Estratégia de negociação quantitativa Double RSI
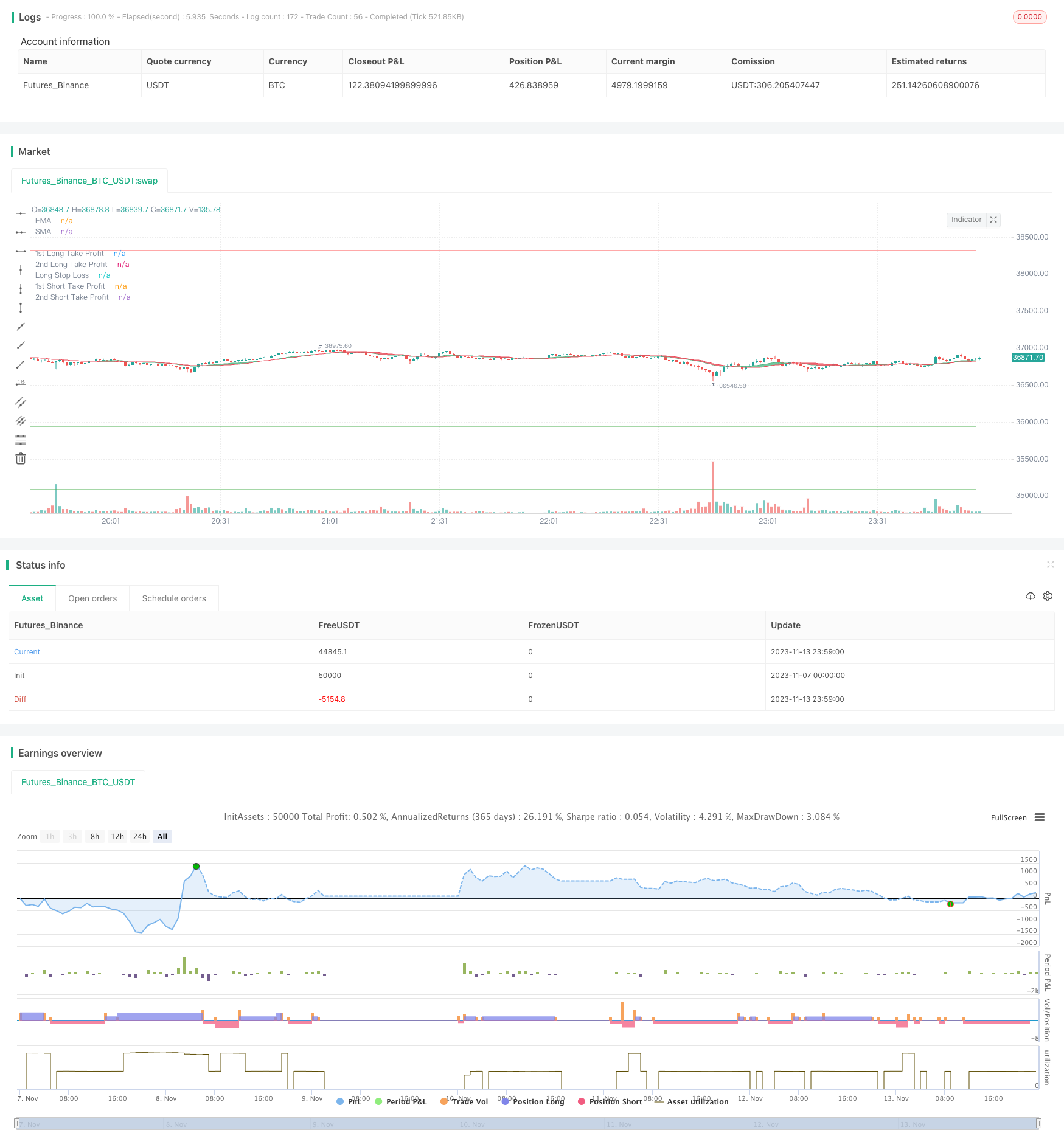
Visão geral
Esta estratégia utiliza o indicador de RSI duplo para a negociação de curto e longo prazo, em combinação com o sistema de equilíbrio para determinar a direção da tendência, pertence à estratégia de quantificação do RSI duplo. A estratégia utiliza primeiro o indicador de RSI para determinar o sinal de carência, em combinação com a direção da tendência para determinar a direção da tendência, e é uma estratégia típica de acompanhamento de tendência.
Análise de princípios
A estratégia de quantificação do RSI duplo usa principalmente o indicador RSI de dois períodos de tempo para julgar sinais de negociação. A estratégia primeiro define dois parâmetros RSI, um período mais longo como julgamento principal de negociação e um período mais curto como filtro auxiliar. Quando o RSI de longo período passa a linha de venda, um sinal de cotação é gerado, e quando o RSI de curto período passa a linha de compra, um sinal de cotação é gerado, formando uma oportunidade de negociação de curto cruzamento.
Para filtrar os sinais falsos, a estratégia também introduz o SMA e a média EMA para o julgamento de tendências. O RSI é considerado um sinal múltiplo somente quando a linha curta de SMA atravessa a linha de EMA longa e o RSI é considerado um sinal de fechamento somente quando a linha curta de SMA atravessa a linha de EMA longa, garantindo que o sinal duplo de RSI esteja de acordo com a direção da tendência e evitando a negociação contra a tendência.
Além disso, a estratégia também configura a lógica de stop loss. A posição é aberta com duas quantidades diferentes de pedidos de stop loss em simultâneo, e a posição de stop loss é definida.
Análise de vantagens
A estratégia de quantificação do RSI duplo tem as seguintes vantagens:
O indicador de RSI de período de tempo duplo pode determinar com mais precisão os sinais de hipocrisia. A combinação cruzada de RSI de período longo e curto pode filtrar alguns sinais falsos e melhorar a qualidade do sinal.
O sistema de linha média ajuda a determinar a direção da grande tendência, evita a negociação contra a tendência, pode filtrar a maior parte da negociação de ruído e aumentar a taxa de vitória.
Mecanismos flexíveis de stop-loss, que permitem obter maiores ganhos através de diferentes configurações de stop-loss, mas também podem ser bloqueados para controlar o risco.
A lógica de negociação estratégica é simples e clara, fácil de entender e de otimizar, adequada para o aprendizado de comerciantes de quantificação.
Análise de Riscos
Apesar das vantagens de uma estratégia de quantificação de dois RSI, há também os seguintes riscos:
O indicador RSI por si só não tem efeito sobre oscilações e reversões de tendência, e a estratégia pode não ser eficaz para o comércio nesses mercados.
Embora o sistema de linha média possa filtrar o ruído de pequena escala, ele não é muito eficaz no julgamento de mudanças de tendência no ciclo intermediário e pode perder o ponto de viragem da tendência.
A configuração inadequada do stop loss pode levar ao stop loss muito amplo ou ao stop loss muito pequeno, reduzindo a eficácia da estratégia.
O excesso de oferta e venda de ações em larga escala pode levar à expansão dos prejuízos, e é necessário controlar o tamanho das posições.
Para os riscos acima, pode-se reduzir o risco, ajustando os parâmetros do RSI, introduzindo tendências mais avançadas e indicadores de reversão, otimizando a lógica de stop loss e controlando a posição.
Direção de otimização
A estratégia de quantificação do RSI duplo pode ser ainda mais otimizada em várias direções:
Tente diferentes combinações de parâmetros, otimize os parâmetros do RSI de ciclo e encontre a melhor combinação de indicadores de RSI de longo e curto período.
Testar diferentes indicadores de mediana, introduzir indicadores como o MACD para avaliar tendências e oportunidades de reversão.
Otimize a estratégia de stop loss, configure o stop loss de rastreamento ou o stop loss móvel, para que o stop loss de stop loss seja mais flexível.
Adição de módulos de controle de posições, controle de mais posições de tomada de posição em diferentes fases da tendência do grande ciclo.
A adição de modelos de aprendizagem de máquina aumenta a precisão das entradas e saídas.
Otimizar o feedback para encontrar as melhores variedades de negócios e períodos de tempo.
Resumir
A estratégia de quantificação do RSI duplo é uma estratégia típica de acompanhamento de tendências. A estratégia que combina os indicadores do RSI duplo para julgar os sinais de negociação e filtrar o ruído do sistema linear é muito clássica e prática. Embora a estratégia também tenha algum espaço para melhorias, a lógica de funcionamento geral é clara, fácil de entender e otimizar.
/*backtest
start: 2023-11-07 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-14 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("Growth Producer", overlay=true, initial_capital = 1000, currency = "USD", pyramiding = 2, commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.07, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value = 100)
//Functions
Atr(p) =>
atr = 0.
Tr = max(high - low, max(abs(high - close[1]), abs(low - close[1])))
atr := nz(atr[1] + (Tr - atr[1])/p,Tr)
/// TREND
ribbon_period = input(19, "Period", step=1)
leadLine1 = ema(close, ribbon_period)
leadLine2 = sma(close, ribbon_period)
p1 = plot(leadLine1, color= #53b987, title="EMA", transp = 50, linewidth = 1)
p2 = plot(leadLine2, color= #eb4d5c, title="SMA", transp = 50, linewidth = 1)
fill(p1, p2, transp = 60, color = leadLine1 > leadLine2 ? #53b987 : #eb4d5c)
// Relative volatility index
length = input(120,"RVI period", minval=1), src = close
len = 14
stddev = stdev(src, length)
upper = ema(change(src) <= 0 ? 0 : stddev, len)
lower = ema(change(src) > 0 ? 0 : stddev, len)
rvi = upper / (upper + lower) * 100
benchmark = input(35, "RVI benchmark", minval=10, maxval=100, step=0.1)
// Plot RVI
// h0 = hline(80, "Upper Band", color=#C0C0C0)
// h1 = hline(20, "Lower Band", color=#C0C0C0)
// fill(h0, h1, color=#996A15, title="Background")
// offset = input(0, "Offset", type = input.integer, minval = -500, maxval = 500)
// plot(rvi, title="RVI", color=#008000, offset = offset)
/// MFI input
mfi_source = hlc3
mfi_length = input(19, "MFI Length", minval=1)
mfi_lower = input(15, "MFI Lower level", minval=0, maxval=50)
mfi_upper = input(90, "MFI Higher level", minval=50, maxval=100)
// MFI
upper_s = sum(volume * (change(mfi_source) <= 0 ? 0 : mfi_source), mfi_length)
lower_s = sum(volume * (change(mfi_source) >= 0 ? 0 : mfi_source), mfi_length)
mf = rsi(upper_s, lower_s)
// mfp = plot(mf, color=color.new(color.gray,0), linewidth=1)
// top = hline(mfi_upper, color=color.new(color.gray, 100), linewidth=1, editable=false)
// bottom = hline(mfi_lower, color=color.new(color.gray,100), linewidth=1, editable=false)
// hline(0, color=color.new(color.black,100), editable=false)
// hline(100, color=color.new(color.black,100), editable=false)
// Breaches
// b_color = (mf > mfi_upper) ? color.new(color.red,70) : (mf < mfi_lower) ? color.new(color.green,60) : na
// bgcolor(HighlightBreaches ? b_color : na)
// fill(top, bottom, color=color.gray, transp=75)
// Initial inputs
Act_RSI_VWAP_long = input(true, "RSI VOLUME WEIGHTED AVERAGE PRICE LONG")
RSI_VWAP_length_long = input(16, "RSI-VWAP LENGTH LONG")
RSI_VWAP_overSold_long = input(13, "RSI-VWAP OVERSOLD LONG", type=input.float)
RSI_VWAP_overBought_long = input(68, "RSI-VWAP OVERBOUGHT LONG", type=input.float)
Act_RSI_VWAP_short = input(true, "RSI VOLUME WEIGHTED AVERAGE PRICE SHORT")
RSI_VWAP_length_short = input(14, "RSI-VWAP LENGTH SHORT")
RSI_VWAP_overSold_short = input(7, "RSI-VWAP OVERSOLD SHORT", type=input.float)
RSI_VWAP_overBought_short = input(68, "RSI-VWAP OVERBOUGHT SHORT", type=input.float)
// RSI with VWAP as source
RSI_VWAP_long = rsi(vwap(close), RSI_VWAP_length_long)
RSI_VWAP_short = rsi(vwap(close), RSI_VWAP_length_short)
// Plot Them Separately.
// Plotting LONG, Put overlay=false
// r=plot(RSI_VWAP_long, color = RSI_VWAP_long > RSI_VWAP_overBought_long ? color.red : RSI_VWAP_lnog < RSI_VWAP_overSold_long ? color.lime : color.blue, title="rsi", linewidth=2, style=plot.style_line)
// h1=plot(RSI_VWAP_overBought_long, color = color.gray, style=plot.style_stepline)
// h2=plot(RSI_VWAP_overSold_long, color = color.gray, style=plot.style_stepline)
// fill(r,h1, color = RSI_VWAP_long > RSI_VWAP_overBought_long ? color.red : na, transp = 60)
// fill(r,h2, color = RSI_VWAP_long < RSI_VWAP_overSold_long ? color.lime : na, transp = 60)
// Plotting SHORT, Put overlay=false
// r=plot(RSI_VWAP_short, color = RSI_VWAP_short > RSI_VWAP_overBought_short ? color.red : RSI_VWAP_short < RSI_VWAP_overSold_short ? color.lime : color.blue, title="rsi", linewidth=2, style=plot.style_line)
// h1=plot(RSI_VWAP_overBought_short, color = color.gray, style=plot.style_stepline)
// h2=plot(RSI_VWAP_overSold_short, color = color.gray, style=plot.style_stepline)
// fill(r,h1, color = RSI_VWAP_short > RSI_VWAP_overBought_short ? color.red : na, transp = 60)
// fill(r,h2, color = RSI_VWAP_short < RSI_VWAP_overSold_short ? color.lime : na, transp = 60)
/////// STRATEGY Take Profit / Stop Loss ////////
////// LONG //////
long_tp1_inp = input(3.3, title='Long Take Profit 1 %', step=0.1)/100
long_tp1_qty = input(15, title="Long Take Profit 1 Qty", step=1)
long_tp2_inp = input(12, title='Long Take Profit 2%', step=0.1)/100
long_tp2_qty = input(100, title="Long Take Profit 2 Qty", step=1)
long_sl_inp = input(3.3, title='Long Stop Loss %', step=0.1)/100
long_take_level_1 = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + long_tp1_inp)
long_take_level_2 = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + long_tp2_inp)
long_stop_level = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - long_sl_inp)
////// SHORT //////
short_tp1_inp = input(3.2, title='Short Take Profit 1 %', step=0.1)/100
short_tp1_qty = input(20, title="Short Take Profit 1 Qty", step=1)
short_tp2_inp = input(5.5, title='Short Take Profit 2%', step=0.1)/100
short_tp2_qty = input(100, title="Short Take Profit 2 Qty", step=1)
short_sl_inp = input(3.2, title='Short Stop Loss %', step=0.1)/100
short_take_level_1 = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - short_tp1_inp)
short_take_level_2 = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - short_tp2_inp)
short_stop_level = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + short_sl_inp)
///Strategy_Conditions
/// LONG ///
entry_long =(crossover(RSI_VWAP_long, RSI_VWAP_overSold_long) and leadLine2<leadLine1) or (crossunder(mf,mfi_lower) and leadLine2<leadLine1)
entry_price_long=valuewhen(entry_long,close,0)
exit_long =crossunder(RSI_VWAP_long, RSI_VWAP_overBought_long)
/// SHORT ///
entry_short =crossunder(RSI_VWAP_short, RSI_VWAP_overBought_short) and leadLine2>leadLine1 or (crossover(mf,mfi_upper) and leadLine2>leadLine1)
entry_price_short=valuewhen(entry_short,close,0)
exit_short =crossover(RSI_VWAP_short, RSI_VWAP_overSold_short)
////// BACKTEST PERIOD ///////
testStartYear = input(2019, "Backtest Start Year")
testStartMonth = input(1, "Backtest Start Month")
testStartDay = input(1, "Backtest Start Day")
testPeriodStart = timestamp(testStartYear,testStartMonth,testStartDay,0,0)
testStopYear = input(2020, "Backtest Stop Year")
testStopMonth = input(12, "Backtest Stop Month")
testStopDay = input(31, "Backtest Stop Day")
testPeriodStop = timestamp(testStopYear,testStopMonth,testStopDay,0,0)
testPeriod() => true
if testPeriod()
if strategy.position_size == 0 or strategy.position_size > 0 and rvi>benchmark
strategy.entry("long", true, when = entry_long, comment="Insert Enter Long Comment")
strategy.exit("TP1","long", qty_percent=long_tp1_qty, limit=long_take_level_1, stop=long_stop_level)
strategy.exit("TP2","long", qty_percent=long_tp2_qty, limit=long_take_level_2, stop=long_stop_level)
strategy.close("long", when=exit_long, comment = "Insert Exit Long Comment")
if strategy.position_size == 0 or strategy.position_size < 0 and rvi>benchmark
strategy.entry("short", false, when = entry_short, comment="Insert Enter Short Comment")
strategy.exit("TP1","short", qty_percent=short_tp1_qty, limit=short_take_level_1, stop=short_stop_level)
strategy.exit("TP2","short", qty_percent=short_tp2_qty, limit=short_take_level_2, stop=short_stop_level)
strategy.close("short", when=exit_short, comment = "Insert Exit Short Comment")
// LONG POSITION
plot(strategy.position_size > 0 ? long_take_level_1 : na, style=plot.style_linebr, color=color.green, linewidth=1, title="1st Long Take Profit")
plot(strategy.position_size > 0 ? long_take_level_2 : na, style=plot.style_linebr, color=color.green, linewidth=1, title="2nd Long Take Profit")
plot(strategy.position_size > 0 ? long_stop_level : na, style=plot.style_linebr, color=color.red, linewidth=1, title="Long Stop Loss")
// SHORT POSITION
plot(strategy.position_size < 0 ? short_take_level_1 : na, style=plot.style_linebr, color=color.green, linewidth=1, title="1st Short Take Profit")
plot(strategy.position_size < 0 ? short_take_level_2 : na, style=plot.style_linebr, color=color.green, linewidth=1, title="2nd Short Take Profit")
plot(strategy.position_size < 0 ? short_stop_level : na, style=plot.style_linebr, color=color.red, linewidth=1, title="Long Stop Loss")