chu kỳ của đường trung bình ba chiều để phù hợp hơn với các đặc điểm của các thị trường khác nhau;
Thêm chỉ số biến động hoặc chỉ số khối lượng giao dịch để xác nhận tín hiệu và tránh bị mắc kẹt trong tình huống biến động;
Kết hợp nhiều yếu tố khác nhau để thiết lập các cơ chế ngăn chặn, theo dõi động lực;
Tối ưu hóa quản lý vị trí, kiểm soát rủi ro đơn lẻ thông qua các phương tiện quản lý tài chính;
Các tham số chiến lược tối ưu hóa động kết hợp với thuật toán học máy.
Tóm tắt
Chiến lược này là chiến lược giao dịch nhanh khi trì hoãn khi đường trung bình thấp. Nó được thiết kế bằng cách trì hoãn thấp, để thực hiện nhanh chóng, phù hợp với giao dịch tần số cao để nắm bắt cơ hội đường ngắn. Ưu điểm lớn nhất của chiến lược này là tín hiệu phán đoán nhanh và chính xác, và nhược điểm lớn nhất là dễ dàng bị trượt trong tình huống xung đột.
||
The strategy is named “Low Lag Triple Moving Average Fast Trading Strategy”. Its main idea is to determine entries and exits based on the golden cross and death cross of three moving averages with different parameters and low lag design.
Strategy Principle
The strategy uses three low-lag moving averages, including 12-, 26-, and 55-period low-lag TEMA. These three MAs represent fast, medium and slow MAs. When the fast MA crosses over the medium MA, a buy signal is generated. When the fast MA crosses below the medium MA, a sell signal is generated. By using the crossover of the three MAs to determine market entry and exit points, high frequency trading can be achieved.
The template function tema() is defined in the code to calculate the low-lag TEMA. Its calculation formula is: TEMA = 2*EMA - EMA(EMA). It uses the double exponential moving average EWMA for calculation. Essentially it is a double smoothed EMA with the main merit of largely reducing the lagging effect. Thus it can respond to price changes faster and improve the timeliness of trading signals.
Specifically, the entry rules of this strategy are: when the fast MA crosses over the medium MA and the fast MA is above the slow MA, a buy signal is generated. When the fast MA crosses below the medium MA and the fast MA is below the slow MA, a sell signal is generated.
Advantage Analysis
The biggest advantage of this strategy is that the entries and exits are determined quickly and accurately. The low-lag design of the three MAs greatly reduces the lagging effect so that they can respond to price changes rapidly. Also, using the crossover of three MAs to determine signals avoids false signals.
In addition, this strategy is suitable for high-frequency trading to capture profits from short-term price fluctuations. Through fast entries and exits it can profit from high volatility markets.
Risk Analysis
The biggest risk is that ultra short-term whipsaws may occur. Due to the high sensitivity to price changes from the low-lag design, some markets may experience high-frequency oscillations. Then whipsaws are very likely to happen.
Also, high-frequency trading requires paying relatively high commissions and slippage costs. If the profiting ability is insufficient, it is easy to suffer losses from the trading costs.
Moreover, this strategy requires the trader to have strong real-time monitoring abilities to update the stop loss and take profit timely.
Optimization Directions
The strategy can be optimized from the following aspects:
Optimize the period parameters of the three MAs to better suit different market characteristics.
Add volatility indicators or volume indicators to confirm signals and avoid whipsaws in ranging markets.
Incorporate more factors to set up dynamic trailing stop mechanisms.
Optimize position sizing to control single trade risks through money management techniques.
Incorporate machine learning algorithms to dynamically optimize the strategy parameters.
Conclusion
This is a low-lag triple moving average fast trading strategy. Through its low-lag design, fast entries and exits can be achieved, which is suitable for high-frequency trading to capture short-term opportunities. The biggest advantage of this strategy is that its signal determination is fast and accurate. The biggest disadvantage is that it is prone to be whipsawed in ranging markets. This article comprehensively summarizes this trading strategy through detailed analysis of its rationale, advantages, risks and optimization directions.
[/trans]
/*backtest
start: 2023-11-24 00:00:00
end: 2023-12-24 00:00:00
period: 4h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("scalping low lag tema etal", shorttitle="Scalping tema",initial_capital=10000, overlay=true)
mav = input(title="Moving Average Type", defval="temadelay", options=["nkclose", "ema", "emadelay", "fastema", "tema", "temadelay"])
lenb = 3
N = input(8)
K = input(1.2)
fracCap = input(1.0)
in = close + K*mom(close,N)
source = close
length = 8
sigma = 12.0
offset = 0.9
p = 4
// length = 10
// sigma = 6.0
// offset = 0.85
tema(src,len) => fastemaOut = 2*ema(src, len) - ema(ema(src, len), len)
a = 0.0
b = 0.0
c = 0.0
if mav == "nkclose"
a := ema(in, 12)
b := a[1]
c := a[2]
if mav == "ema"
a := ema(close, 12)
b := ema(close, 26)
c := ema(close, 55)
if mav == "emadelay"
a := ema(close, 12)
b := a[1]
c := a[2]
if mav == "fastema"
a := ema(in, 12)
b := ema(in, 26)
c := ema(in, 55)
if mav == "tema"
a := tema(close, 12)
b := tema(close, 26)
c := tema(close, 55)
if mav == "temadelay"
a := tema(close, 12)
b := a[1]
c := a[2]
TP = input(200)
SL = input(130)
TS = input(1)
// TP = input(50)
// SL = input(110)
// TS = input(1)
orderSize = floor((fracCap * strategy.equity) / close)
long = cross(a, c) and a > b
short = cross(a, c) and a < b
plot(a, title="12", color=color.red, linewidth=1)
plot(b, title="26", color=color.blue, linewidth=1)
plot(c, title="55", color=color.green, linewidth=1)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, qty=orderSize, when=long)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, qty=orderSize, when=short)
// strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, 100.0, when=long)
// strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, 100.0, when=short)
// strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, 100.0, when=long)
// strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, 100.0, when=short)
// strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, 1.0, when=long)
// strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, 1.0, when=short)
TPP = (TP > 0) ? TP : na
SLP = (SL > 0) ? SL : na
TSP = (TS > 0) ? TS : na
// strategy.exit("Close Short", "Short", qty_percent=100, profit=TPP, loss=SLP, trail_points=TSP, when=long)
// strategy.exit("Close Long", "Long", qty_percent=100, profit=TPP, loss=SLP, trail_points=TSP, when=short)
// strategy.exit("Close Long", "Long", qty_percent=100, profit=TPP, loss=SLP, trail_points=TSP, when=long[1])
// strategy.exit("Close Short", "Short", qty_percent=100, profit=TPP, loss=SLP, trail_points=TSP, when=short[1])
strategy.exit("Close Long", "Long", qty_percent=100, profit=TPP, loss=SLP, trail_points=TSP)
strategy.exit("Close Short", "Short", qty_percent=100, profit=TPP, loss=SLP, trail_points=TSP)